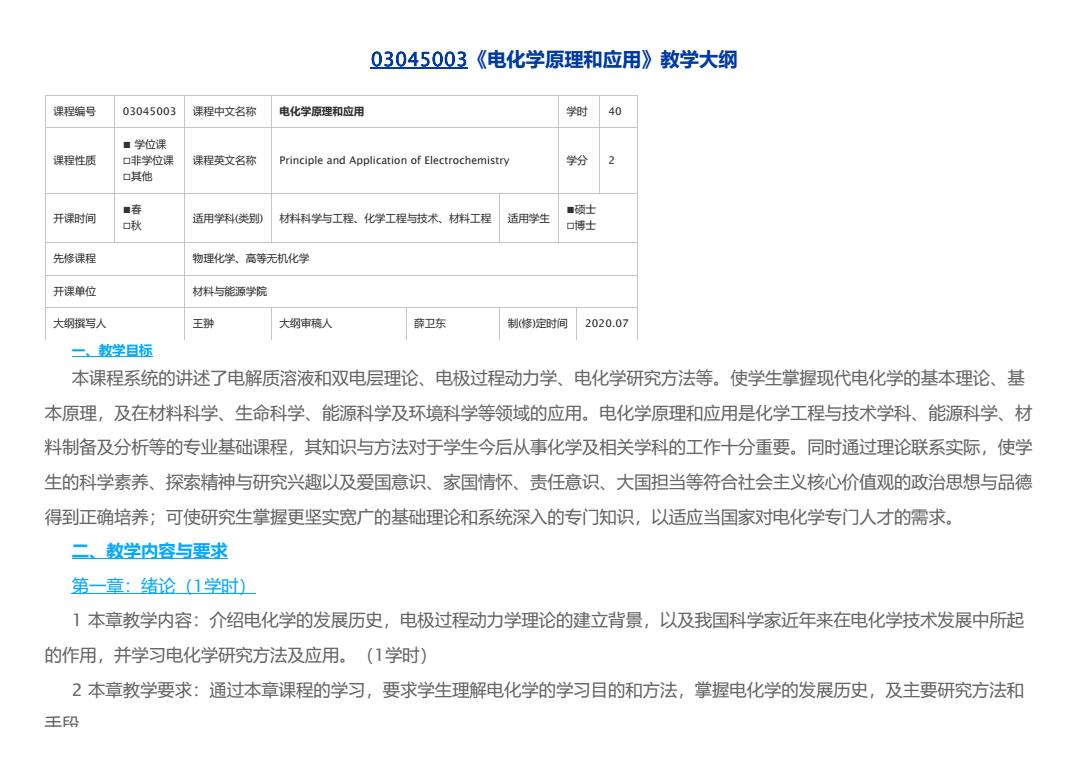
03045003《电化学原理和应用》教学大纲 课程编号 03045003 课程中文名称 电化学原理和应用 学时 40 ■学位课 课程性质 口非学位课 课程英文名称 Principle and Application of Electrochemistry 学分 2 口其他 开课时间 ■春 ■项士 球 适用学科类别 材料科学与工程、化学工程与技术、材料工程 适用学生 博士 先修课程 物理化学、高等无机化学 开课单位 材料与能源学院 大纲撰写人 王 大纲审稿人 薛卫东 制修)定时间 2020.07 二教学目标 本课程系统的讲述了电解质溶液和双电层理论、电极过程动力学、电化学研究方法等。使学生掌握现代电化学的基本理论、基 本原理,及在材料科学、生命科学、能源科学及环境科学等领域的应用。电化学原理和应用是化学工程与技术学科、能源科学、材 料制备及分析等的专业基础课程,其知识与方法对于学生今后从事化学及相关学科的工作十分重要。同时通过理论联系实际,使学 生的科学素养、探索精神与研究兴趣以及爱国意识、家国情怀、责任意识、大国担当等符合社会主义核心价值观的政治思想与品德 得到正确培养;可使研究生掌握更坚实宽广的基础理论和系统深入的专门知识,以适应当国家对电化学专门人才的需求。 二、教学内容与要求 第一章:绪论(1学时) 1本章教学内容:介绍电化学的发展历史,电极过程动力学理论的建立背景,以及我国科学家近年来在电化学技术发展中所起 的作用,并学习电化学研究方法及应用。(1学时) 2本章教学要求:通过本章课程的学习,要求学生理解电化学的学习目的和方法,掌握电化学的发展历史,及主要研究方法和 王玛
03045003《电化学原理和应用》教学大纲 课程编号 03045003 课程中文名称 电化学原理和应用 学时 40 课程性质 ■ 学位课 □非学位课 □其他 课程英文名称 Principle and Application of Electrochemistry 学分 2 开课时间 ■春 □秋 适用学科(类别) 材料科学与工程、化学工程与技术、材料工程 适用学生 ■硕士 □博士 先修课程 物理化学、高等无机化学 开课单位 材料与能源学院 大纲撰写人 王翀 大纲审稿人 薛卫东 制(修)定时间 2020.07 一、教学目标 本课程系统的讲述了电解质溶液和双电层理论、电极过程动力学、电化学研究方法等。使学生掌握现代电化学的基本理论、基 本原理,及在材料科学、生命科学、能源科学及环境科学等领域的应用。电化学原理和应用是化学工程与技术学科、能源科学、材 料制备及分析等的专业基础课程,其知识与方法对于学生今后从事化学及相关学科的工作十分重要。同时通过理论联系实际,使学 生的科学素养、探索精神与研究兴趣以及爱国意识、家国情怀、责任意识、大国担当等符合社会主义核心价值观的政治思想与品德 得到正确培养;可使研究生掌握更坚实宽广的基础理论和系统深入的专门知识,以适应当国家对电化学专门人才的需求。 二、教学内容与要求 第一章:绪论(1学时) 1 本章教学内容:介绍电化学的发展历史,电极过程动力学理论的建立背景,以及我国科学家近年来在电化学技术发展中所起 的作用,并学习电化学研究方法及应用。(1学时) 2 本章教学要求:通过本章课程的学习,要求学生理解电化学的学习目的和方法,掌握电化学的发展历史,及主要研究方法和 手段

位差,电毛细现象,双电层的结构模型,零电荷电位及半导体电极与溶液介面间的双电层结构等。了解零电荷电位的定义、测定方 法、用途,通过引起相间电位的四种情况,了解零电荷电位不在氢标电位零点的原因,进一步认识剩余电荷对相间电位的影响。了 解“中国制造2025”在能源电池方面的目标和任务。 3本章教学重点:(1)理想极化电极的概念与模型、吉布斯吸附等温式的推导与应用,(2)电毛细曲线测量方法及原理图、 电毛细方程推导与讨论、离子表面剩余量的数学表达式的推导;(3)双电层电容的特性、微分电容的测定原理与方法、双电层微 分电容曲线的特点;(4)电极/溶液界面相间的相互作用、斯特恩双电层静电模型的建立及局限性、BDM双电层结构的紧密层模 型的建立与应用、特性吸附的类型与特征;(5)零电荷电位的测定方法、零电荷电位的用途、零标电位的定义及与氢标电位的关 系。 4本章教学难点:(1)双电层的结构模型, (2)电毛细曲线和微分电容曲线与双电层结构的关系。 作业: (1)电导电极为何要镀铂黑?类型:平时作业 (2)如何确定双电层的结构模型的准确性?类型:平时作业 本章课堂讨论题目一:超级电容器的原理及其应用。 讨论要求:针对双电层的结构,探讨超级电容器容量增大的方法和途径,并且认识影响超级电容器容量、功率和循环性能的本 质。 第四章:电极过程动力学(6学时) 1本章教学内容:(1)电极过程动力学概述(2学时),(2)电化学控制步骤的动力学(2学时),(3)金属的阳极极化过 程(2学时)。 2本章教学要求:通过本章课程的学习,要求学生了解电极过程的特征及研究方法;理解电极过程的机理及速度控制步骤;了 解电化学步骤的动力学模型及结论;理解稳态电化学极化规律;掌握电极过程动力学方程的建立,电极过程与控制步骤,电极反应
位差,电毛细现象,双电层的结构模型,零电荷电位及半导体电极与溶液介面间的双电层结构等。了解零电荷电位的定义、测定方 法、用途,通过引起相间电位的四种情况,了解零电荷电位不在氢标电位零点的原因,进一步认识剩余电荷对相间电位的影响。了 解“中国制造2025”在能源电池方面的目标和任务。 3 本章教学重点:(1)理想极化电极的概念与模型、吉布斯吸附等温式的推导与应用,(2)电毛细曲线测量方法及原理图、 电毛细方程推导与讨论、离子表面剩余量的数学表达式的推导;(3)双电层电容的特性、微分电容的测定原理与方法、双电层微 分电容曲线的特点;(4)电极/溶液界面相间的相互作用、斯特恩双电层静电模型的建立及局限性、BDM双电层结构的紧密层模 型的建立与应用、特性吸附的类型与特征;(5)零电荷电位的测定方法、零电荷电位的用途、零标电位的定义及与氢标电位的关 系。 4 本章教学难点:(1)双电层的结构模型,(2)电毛细曲线和微分电容曲线与双电层结构的关系。 作业: (1)电导电极为何要镀铂黑?类型:平时作业 (2)如何确定双电层的结构模型的准确性?类型:平时作业 本章课堂讨论题目一:超级电容器的原理及其应用。 讨论要求:针对双电层的结构,探讨超级电容器容量增大的方法和途径,并且认识影响超级电容器容量、功率和循环性能的本 质。 第四章:电极过程动力学(6学时) 1 本章教学内容:(1)电极过程动力学概述(2学时),(2)电化学控制步骤的动力学(2学时),(3)金属的阳极极化过 程(2学时)。 2 本章教学要求:通过本章课程的学习,要求学生了解电极过程的特征及研究方法;理解电极过程的机理及速度控制步骤;了 解电化学步骤的动力学模型及结论;理解稳态电化学极化规律;掌握电极过程动力学方程的建立,电极过程与控制步骤,电极反应

的稳态研究方法,极化曲线的测量方式,测量稳态曲线的意义,多孔电极的稳态极化。了解暂态电流的类型及产生原理,了解双电 层充(放)电电流对法拉第电流测量的干扰,了解按控制方式进行稳态极化测量方法的分类,了解恒电流法和恒电势法的原理、特 点及应用范围。并能够理解循环伏安(CV)实验方法、电化学交流阻抗方法(ES)等重要暂态分析方法的原理,如电极的等效电 阻,电化学反应电阻,溶液的浓差阻抗、电路描述码(CDC)、电极等效电路的简化与解析、几种典型阻抗的等效电路、复数平面 图解法等。掌握控制电位法和控制电流法,电位阶跃一一计时电流法与计时电量法;电位扫描法一一线性电位扫描法,循环伏安 法;旋转圆盘电极、旋转环盘电极法(RDE、RRDE),交流阻抗法,电流阶跃法。 3本章教学重点:(1)电化学研究方法的类型与范围、稳态系统的条件、法拉第电流与非法拉第电流;(2)稳态极化测量方 法的分类、稳态极化测量方法的特点;(3)暂态测量方法的优点、电势阶跃下的电化学反应一一控制电位技术、电位扫描下的电 化学反应一一电位扫描技术、控制电流下的电化学反应一一恒电流电解技术和交流阻抗测量方法与特点等。 4本章教学难点:(1)流体动力学模型的稳态研究方法,(2)等效电路的表示方法一一电路描述码。 作业: (1)什么是合理的等效电路。类型:平时作业 (2)用电路描述码表示等效电路的原则是什么,试举例说明。类型:平时作业 本章课堂讨论题目一:电化学工作站原理与电化学测量谱图解析。 讨论要求:先由重点讲解瑞士万通电化学工作站的结构、原理及其测试中的问题。同学们根据之前应用时遇到的测试问题、图 形问题、电极处理等问题进行研讨。 第六章电化学实验设计(6学时) 1本章教学内容:(1)电化学实验体系的基本概念(1学时),(2)工作电极及其实验设计(2学时),(3)参比电极及其使用 (1学时),(4)电流分布理论与电解池设计(1学时),(5)谱学电化学(1学时)。 2本章教学要求:通过本章课程的学习,要求学生了解电化学实验的设计方法和原因;掌握电化学实验设计的一般流程,能够
的稳态研究方法,极化曲线的测量方式,测量稳态曲线的意义,多孔电极的稳态极化。了解暂态电流的类型及产生原理,了解双电 层充(放)电电流对法拉第电流测量的干扰,了解按控制方式进行稳态极化测量方法的分类,了解恒电流法和恒电势法的原理、特 点及应用范围。并能够理解循环伏安(CV)实验方法、电化学交流阻抗方法(EIS)等重要暂态分析方法的原理,如电极的等效电 阻,电化学反应电阻,溶液的浓差阻抗、电路描述码(CDC)、电极等效电路的简化与解析、几种典型阻抗的等效电路、复数平面 图解法等。掌握控制电位法和控制电流法,电位阶跃——计时电流法与计时电量法;电位扫描法——线性电位扫描法,循环伏安 法;旋转圆盘电极、旋转环盘电极法(RDE、RRDE),交流阻抗法,电流阶跃法。 3 本章教学重点:(1)电化学研究方法的类型与范围、稳态系统的条件、法拉第电流与非法拉第电流;(2)稳态极化测量方 法的分类、稳态极化测量方法的特点;(3)暂态测量方法的优点、电势阶跃下的电化学反应——控制电位技术、电位扫描下的电 化学反应——电位扫描技术、控制电流下的电化学反应——恒电流电解技术和交流阻抗测量方法与特点等。 4 本章教学难点:(1)流体动力学模型的稳态研究方法,(2)等效电路的表示方法——电路描述码。 作业: (1)什么是合理的等效电路。 类型:平时作业 (2)用电路描述码表示等效电路的原则是什么,试举例说明。 类型:平时作业 本章课堂讨论题目一:电化学工作站原理与电化学测量谱图解析。 讨论要求:先由重点讲解瑞士万通电化学工作站的结构、原理及其测试中的问题。同学们根据之前应用时遇到的测试问题、图 形问题、电极处理等问题进行研讨。 第六章 电化学实验设计(6学时) 1 本章教学内容:(1) 电化学实验体系的基本概念(1学时),(2) 工作电极及其实验设计(2学时),(3)参比电极及其使用 (1学时),(4)电流分布理论与电解池设计(1学时),(5)谱学电化学(1学时)。 2 本章教学要求:通过本章课程的学习,要求学生了解电化学实验的设计方法和原因;掌握电化学实验设计的一般流程,能够

考勤:5%,课堂互动:15%,平时作业:10%。 (2)期末考核占70%。 五、教材及主要参考书目 教材: [1]《电化学原理(第四版)》,李荻等编著,北航出版社,2021年 参考书目: [1]《电化学方法原理及应用(第二版)》,[美]AJ.巴德,L.R福克纳编著,化学工业出版社,2005年 [2]《电化学(第二版)》,C.H.哈曼编著,化工出版社,2009年 [3]《电极过程动力学》,查全性编著,科学出版社,2002年 [4]《应用电化学》,贾梦秋、杨文胜主编,高等教育出版社,2004年 03045003 Syllabus of Principle and Application of Electrochemistry Class Course Code 03045003 40 Hours Course Name Principle and Application of Electrochemistry ■Degree Course Nature Credit Non-DegreenOthers Semester ()Fall/(P)Spring Students (P)Master/()Ph.D Discipline Materials Science and Engineering,Chemical Engineering and Technology.Materials Engigeering Prerequisites Physical Chemistry.Advanced Inorganic Chemistry School Materials and Energy Written by Chong Wang Reviewed by Weidong Xue Date July,2020
考勤:5%,课堂互动:15 %,平时作业:10%。 (2)期末考核占70%。 五、教材及主要参考书目 教材: [1] 《电化学原理(第四版)》,李荻等编著,北航出版社,2021年 参考书目: [1] 《电化学方法原理及应用(第二版)》,[美]A.J.巴德,L.R.福克纳编著,化学工业出版社,2005年 [2]《电化学(第二版)》,C.H.哈曼编著,化工出版社,2009年 [3]《电极过程动力学》,査全性编著,科学出版社,2002年 [4]《应用电化学》,贾梦秋、杨文胜主编,高等教育出版社,2004年 03045003 Syllabus of Principle and Application of Electrochemistry Course Code 03045003 Course Name Principle and Application of Electrochemistry Class Hours 40 Course Nature ■Degree □Non-Degree□Others Credit 2 Semester ( )Fall/(P)Spring Students (P)Master/( )Ph.D Discipline Materials Science and Engineering, Chemical Engineering and Technology, Materials Engigeering Prerequisites Physical Chemistry, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry School Materials and Energy Written by Chong Wang Reviewed by Weidong Xue Date July, 2020

1 Contents of this chapter:(1)Overview of electrode interface and electric double layer theory (2 classes),(2)electric capillary phenomenon(2 classes),(3)differential capacitance of electric double layer(2 classes),(4)double Structure of the electric layer(2 classes),(5)Zero charge potential (1 classes) 2 Teaching requirements:Students are required to understand the significance of the properties of the electrode/solution interface;understand the properties and conditions of the ideal polarized electrode;understand the Gibbs isotherm adsorption on the electrode surface,and to establish the relative adsorption amount interfacial tension,and quantitative relationship.Understand the electric capillary curve and its determination method; understand the calculation method and principle of the residual surface of the ion surface.Understand the definition of differential capacitance, understand the electric capillary curve and its measurement method,and understand the differential capacitance of the electric double layer and its measurement method.Master the potential difference between the electrode and the solution interface,the electro-capillary phenomenon,the structural model of the electric double layer,the zero charge potential and the electric double layer structure between the semiconductor electrode and the solution interface.Understand the definition,measurement method and use of zero charge potential,and understand the reason why the zero charge potential is not at the zero point of the hydrogen target potential by causing the four cases of phase potential,and further understand the influence of residual charge on the phase potential. 3 Key points of this chapter are:(1)the concept and model of ideal polarized electrodes,the derivation and application of Gibbs isotherm adsorption,(2)the measurement method and schematic diagram of electric capillary curve,the derivation and discussion of electric capillary equations,and the remaining surface of ions The derivation of the mathematical expression of the quantity;(3)the characteristics of the electric double layer capacitor,the principle and method of measuring the differential capacitance,the characteristics of the electric double layer differential capacitance curve;(4)the interaction between the electrode/solution interface phase,Stern model and its limitation in electric double layer,the establishment and application of the compact layer model of the BDM electric double layer structure,the type and characteristics of the characteristic adsorption;(5)The measurement method of the zero charge potential,the use of the zero charge potential,the zero mark The definition of the potential and the relationship with the potential of the hydrogen standard. 4 Teaching difficulties:(1)structural model of electric double layer,(2)relationship between electric capillary curve,differential capacitance curve and structure of electric double layer. Homework: (1)Why black Pt is plated on the conductivity electrode? (2)How to determine the accuracy of the structural model of the electric double layer? In class discussion topic:the principle and application of super-capacitors. Discussion requirements:For the structure of the electric double layer,explore the methods and ways to increase the capacity of super-capacitors, and understand the nature of the capacity,power and cycle performance of super-capacitors. Chapter 4:Electrode kinetics (6 classes) 1 Contents of this chapter:(1)Overview of electrode kinetics(2 classes),(2)Kinetics of electrochemical control steps(2 classes),(3)Anodic polarization of metals(2 classes). 2 Teaching requirements:Students are required to understand the characteristics and research methods of the electrode kinetics;understand the mechanism and speed control steps of the electrode process;understand the kinetic model and electrochemical control step:understand the steady-
1 Contents of this chapter: (1) Overview of electrode interface and electric double layer theory (2 classes), (2) electric capillary phenomenon (2 classes), (3) differential capacitance of electric double layer (2 classes), (4) double Structure of the electric layer (2 classes), (5) Zero charge potential (1 classes) 2 Teaching requirements: Students are required to understand the significance of the properties of the electrode/solution interface; understand the properties and conditions of the ideal polarized electrode; understand the Gibbs isotherm adsorption on the electrode surface, and to establish the relative adsorption amount interfacial tension, and quantitative relationship. Understand the electric capillary curve and its determination method; understand the calculation method and principle of the residual surface of the ion surface. Understand the definition of differential capacitance, understand the electric capillary curve and its measurement method, and understand the differential capacitance of the electric double layer and its measurement method. Master the potential difference between the electrode and the solution interface, the electro-capillary phenomenon, the structural model of the electric double layer, the zero charge potential and the electric double layer structure between the semiconductor electrode and the solution interface. Understand the definition, measurement method and use of zero charge potential, and understand the reason why the zero charge potential is not at the zero point of the hydrogen target potential by causing the four cases of phase potential, and further understand the influence of residual charge on the phase potential. 3 Key points of this chapter are: (1) the concept and model of ideal polarized electrodes, the derivation and application of Gibbs isotherm adsorption, (2) the measurement method and schematic diagram of electric capillary curve, the derivation and discussion of electric capillary equations, and the remaining surface of ions The derivation of the mathematical expression of the quantity; (3) the characteristics of the electric double layer capacitor, the principle and method of measuring the differential capacitance, the characteristics of the electric double layer differential capacitance curve; (4) the interaction between the electrode/solution interface phase, Stern model and its limitation in electric double layer, the establishment and application of the compact layer model of the BDM electric double layer structure, the type and characteristics of the characteristic adsorption; (5) The measurement method of the zero charge potential, the use of the zero charge potential, the zero mark The definition of the potential and the relationship with the potential of the hydrogen standard. 4 Teaching difficulties: (1) structural model of electric double layer, (2) relationship between electric capillary curve, differential capacitance curve and structure of electric double layer. Homework: (1) Why black Pt is plated on the conductivity electrode? (2) How to determine the accuracy of the structural model of the electric double layer? In class discussion topic: the principle and application of super-capacitors. Discussion requirements: For the structure of the electric double layer, explore the methods and ways to increase the capacity of super-capacitors, and understand the nature of the capacity, power and cycle performance of super-capacitors. Chapter 4: Electrode kinetics (6 classes) 1 Contents of this chapter: (1) Overview of electrode kinetics (2 classes), (2) Kinetics of electrochemical control steps (2 classes), (3) Anodic polarization of metals (2 classes). 2 Teaching requirements: Students are required to understand the characteristics and research methods of the electrode kinetics; understand the mechanism and speed control steps of the electrode process; understand the kinetic model and electrochemical control step; understand the steady-

3 Key points of this chapter are:(1)the type and scope of electrochemical research methods,the conditions of steady-state systems,the Faraday current and the illegal pull current;(2)the classification of steady-state polarization measurement methods,the characteristics of steady-state polarization measurement methods(3)Advantages of transient measurement methods,electrochemical reactions under potential step-control potential technique,electrochemical reaction under potential scanning -potential scanning technique,electrochemical reaction under controlled current-constant current electrolysis Technical and AC impedance measurement methods and features. 4 Teaching difficulties in this chapter:(1)Steady-state research methods of fluid dynamics models,(2)Representation methods of equivalent circuits circuit description codes. Homework: (1)What is a reasonable equivalent circuit? (2)What is the principle of using the circuit description code to represent the equivalent circuit? In class discussion topic:the principle and practice of electrochemical workstations. Discussion requirements:First,focus on the structure,principle and problems in the testing of Metrohm Electrochemical Workstation.The students discussed the problems encountered in the previous application,such as test problems,graphic problems,and electrode treatment. Chapter 6 Voltammetric Analysis and Its Application(6 classes) 1 Contents of this chapter:(1)Polarographic interference current and its elimination method(2 classes),(2)Characteristics and special conditions of voltammetry(2 classes),(3)Principle and application of cyclic voltammetry(2 classes). 2 Teaching requirements:Students are required to understand the history and classification of voltammetric analysis;understand the basic principles,devices,polar wave types,polarographic wave equations of polarographic analysis,and learn about several new poles.Spectral and voltammetric analysis.Master the polarographic interference current and its residual current,migration current,polarographic maximum,oxygen wave,hydrogen wave,etc.;master the application of polarographic quantitative analysis method and cyclic voltammetry. 3 Key points of this chapter are:(1)the basic principles of polarographic analysis,the types of polarographic waves and the polarographic wave equation;(2)the polarographic interference current and its residual current,the migration current,the polar spectrum,the oxygen wave,A method of eliminating hydrogen waves or the like. 4 Teaching difficulties in this chapter:(1)polarographic quantitative analysis method,(2)application of cyclic voltammetry. Homework: (1)Understand the structure and application range of the electrochemical workstation,and determine its volt-ampere curve by an electrochemical system. (2)Design a method for determining the diffusion coefficient according to the principle of electrochemistry. In class discussion topic:research progress of lithium batteries and their electrolytes. Discussion requirements:Why the positive active material of lithium ion battery is the transition metal salt,the coating modification of carbon negative electrode material,the formation mechanism of SEl film and the influence on capacity. Chapter 7 Electrochemical Applications(4 classes) 1 Contents of this chapter:(1)Structure and performance of photoelectrochemical cell(2 classes),(2)Electrochemical new energy system,lithium ion battery (2 classes)
3 Key points of this chapter are: (1) the type and scope of electrochemical research methods, the conditions of steady-state systems, the Faraday current and the illegal pull current; (2) the classification of steady-state polarization measurement methods, the characteristics of steady-state polarization measurement methods (3) Advantages of transient measurement methods, electrochemical reactions under potential step - control potential technique, electrochemical reaction under potential scanning - potential scanning technique, electrochemical reaction under controlled current - constant current electrolysis Technical and AC impedance measurement methods and features. 4 Teaching difficulties in this chapter: (1) Steady-state research methods of fluid dynamics models, (2) Representation methods of equivalent circuits - circuit description codes. Homework: (1) What is a reasonable equivalent circuit? (2) What is the principle of using the circuit description code to represent the equivalent circuit? In class discussion topic: the principle and practice of electrochemical workstations. Discussion requirements: First, focus on the structure, principle and problems in the testing of Metrohm Electrochemical Workstation. The students discussed the problems encountered in the previous application, such as test problems, graphic problems, and electrode treatment. Chapter 6 Voltammetric Analysis and Its Application (6 classes) 1 Contents of this chapter: (1) Polarographic interference current and its elimination method (2 classes), (2) Characteristics and special conditions of voltammetry (2 classes), (3) Principle and application of cyclic voltammetry (2 classes). 2 Teaching requirements: Students are required to understand the history and classification of voltammetric analysis; understand the basic principles, devices, polar wave types, polarographic wave equations of polarographic analysis, and learn about several new poles. Spectral and voltammetric analysis. Master the polarographic interference current and its residual current, migration current, polarographic maximum, oxygen wave, hydrogen wave, etc.; master the application of polarographic quantitative analysis method and cyclic voltammetry. 3 Key points of this chapter are: (1) the basic principles of polarographic analysis, the types of polarographic waves and the polarographic wave equation; (2) the polarographic interference current and its residual current, the migration current, the polar spectrum, the oxygen wave, A method of eliminating hydrogen waves or the like. 4 Teaching difficulties in this chapter: (1) polarographic quantitative analysis method, (2) application of cyclic voltammetry. Homework: (1) Understand the structure and application range of the electrochemical workstation, and determine its volt-ampere curve by an electrochemical system. (2) Design a method for determining the diffusion coefficient according to the principle of electrochemistry. In class discussion topic: research progress of lithium batteries and their electrolytes. Discussion requirements: Why the positive active material of lithium ion battery is the transition metal salt, the coating modification of carbon negative electrode material, the formation mechanism of SEI film and the influence on capacity. Chapter 7 Electrochemical Applications (4 classes) 1 Contents of this chapter: (1) Structure and performance of photoelectrochemical cell (2 classes), (2) Electrochemical new energy system, lithium ion battery (2 classes)