
Integrated Management of Pregnancy and Childbirth Pregnancy,Childbirth,Postpartum and Newborn Care: A guide for essential practice 2nd Edition ●●● World Health Organization ●●UNFPA unicef ●●● The World Bank Group Department of Making Pregnancy Safer
Department of Making Pregnancy Safer 2nd Edition

FOREWORD In modern times,improvements in knowledge and technological advances have greatly improved the It is against this background that we are proud to present the document Pregnancy,Childbirth. health of mother and children.However,the past decade was marked by limited progress in reducing Postpartum and Newbor Care:A guide for essential practice,as new additions to the Integrated matemal mortality and a slow-down in the steady decline of childhood mortality observed since the Management of Pregnancy and Childbirth tool kit.The guide provides a full range of updated, mid 1950s in many countries,the latter being largely due to a failure to reduce neonatal mortality. evidence-based norms and standards that will enable health care providers to give high quality care during pregnancy.delivery and in the postpartum period,considering the needs of the mother and her Every year,over four million babies less than one month of age die,most of them during the critical newborn baby. first week of life:and for every newborn who dies,another is stillborn.Most of these deaths are a consequence of the poor health and nutritional status of the mother coupled with inadequate care We hope that the guide will be helpful for decision-makers,programme managers and health care before,during.and after delivery.Unfortunately,the problem remains unrecognized or-worse-accepted providers in charting out their roadmap towards meeting the health needs of all mothers and children. as inevitable in many societies,in large part because it is so common. We have the knowledge,our major challenge now is to translate this into action and to reach those women and children who are most in need. Recognizing the large burden of matemnal and neonatal ill-health on the development capacity of individuals.communities and societies,world leaders reaffirmed their commitment to invest in mothers and children by adopting specific goals and targets to reduce matemal and childhood-infant mortality as part of the Millennium Declaration. There is a widely shared but mistaken idea that improvements in newbom health require sophisticated and expensive technologies and highly specialized staff.The reality is that many conditions that result in perinatal death can be prevented or treated without sophisticated and expensive technology.What is required is essential care during pregnancy,the assistance of a person with midwifery skills during Dr.Tomris Turmen childbirth and the immediate postpartum period,and a few critical interventions for the newbom Executive director during the first days of life. Family and Community Health(FCH) QHOM3HO Foreword
Foreword FOREWORD In modern times, improvements in knowledge and technological advances have greatly improved the health of mother and children. However, the past decade was marked by limited progress in reducing maternal mortality and a slow-down in the steady decline of childhood mortality observed since the mid 1950s in many countries, the latter being largely due to a failure to reduce neonatal mortality. Every year, over four million babies less than one month of age die, most of them during the critical first week of life; and for every newborn who dies, another is stillborn. Most of these deaths are a consequence of the poor health and nutritional status of the mother coupled with inadequate care before, during, and after delivery. Unfortunately, the problem remains unrecognized or- worse- accepted as inevitable in many societies, in large part because it is so common. Recognizing the large burden of maternal and neonatal ill-health on the development capacity of individuals, communities and societies, world leaders reaffirmed their commitment to invest in mothers and children by adopting specific goals and targets to reduce maternal and childhood-infant mortality as part of the Millennium Declaration. There is a widely shared but mistaken idea that improvements in newborn health require sophisticated and expensive technologies and highly specialized staff. The reality is that many conditions that result in perinatal death can be prevented or treated without sophisticated and expensive technology. What is required is essential care during pregnancy, the assistance of a person with midwifery skills during childbirth and the immediate postpartum period, and a few critical interventions for the newborn during the first days of life. It is against this background that we are proud to present the document Pregnancy, Childbirth, Postpartum and Newborn Care: A guide for essential practice, as new additions to the Integrated Management of Pregnancy and Childbirth tool kit. The guide provides a full range of updated, evidence-based norms and standards that will enable health care providers to give high quality care during pregnancy, delivery and in the postpartum period, considering the needs of the mother and her newborn baby. We hope that the guide will be helpful for decision-makers, programme managers and health care providers in charting out their roadmap towards meeting the health needs of all mothers and children. We have the knowledge, our major challenge now is to translate this into action and to reach those women and children who are most in need. Dr. Tomris Türmen Executive director Family and Community Health (FCH) FOREWORD

Acknowledgements SIN3 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS 远 The Guide was prepared by a team of the World Health Organization.Department of Reproductive This guide represents a common understanding between WHO.UNFPA,UNICEF and the World Bank Health and Research(RHR).led by Jerker Liljestrand and Jelka Zupan. of key elements of an approach to reducing matemal and perinatal mortality and morbidity.These agencies co-operate closely in efforts to reduce maternal and perinatal mortality and morbidity. The concept and first drafts were developed by Sandra Gove and Patricia Whitesell/ACT Intemational, The principles and policies of each agency are govemed by the relevant decisions of each agency's Atlanta,Jerker Liljestrand.Denise Roth.Betty Sweet.Anne Thompson,and Jelka Zupan. goveming body and each agency implements the interventions described in this document in accordance with these principles and policies and within the scope of its mandate. Revisions were subsequently carried out by Annie Portela,Luc de Bemis.Omella Lincetto,Rita Kabra. Maggie Usher,Agostino Borra,Rick Guidotti,Elisabeth Hoff,Mathews Matthai,Monir Islam, The guide has also been reviewed and endorsed by the International Confederation of Midwives,the Felicity Savage,Adepeyu Olukoya,Aafje Rietveld,TinTin Sint,Ekpini Ehounu,Suman Mehta. International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics and Intemational Pediatric Association. Valuable inputs were provided by WHO Regional Offices and WHO departments: Reproductive Health and Research Child and Adolescent Health and Development ■HV/AIDS Communicable Diseases Nutrition for Health and Development Intemational Essential Drugs and Medicines Policy Gm6 calgy and正srks PedlatricAssodation Vaccines and Biologicals Mental Health and Substance Dependence The financial support towards the preparation and production of this document provided by UNFPA and Gender and Women's Health the Governments of Australia.Japan and the United States of America is gratefully acknowledged. Blindness and Deafness as is financial support received from The World Bank.In addition,WHO's Making Pregnancy Safer initiative is grateful to the programme support received from the Govemments of the Netherlands. Editing:Nina Mattock,Richard Casna Norway,Sweden and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northem Ireland. Layout:rsdesigns.com sarl Cover design:Maire Ni Mhearain WHO acknowledges with gratitude the generous contribution of over 100 individuals and organizations in the field of matemal and newborn health,who took time to review this document at different stages of its development They came from over 35 countries and brought their expertise and wide experence to the final text
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The Guide was prepared by a team of the World Health Organization, Department of Reproductive Health and Research (RHR), led by Jerker Liljestrand and Jelka Zupan. The concept and first drafts were developed by Sandra Gove and Patricia Whitesell/ACT International, Atlanta, Jerker Liljestrand, Denise Roth, Betty Sweet, Anne Thompson, and Jelka Zupan. Revisions were subsequently carried out by Annie Portela, Luc de Bernis, Ornella Lincetto, Rita Kabra, Maggie Usher, Agostino Borra, Rick Guidotti, Elisabeth Hoff, Mathews Matthai, Monir Islam, Felicity Savage, Adepeyu Olukoya, Aafje Rietveld, TinTin Sint, Ekpini Ehounu, Suman Mehta. Valuable inputs were provided by WHO Regional Offices and WHO departments: N Reproductive Health and Research N Child and Adolescent Health and Development N HIV/AIDS N Communicable Diseases N Nutrition for Health and Development N Essential Drugs and Medicines Policy N Vaccines and Biologicals N Mental Health and Substance Dependence N Gender and Women’s Health N Blindness and Deafness Editing: Nina Mattock, Richard Casna Layout: rsdesigns.com sàrl Cover design: Maíre Ní Mhearáin WHO acknowledges with gratitude the generous contribution of over 100 individuals and organizations in the field of maternal and newborn health, who took time to review this document at different stages of its development. They came from over 35 countries and brought their expertise and wide experience to the final text. This guide represents a common understanding between WHO, UNFPA, UNICEF, and the World Bank of key elements of an approach to reducing maternal and perinatal mortality and morbidity. These agencies co-operate closely in efforts to reduce maternal and perinatal mortality and morbidity. The principles and policies of each agency are governed by the relevant decisions of each agency’s governing body and each agency implements the interventions described in this document in accordance with these principles and policies and within the scope of its mandate. The guide has also been reviewed and endorsed by the International Confederation of Midwives, the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics and International Pediatric Association. The financial support towards the preparation and production of this document provided by UNFPA and the Governments of Australia, Japan and the United States of America is gratefully acknowledged, as is financial support received from The World Bank. In addition, WHO’s Making Pregnancy Safer initiative is grateful to the programme support received from the Governments of the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Acknowledgements ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS International Pediatric Association International Confederation of Midwives International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
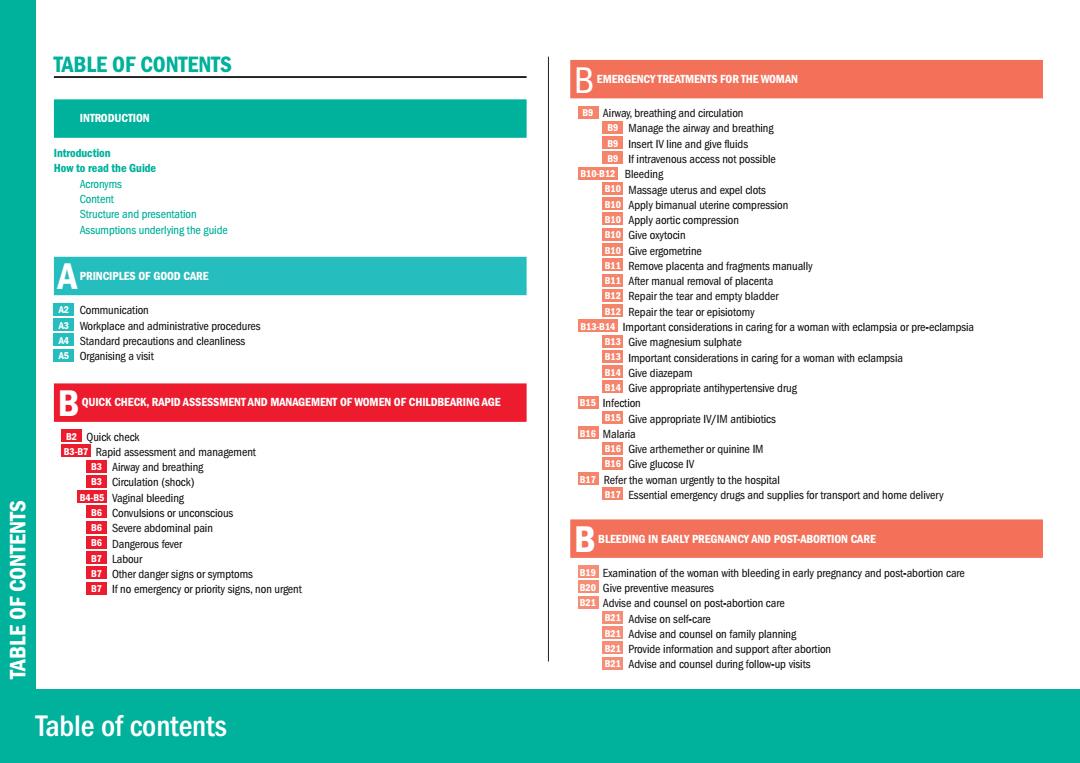
TABLE OF CONTENTS B EMERGENCY TREATMENTS FOR THE WOMAN INTRODUCTION B Airway,breathing and circulation Manage the airway and breathing B Insert IV line and give fluids Introduction If intravenous access not possible How to read the Guide E1002 Bleeding Acronyms Massage uterus and expel clots Content Apply bimanual uterine compression Structure and presentation B10 Apply aortic compression Assumptions underlying the guide B10 Give oxytocin B10 Give ergometrine Remove placenta and fragments manually PRINCIPLES OF GOOD CARE After manual removal of placenta Repair the tear and empty bladder A2: Communication Repair the tear or episiotomy A好 Workplace and administrative procedures Important considerations in caring for a woman with eclampsia or pre-eclampsia M Standard precautions and cleanliness Eh Give magnesium sulphate 5Organising a visit Important considerations in caring for a woman with eclampsia B Give diazepam Give appropriate antihypertensive drug QUICK CHECK.RAPID ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF WOMEN OF CHILDBEARING AGE 15Infection Give appropriate IV/IM antibiotics 2 Quick check B16 Malaria B6-B Rapid assessment and management GGive arthemether or quinine IM Bs Airway and breathing ENG Give glucose IV B3 Circulation(shock) Refer the woman urgently to the hospital B4-85 Vaginal bleeding Essential emergency drugs and supplies for transport and home delivery B6 Corulsions or unconscious SIN3INOO 86 Severe abdominal pain B6 Dangerous fever BLEEDING IN EARLY PREGNANCY AND POST-ABORTION CARE B7 Labour Other danger signs or symptoms Examination of the woman with bleeding in early pregnancy and post-abortion care If no emergency or priority signs,non urgent 20 Give preventive measures Advise and counsel on post-abortion care Advise on self-care Advise and counsel on family planning B21 Provide information and support after abortion Advise and counsel during follow-up visits Table of contents
Table of contents TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS A INTRODUCTION Introduction How to read the Guide Acronyms Content Structure and presentation Assumptions underlying the guide A PRINCIPLES OF GOOD CARE A2 Communication A3 Workplace and administrative procedures A4 Standard precautions and cleanliness A5 Organising a visit B QUICK CHECK, RAPID ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF WOMEN OF CHILDBEARING AGE B2 Quick check B3-B7 Rapid assessment and management B3 Airway and breathing B3 Circulation (shock) B4-B5 Vaginal bleeding B6 Convulsions or unconscious B6 Severe abdominal pain B6 Dangerous fever B7 Labour B7 Other danger signs or symptoms B7 If no emergency or priority signs, non urgent BEMERGENCY TREATMENTS FOR THE WOMAN B9 Airway, breathing and circulation B9 Manage the airway and breathing B9 Insert IV line and give fluids B9 If intravenous access not possible B10-B12 Bleeding B10 Massage uterus and expel clots B10 Apply bimanual uterine compression B10 Apply aortic compression B10 Give oxytocin B10 Give ergometrine B11 Remove placenta and fragments manually B11 After manual removal of placenta B12 Repair the tear and empty bladder B12 Repair the tear or episiotomy B13-B14 Important considerations in caring for a woman with eclampsia or pre-eclampsia B13 Give magnesium sulphate B13 Important considerations in caring for a woman with eclampsia B14 Give diazepam B14 Give appropriate antihypertensive drug B15 Infection B15 Give appropriate IV/IM antibiotics B16 Malaria B16 Give arthemether or quinine IM B16 Give glucose IV B17 Refer the woman urgently to the hospital B17 Essential emergency drugs and supplies for transport and home delivery B BLEEDING IN EARLY PREGNANCY AND POST-ABORTION CARE B19 Examination of the woman with bleeding in early pregnancy and post-abortion care B20 Give preventive measures B21 Advise and counsel on post-abortion care B21 Advise on self-care B21 Advise and counsel on family planning B21 Provide information and support after abortion B21 Advise and counsel during follow-up visits

Table of contents SIN3INOO ANTENATAL CARE D CHILDBIRTH-LABOUR,DELIVERY AND IMMEDIATE POSTPARTUM CARE Assess the pregnant woman:pregnancy status,birth and emergency plan D2 Examine the woman in labour or with ruptured membranes Check for pre-eclampsia Decide stage of labour C4 Check for anaemia DD5 Respond to obstetrical problems on admission 5Check for syphilis DGive supportive care throughout labour C Check for HIV status DCommunication Respond to observed signs or volunteered problems D6 Cleanliness If no fetal movement D6 Mobility C7 If ruptured membranes and no labour D6 Urination C8 If fever or burning on urination D3 Eating.drinking c9 If vaginal discharge D6 Breathing technique If signs suggesting HIV infection Pain and discomfort relief c10 If smoking.alcohol or drug abuse,or history of violence D Birth companion G11 If cough or breathing difficulty D3 First stage of labour If taking antituberculosis drugs DB Not in active labour Give preventive measures D9 In active labour Advise and counsel on nutrition and self-care Second stage of labour:deliver the baby and give immediate newbom care Develop a birth and emergency plan Third stage of labour:deliver the placenta Facility delivery Respond to problems during labour and delivery c14 Home delivery with a skilled attendant DIf fetal heart rate 160 beats per minute G15 Advise on labour signs D15 If prolapsed cord C5Advise on danger signs D1G If breech presentation Discuss how to prepare for an emergency in pregnancy If stuck shoulders(Shoulder dystocia) GAdvise and counsel on family planning D3 If multiple births 16 Counsel on the importance of family planning Care of the mother and newborn within first hour of delivery of placenta Special consideration for family planning counselling during pregnancy Care of the mother one hour after delivery of placenta Advise on routine and follow-up visits Assess the mother after delivery C18 Home delivery without a skilled attendant Respond to problems immediately postpartum Assess eligibility of ARV for HIV-positive pregnant woman If vaginal bleeding 22If fever (temperature >38C) If perineal tear or episiotomy(done for lifesaving circumstances) If elevated diastolic blood pressure 0 If pallor on screening.check for anaemia 20If mother severely ill or separated from the child 0 If baby stillbom or dead D25 Give preventive measures
Table of contents TABLE OF CONTENTS C ANTENATAL CARE C2 Assess the pregnant woman: pregnancy status, birth and emergency plan C3 Check for pre-eclampsia C4 Check for anaemia C5 Check for syphilis C6 Check for HIV status C7 Respond to observed signs or volunteered problems C7 If no fetal movement C7 If ruptured membranes and no labour C8 If fever or burning on urination C9 If vaginal discharge C10 If signs suggesting HIV infection C10 If smoking, alcohol or drug abuse, or history of violence C11 If cough or breathing difficulty C11 If taking antituberculosis drugs C12 Give preventive measures C13 Advise and counsel on nutrition and self-care C14-C15 Develop a birth and emergency plan C14 Facility delivery C14 Home delivery with a skilled attendant C15 Advise on labour signs C15 Advise on danger signs C15 Discuss how to prepare for an emergency in pregnancy C16 Advise and counsel on family planning C16 Counsel on the importance of family planning C16 Special consideration for family planning counselling during pregnancy C17 Advise on routine and follow-up visits C18 Home delivery without a skilled attendant C19 Assess eligibility of ARV for HIV-positive pregnant woman D CHILDBIRTH – LABOUR, DELIVERY AND IMMEDIATE POSTPARTUM CARE D2 Examine the woman in labour or with ruptured membranes D3 Decide stage of labour D4-D5 Respond to obstetrical problems on admission D6-D7 Give supportive care throughout labour D6 Communication D6 Cleanliness D6 Mobility D6 Urination D6 Eating, drinking D6 Breathing technique D6 Pain and discomfort relief D7 Birth companion D8-D9 First stage of labour D8 Not in active labour D9 In active labour D10-D11 Second stage of labour: deliver the baby and give immediate newborn care D12-D13 Third stage of labour: deliver the placenta D14-D18 Respond to problems during labour and delivery D14 If fetal heart rate 160 beats per minute D15 If prolapsed cord D16 If breech presentation D17 If stuck shoulders (Shoulder dystocia) D18 If multiple births D19 Care of the mother and newborn within first hour of delivery of placenta D20 Care of the mother one hour after delivery of placenta D21 Assess the mother after delivery D22-D25 Respond to problems immediately postpartum D22 If vaginal bleeding D22 If fever (temperature >38°C) D22 If perineal tear or episiotomy (done for lifesaving circumstances) D23 If elevated diastolic blood pressure D24 If pallor on screening, check for anaemia D24 If mother severely ill or separated from the child D24 If baby stillborn or dead D25 Give preventive measures
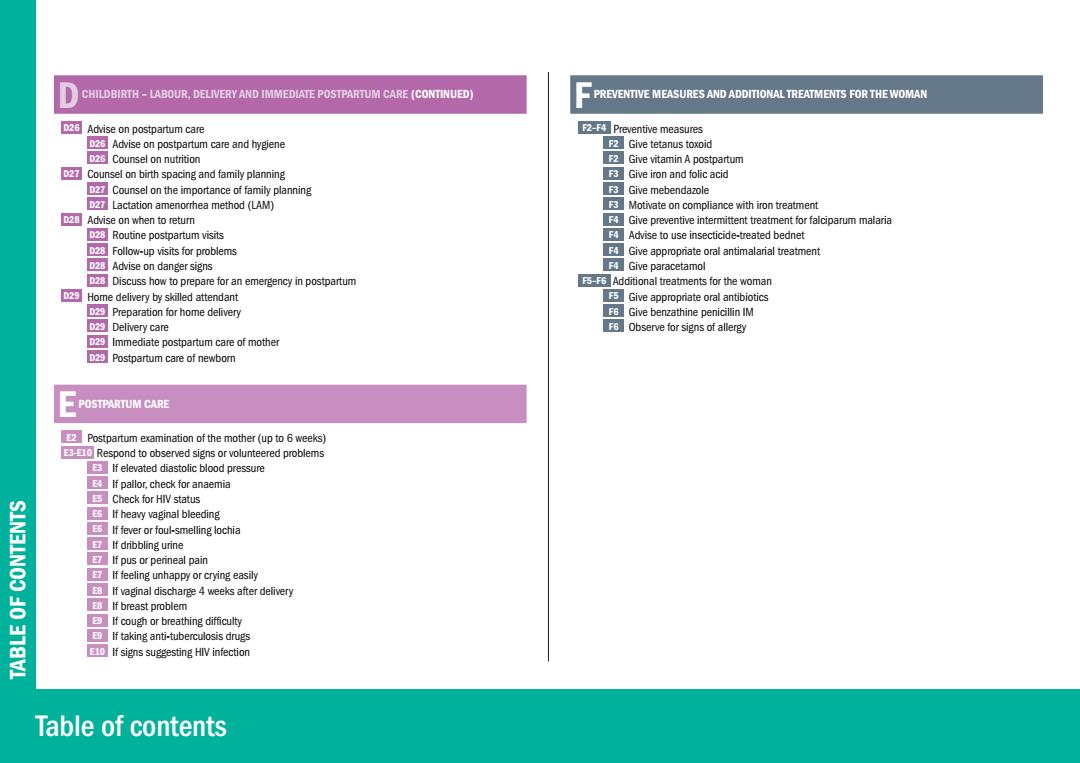
CHILDBIRTH-LABOUR.DELIVERY AND IMMEDIATE POSTPARTUM CARE (CONTINUED PREVENTIVE MEASURES AND ADDITIONAL TREATMENTS FOR THE WOMAN 2G Advise on postpartum care 2Preventive measures 2G Advise on postpartum care and hygiene Give tetanus toxoid D25 Counsel on nutrition Give vitamin A postpartum Counsel on birth spacing and family planning Give iron and folic acid Counsel on the importance of family planning Give mebendazole D2 Lactation amenorrhea method (LAM) Motivate on compliance with iron treatment 23 Advise on when to return ROGive preventive intermittent treatment for falciparum malaria 23 Routine postpartum visits Advise to use insecticide-treated bednet 2Follow-up visits for problems Give appropriate oral antimalarial treatment 2 Advise on danger signs R Give paracetamol 2Discuss how to prepare for an emergency in postpartum Additional treatments for the woman Home delivery by skilled attendant Give appropriate oral antibiotics 2Preparation for home delivery Give benzathine penicillin IM D2 Delivery care 3 Observe for signs of allergy 2Immediate postpartum care of mother 2Postpartum care of newborn POSTPARTUM CARE Postpartum examination of the mother(up to 6 weeks) 3 Respond to observed signs or volunteered problems If elevated diastolic blood pressure 3 If pallor.check for anaemia Check for HIV status E6 If heavy vaginal bleeding E5 If fever or foul-smelling lochia If dribbling urine If pus or perineal pain If feeling unhappy or crying easily 3If vaginal discharge 4 weeks after delivery 告 33 If breast problem EIf cough or breathing difficulty If taking anti-tuberculosis drugs If signs suggesting HIV infection Table of contents
Table of contents TABLE OF CONTENTS D CHILDBIRTH – LABOUR, DELIVERY AND IMMEDIATE POSTPARTUM CARE (CONTINUED) D26 Advise on postpartum care D26 Advise on postpartum care and hygiene D26 Counsel on nutrition D27 Counsel on birth spacing and family planning D27 Counsel on the importance of family planning D27 Lactation amenorrhea method (LAM) D28 Advise on when to return D28 Routine postpartum visits D28 Follow-up visits for problems D28 Advise on danger signs D28 Discuss how to prepare for an emergency in postpartum D29 Home delivery by skilled attendant D29 Preparation for home delivery D29 Delivery care D29 Immediate postpartum care of mother D29 Postpartum care of newborn E POSTPARTUM CARE E2 Postpartum examination of the mother (up to 6 weeks) E3-E10 Respond to observed signs or volunteered problems E3 If elevated diastolic blood pressure E4 If pallor, check for anaemia E5 Check for HIV status E6 If heavy vaginal bleeding E6 If fever or foul-smelling lochia E7 If dribbling urine E7 If pus or perineal pain E7 If feeling unhappy or crying easily E8 If vaginal discharge 4 weeks after delivery E8 If breast problem E9 If cough or breathing difficulty E9 If taking anti-tuberculosis drugs E10 If signs suggesting HIV infection F PREVENTIVE MEASURES AND ADDITIONAL TREATMENTS FOR THE WOMAN F2–F4 Preventive measures F2 Give tetanus toxoid F2 Give vitamin A postpartum F3 Give iron and folic acid F3 Give mebendazole F3 Motivate on compliance with iron treatment F4 Give preventive intermittent treatment for falciparum malaria F4 Advise to use insecticide-treated bednet F4 Give appropriate oral antimalarial treatment F4 Give paracetamol F5–F6 Additional treatments for the woman F5 Give appropriate oral antibiotics F6 Give benzathine penicillin IM F6 Observe for signs of allergy
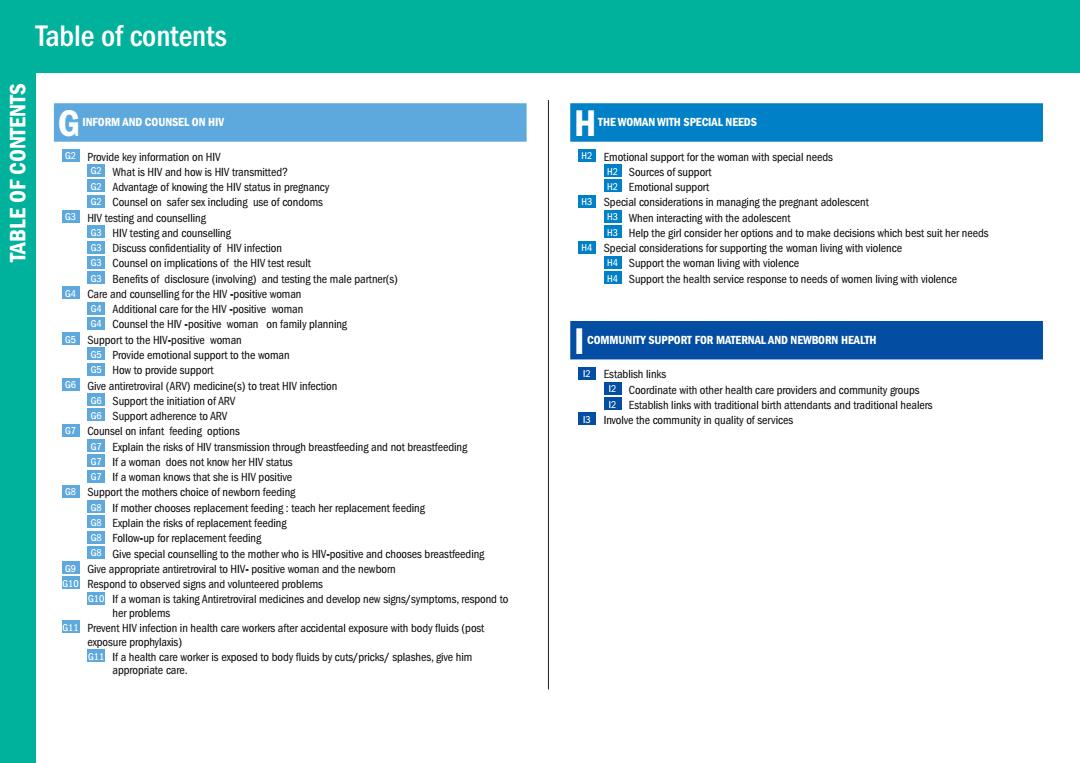
Table of contents SIN3INOO G NFORM AND COUNSEL ON HIV H THE WOMAN WITH SPECIAL NEEDS Provide key information on HIV 2 Emotional support for the woman with special needs What is HIV and how is HIV transmitted? 2 Sources of support GAdvantage of knowing the HIV status in pregnancy 2Emotional support Counsel on safer sex including use of condoms Special considerations in managing the pregnant adolescent GHIV testing and counselling GEWhen interacting with the adolescent G3 HIV testing and counselling Help the girl consider her options and to make decisions which best suit her needs 63 Discuss confidentiality of HIV infection Special considerations for supporting the woman living with violence G3 Counsel on implications of the HIV test result HSupport the woman living with violence Benefits of disclosure (involving)and testing the male partner(s) Support the health service response to needs of women living with violence Care and counselling for the HIV-positive woman Additional care for the HIV-positive woman G4 Counsel the HIV-positive woman on family planning 5Support to the HIV-positive woman COMMUNITY SUPPORT FOR MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH Provide emotional support to the woman C5How to provide support 2Establish links 06 Give antiretroviral (ARV)medicine(s)to treat HIV infection 2 Coordinate with other health care providers and community groups Support the initiation of ARV Establish links with traditional birth attendants and traditional healers Support adherence to ARV Involve the community in quality of services Counsel on infant feeding options Explain the risks of HIV transmission through breastfeeding and not breastfeeding o If a woman does not know her HIV status If a woman knows that she is HIV positive Support the mothers choice of newbom feeding G If mother chooses replacement feeding:teach her replacement feeding GB Explain the risks of replacement feeding G8 Follow-up for replacement feeding Give special counselling to the mother who is HlV-positive and chooses breastfeeding Give appropriate antiretroviral to HIV-positive woman and the newbor 10 Respond to observed signs and volunteered problems If a woman is taking Antiretroviral medicines and develop new signs/symptoms,respond to her problems 旺国 Prevent HIV infection in health care workers after accidental exposure with body fluids(post exposure prophylaxis) If a health care worker is exposed to body fluids by cuts/pricks/splashes,give him appropriate care
Table of contents TABLE OF CONTENTS G INFORM AND COUNSEL ON HIV G2 Provide key information on HIV G2 What is HIV and how is HIV transmitted? G2 Advantage of knowing the HIV status in pregnancy G2 Counsel on safer sex including use of condoms G3 HIV testing and counselling G3 HIV testing and counselling G3 Discuss confidentiality of HIV infection G3 Counsel on implications of the HIV test result G3 Benefits of disclosure (involving) and testing the male partner(s) G4 Care and counselling for the HIV -positive woman G4 Additional care for the HIV -positive woman G4 Counsel the HIV -positive woman on family planning G5 Support to the HIV-positive woman G5 Provide emotional support to the woman G5 How to provide support G6 Give antiretroviral (ARV) medicine(s) to treat HIV infection G6 Support the initiation of ARV G6 Support adherence to ARV G7 Counsel on infant feeding options G7 Explain the risks of HIV transmission through breastfeeding and not breastfeeding G7 If a woman does not know her HIV status G7 If a woman knows that she is HIV positive G8 Support the mothers choice of newborn feeding G8 If mother chooses replacement feeding : teach her replacement feeding G8 Explain the risks of replacement feeding G8 Follow-up for replacement feeding G8 Give special counselling to the mother who is HIV-positive and chooses breastfeeding G9 Give appropriate antiretroviral to HIV- positive woman and the newborn G10 Respond to observed signs and volunteered problems G10 If a woman is taking Antiretroviral medicines and develop new signs/symptoms, respond to her problems G11 Prevent HIV infection in health care workers after accidental exposure with body fluids (post exposure prophylaxis) G11 If a health care worker is exposed to body fluids by cuts/pricks/ splashes, give him appropriate care. H THE WOMAN WITH SPECIAL NEEDS H2 Emotional support for the woman with special needs H2 Sources of support H2 Emotional support H3 Special considerations in managing the pregnant adolescent H3 When interacting with the adolescent H3 Help the girl consider her options and to make decisions which best suit her needs H4 Special considerations for supporting the woman living with violence H4 Support the woman living with violence H4 Support the health service response to needs of women living with violence I COMMUNITY SUPPORT FOR MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH I2 Establish links I2 Coordinate with other health care providers and community groups I2 Establish links with traditional birth attendants and traditional healers I3 Involve the community in quality of services

四 Other breastfeeding support NEWBORN CARE 超 Give special support to the mother who is not yet breastfeeding If the baby does not have a mother 2 Examine the newbom Advise the mother who is not breastfeeding at all on how to relieve engorgement If preterm,birth weight <2500 g or twin a Ensure warmth for the baby Assess breastfeeding @ Keep the baby warm Check for special treatment needs Keep a small baby warm J6 Look for signs of jaundice and local infection @ Rewarm the baby skin-to-skin 7 If danger signs Other baby care 8 If swelling,bruises or malformation Cord care Assess the mother's breasts if complaining of nipple or breast pain Sleeping 10 Care of the newborn 0Hygiene 11 Additional care of a small baby (or twin) Newborn resuscitation 2 Assess replacement feeding 型 Keep the baby warm Open the airway 1 If still not breathing,ventilate BREASTFEEDING,CARE,PREVENTIVE MEASURES AND TREATMENT FOR THE NEWBORN If breathing less than 30 breaths per minute or severe chest in-drawing.stop ventilating If not breathing or gasping at all after 20 minutes of ventilation Counsel on breastfeeding Treat and immunize the baby 应 Counsel on importance of exclusive breastfeeding Treat the baby 12 Give 2 IM antibiotics (first week of life) Help the mother to initiate breastfeeding 3 Support exclusive breastfeeding K12 Give IM benzathine penicillin to baby (single dose)if mother tested RPR-positive 3 Teach comect positioning and attachment for breastfeeding Give IM antibiotic for possible gonococcal eye infection(single dose) Give special support to breastfeed the small baby (preterm and/or low birth weight) Teach the mother to give treatment to the baby at home M K13 Give special support to breastfeed twins Treat local infection GAlternative feeding methods 13 Give isoniazid (INH)prophylaxis to newbom 13 Express breast milk Immunize the newborn Hand express breast milk directly into the baby's mouth Give antiretroviral (ARV)medicine to newborn Cup feeding expressed breast milk Advise when to retum with the baby 船 14 Quantity to feed by cup Routine visits Signs that baby is receiving adequate amount of milk Follow-up visits Weigh and assess weight gain 14 Advise the mother to seek care for the baby Weigh baby in the first month of life 14 Refer baby urgently to hospital Assess weight gain 告 Scale maintenance Table of contents
Table of contents TABLE OF CONTENTS J NEWBORN CARE J2 Examine the newborn J3 If preterm, birth weight <2500 g or twin J4 Assess breastfeeding J5 Check for special treatment needs J6 Look for signs of jaundice and local infection J7 If danger signs J8 If swelling, bruises or malformation J9 Assess the mother’s breasts if complaining of nipple or breast pain J10 Care of the newborn J11 Additional care of a small baby (or twin) J12 Assess replacement feeding K BREASTFEEDING, CARE, PREVENTIVE MEASURES AND TREATMENT FOR THE NEWBORN K2 Counsel on breastfeeding K2 Counsel on importance of exclusive breastfeeding K2 Help the mother to initiate breastfeeding K3 Support exclusive breastfeeding K3 Teach correct positioning and attachment for breastfeeding K4 Give special support to breastfeed the small baby (preterm and/or low birth weight) K4 Give special support to breastfeed twins K5 Alternative feeding methods K5 Express breast milk K5 Hand express breast milk directly into the baby’s mouth K6 Cup feeding expressed breast milk K6 Quantity to feed by cup K6 Signs that baby is receiving adequate amount of milk K7 Weigh and assess weight gain K7 Weigh baby in the first month of life K7 Assess weight gain K7 Scale maintenance K8 Other breastfeeding support K8 Give special support to the mother who is not yet breastfeeding K8 If the baby does not have a mother K8 Advise the mother who is not breastfeeding at all on how to relieve engorgement K9 Ensure warmth for the baby K9 Keep the baby warm K9 Keep a small baby warm K9 Rewarm the baby skin-to-skin K10 Other baby care K10 Cord care K10 Sleeping K10 Hygiene K11 Newborn resuscitation K11 Keep the baby warm K11 Open the airway K11 If still not breathing, ventilate K11 If breathing less than 30 breaths per minute or severe chest in-drawing, stop ventilating K11 If not breathing or gasping at all after 20 minutes of ventilation K12 Treat and immunize the baby K12 Treat the baby K12 Give 2 IM antibiotics (first week of life) K12 Give IM benzathine penicillin to baby (single dose) if mother tested RPR-positive K12 Give IM antibiotic for possible gonococcal eye infection (single dose) K13 Teach the mother to give treatment to the baby at home K13 Treat local infection K13 Give isoniazid (INH) prophylaxis to newborn K13 Immunize the newborn K13 Give antiretroviral (ARV) medicine to newborn K14 Advise when to return with the baby K14 Routine visits K14 Follow-up visits K14 Advise the mother to seek care for the baby K14 Refer baby urgently to hospital

Table of contents SIN3LNOO EQUIPMENT,SUPPLIES,DRUGS AND LABORATORY TESTS 2 Equipment,supplies,drugs and tests for pregnancy and postpartum care 3 Equipment,supplies and drugs for childbirth care 告 LA Laboratory tests Check urine for protein 18V Check haemoglobin Perform rapid plamareagin(RPR)test for syphilis 5Interpreting results 6 Perform rapid test for HIV INFORMATION AND COUNSELLING SHEETS M2 Care during pregnancy Preparing a birth and emergency plan Care for the mother after birth M5 Care after an abortion Care for the baby after birth MZ Breastfeeding E Clean home delivery RECORDS AND FORMS 2 Referral record Feedback record Labour record 阿 Partograph Postpartum record International form of medical certificate of cause of death GLOSSARY AND ACRONYMS
Table of contents TABLE OF CONTENTS L EQUIPMENT, SUPPLIES, DRUGS AND LABORATORY TESTS L2 Equipment, supplies, drugs and tests for pregnancy and postpartum care L3 Equipment, supplies and drugs for childbirth care L4 Laboratory tests L4 Check urine for protein L4 Check haemoglobin L5 Perform rapid plamareagin (RPR) test for syphilis L5 Interpreting results L6 Perform rapid test for HIV M INFORMATION AND COUNSELLING SHEETS M2 Care during pregnancy M3 Preparing a birth and emergency plan M4 Care for the mother after birth M5 Care after an abortion M6 Care for the baby after birth M7 Breastfeeding M8-M9 Clean home delivery N RECORDS AND FORMS N2 Referral record N3 Feedback record N4 Labour record N5 Partograph N6 Postpartum record N7 International form of medical certificate of cause of death O GLOSSARY AND ACRONYMS

INTRODUCTION The aim of Pregnancy,childbirth,postpartum and newborn care guide for essential practice (PCPNC)is The Guide has been developed by the Department of Reproductive Health and Research with to provide evidence-based recommendations to guide health care professionals in the management of contributions from the following WHO programmes: women during pregnancy,childbirth and postpartum,and post abortion,and newboms during their first week of life,including management of endemic diseases like malaria,HIV/AIDS,TB and anaemia. Child and Adolesscent Health and Development ■HV/AIDS All recommendations are for skilled attendants working at the primary level of health care,either at the Nutrition for Health and Development facility or in the community.They apply to all women attending antenatal care,in delivery,postpartum Essential drugs and Medicines Policy or post abortion care,or who come for emergency care,and to all newbomns at birth and during the first Vaccines and Biologicals week of life (or later)for routine and emergency care. Communicable Diseases Control.Prevention and Eradication(tuberculosis.malaria.helminthiasis) Gender and Women's Health The PCPNC is a guide for clinical decision-making.It facilitates the collection,analysis,classification and Mental Health and Substance Dependence use of relevant information by suggesting key questions,essential observations and/or examinations, Blindness and Deafness and recommending appropriate research-based interventions.It promotes the early detection of complications and the initiation of early and appropriate treatment,including timely referral,if necessary. Correct use of this guide should help reduce the high maternal and perinatal mortality and morbidity rates prevalent in many parts of the developing world,thereby making pregnancy and childbirth safer. The guide is not designed for immediate use.It is a generic guide and should first be adapted to local needs and resources.It should cover the most serious endemic conditions that the skilled birth attendant must be able to treat,and be made consistent with national treatment guidelines and other policies.It is accompanied by an adaptation guide to help countries prepare their own national guides and training and other supporting materials NOILO The first section,How to use the guide,describes how the guide is organized,the overall content and presentation.Each chapter begins with a short description of how to read and use it,to help the reader use the guide correctly. Introduction
The aim of Pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum and newborn care guide for essential practice (PCPNC) is to provide evidence-based recommendations to guide health care professionals in the management of women during pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum, and post abortion, and newborns during their first week of life, including management of endemic diseases like malaria, HIV/AIDS, TB and anaemia. All recommendations are for skilled attendants working at the primary level of health care, either at the facility or in the community. They apply to all women attending antenatal care, in delivery, postpartum or post abortion care, or who come for emergency care, and to all newborns at birth and during the first week of life (or later) for routine and emergency care. The PCPNC is a guide for clinical decision-making. It facilitates the collection, analysis, classification and use of relevant information by suggesting key questions, essential observations and/or examinations, and recommending appropriate research-based interventions. It promotes the early detection of complications and the initiation of early and appropriate treatment, including timely referral, if necessary. Correct use of this guide should help reduce the high maternal and perinatal mortality and morbidity rates prevalent in many parts of the developing world, thereby making pregnancy and childbirth safer. The guide is not designed for immediate use. It is a generic guide and should first be adapted to local needs and resources. It should cover the most serious endemic conditions that the skilled birth attendant must be able to treat, and be made consistent with national treatment guidelines and other policies. It is accompanied by an adaptation guide to help countries prepare their own national guides and training and other supporting materials. The first section, How to use the guide, describes how the guide is organized, the overall content and presentation. Each chapter begins with a short description of how to read and use it, to help the reader use the guide correctly. The Guide has been developed by the Department of Reproductive Health and Research with contributions from the following WHO programmes: N Child and Adolesscent Health and Development N HIV/AIDS N Nutrition for Health and Development N Essential drugs and Medicines Policy N Vaccines and Biologicals N Communicable Diseases Control, Prevention and Eradication (tuberculosis, malaria, helminthiasis) N Gender and Women’s Health N Mental Health and Substance Dependence N Blindness and Deafness INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Introduction