
第四章变量类型和函数 Variable Types and Functions
Variable Types and Functions

4.1变量类型(Class) 。字符串变量(char) 。数值型变量,包括双精度(double)、单精度 (single)等。 >clear all >str='Every good boy does fine.'; >x=1:5:100 >class(str) ans char >>class(x) ans double
l 字符串变量(char) l 数值型变量,包括双精度(double)、单精度 (single)等
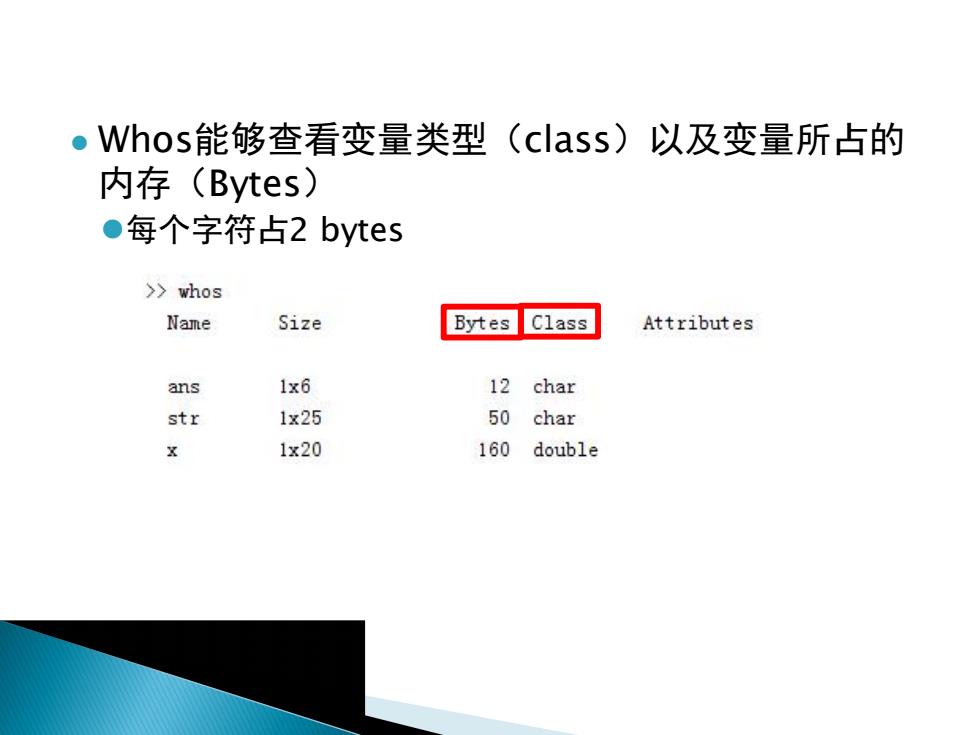
●Whos能够查看变量类型(class)以及变量所占的 内存(Bytes) ●每个字符占2 bytes >whos Name Size Bytes Class Attributes ans 1x6 12 char str 1x25 50 char 1x20 160 double
l Whos能够查看变量类型(class)以及变量所占的 内存(Bytes) l每个字符占2 bytes

●Help class可提供所有变量类型 ·字符、数值、逻辑(logical)、结构(struct)、 单元(cell)等 >help class CLASS Return class name of object. S CLASS (OBJ)returns the name of the class of object OBJ. Possibilities are: double -Double precision floating point number array (this is the traditional MAILAB matrix or array) single -Single precision floating point number array logical -Logical array char -Character array cell -Cell array struct -Structure array function_handle -Function Handle int8 -8-bit signed integer array uint8 -8-bit usigned integer array int16 -16-bit signed integer array uint16 -16-bit usigned integer array int32 -32-bit signed integer array uint32 -32-bit unsigned integer array int64 -64-bit signed integer array uint64 -64-bit unsigned integer array -MATLAB class name for MATLAB objects <java_class〉 -Java class name for java objects
l Help class可提供所有变量类型 l 字符、数值、逻辑(logical)、结构(struct)、 单元(cell)等

4.2结构变量(struct) ·如何把实验被试的个人信息保存到一个变量里? >subject.id 213; subject.age 28; subject.hand =0; subject.gender 1; >>subject 变量名称 subject >subject.age ans id 213 子变量(fields)/字段名称 age 28 28 hand gender
l 如何把实验被试的个人信息保存到一个变量里? 变量名称 子变量(fields)/字段名称

·如何把所有被试的个人信息保存在一个变量里? ●结构变量本身也可以是数组/向量或矩阵 >subject(2).id 301; subject(2).age 25; subject (2).hand =0; >subject(1).data rand(1,5); subject (2).gender =0; subject (2).data rand(1,7); subject (3).data rand(1,4); subject (3).age 43; subject (3).id 200; 子变量data的内容是数组/向量 subject(3).hand 1; subject (3).gender =0;
l 如何把所有被试的个人信息保存在一个变量里? l结构变量本身也可以是数组/向量或矩阵 子变量data的内容是数组/向量

●对结构变量的内容进行操作。 ●例如,计算每个左利手的被试的所有实验试次(triall) 的平均数据。 >count =0; for i=1:length(subject) if subject(i).hand ==0 是否为左利手被试 count count+1; 共有几个左利手被试 meanData(count)=nean(subject(i).data):计算平均数据 end end 试一试: meanData meanData(1,count)=subject(i).id; meanData(2,count)=mean(subject(i),data); meanData 0.4513 0.5012 mean是matlab自带,计算平均值 std是matlab自带,可计算标准差
l 对结构变量的内容进行操作。 l例如,计算每个左利手的被试的所有实验试次(trial) 的平均数据。 是否为左利手被试 共有几个左利手被试 计算平均数据 mean是matlab自带,计算平均值 std是matlab自带,可计算标准差 试一试: meanData(1,count)=subject(i).id; meanData(2,count)=mean(subject(i),data);

·结构变量的子变量可以是任何变量类型。 >subject(1).hand='1eft';子变量hand的类型是字符串 >subject(1) ans id:213 age:28 hand:'left' gender:1 data:[0.15880.59970.47890.88520.1340]
l 结构变量的子变量可以是任何变量类型。 子变量hand的类型是字符串

●结构变量的子变量(fields)也可以是结构变量! >animalSubject(1).id 23; animalSubject(1).data rand(1,5); animalSubject(2).id 46; animalSubject(2).data rand(1,4); >allSubjects.human(3).age >allSubjects.human subject; allSubjects.animal animalSubject ans allSubjects 43 allSubjects 子变量animal和自变量human的 human:[1x3 struct] 类型都是结构变量 animal:[1x2 struct]
l 结构变量的子变量(fields)也可以是结构变量! 子变量animal和自变量human的 类型都是结构变量

4.3单元变量(cell) 。如何把不同长度的字符串放在一个变量里? >days =['Monday','Iuesday','Wednesday','Ihursday','Friday' days MondayTuesdayWednesdayThursdayFriday >days ['Monday';'Tuesday';'Wednesday';'Thursday';'Friday' ??Error using ==vertcat CAI arguments dimensions are not consistent. >>days Monday','Iuesday','Wednesday','Thursday','Friday'} days 'Monday' Iuesday' 'Wednesday' Thursday' 'Friday
l 如何把不同长度的字符串放在一个变量里?