
Conditions and Process of Taiwan's Democratization Week 3
Conditions and Process of Taiwan’s Democratization Week 3

Week 3:Teaching Outline Theories of Democratization From Authoritarianism to Constitutionalism
Week 3: Teaching Outline • Theories of Democratization • From Authoritarianism to Constitutionalism

1.Theories of Democratization Modernization theory (developmental approach) Economic growth,social equality,and pluralism are three compatible goals Economic growth that presupposes market freedom will lead to information (literacy,education and media) diffusion and social equality (equal distribution of social wealth)
1.Theories of Democratization • Modernization theory (developmental approach) • Economic growth, social equality, and pluralism are three compatible goals • Economic growth that presupposes market freedom will lead to – information (literacy, education and media) diffusion and social equality (equal distribution of social wealth)

1.Theories of Democratization -social plurality,autonomy,differentiation, specialization cultural secularization,individualization and rationalization -rise of middle class and interest group political mobilization and competition democratic transition
1.Theories of Democratization – social plurality, autonomy, differentiation, specialization – cultural secularization, individualization and rationalization – rise of middle class and interest group – political mobilization and competition – democratic transition

1.Theories of Democratization Two competitive paradigms(structure- agent debate) School of democratic conditions,or structure- oriented approach,assuming "political actors' face limited choice sets What makes democracy possible,and when? -School of democratic process,focusing on the strategic moves of the actors Who wants democracy and how?
1.Theories of Democratization • Two competitive paradigms (structure- agent debate) – School of democratic conditions, or structure- oriented approach, assuming “political actors” face limited choice sets • What makes democracy possible, and when? – School of democratic process, focusing on the strategic moves of the actors • Who wants democracy and how?

Socioeconomic Approach ·Strengths -theoretical elegance methodological measurability -empirical verifiability ·Veakness the exact correlation between socioeconomic development and democratization The Predicting power of per capita GDP Taiwan,SK in 1970s,and Singapore
Socioeconomic Approach • Strengths – theoretical elegance – methodological measurability – empirical verifiability • Weakness – the exact correlation between socioeconomic development and democratization • The Predicting power of per capita GDP • Taiwan, SK in 1970s, and Singapore

Methodological Problem? ·Wila“modern dynamic pluralist society" necessarily lead to democracy? Socioeconomic developments as independent and continual variables Democratization as a dependent and dichotomous(democracy or non-democracy) variable Can we employ quantitative changes in social structure to explain a qualitative breakthrough in the political system?
Methodological Problem? • Will a “modern dynamic pluralist society” necessarily lead to democracy? • Socioeconomic developments as independent and continual variables • Democratization as a dependent and dichotomous (democracy or non-democracy) variable • Can we employ quantitative changes in social structure to explain a qualitative breakthrough in the political system?

Who Wants Democracy? Bourgeoisie in England and France Military in Portuguese Organized workers in Poland Students in South Korea Native opposition groups in Taiwan Strategic choices of different actors
Who Wants Democracy? • Bourgeoisie in England and France • Military in Portuguese • Organized workers in Poland • Students in South Korea • Native opposition groups in Taiwan • Strategic choices of different actors

Three typologies of democratic transition democratic transformation initiated by the leading elite on the top (Taiwan?) -Transaction (Share Mainwaring) democratic replacement initiated by civil society (collapse,Share Mainwaring) democratic transplacement contributed by both the leading elite and civil society
Three typologies of democratic transition • democratic transformation initiated by the leading elite on the top (Taiwan?) –Transaction (Share & Mainwaring) • democratic replacement initiated by civil society (collapse, Share & Mainwaring) • democratic transplacement contributed by both the leading elite and civil society
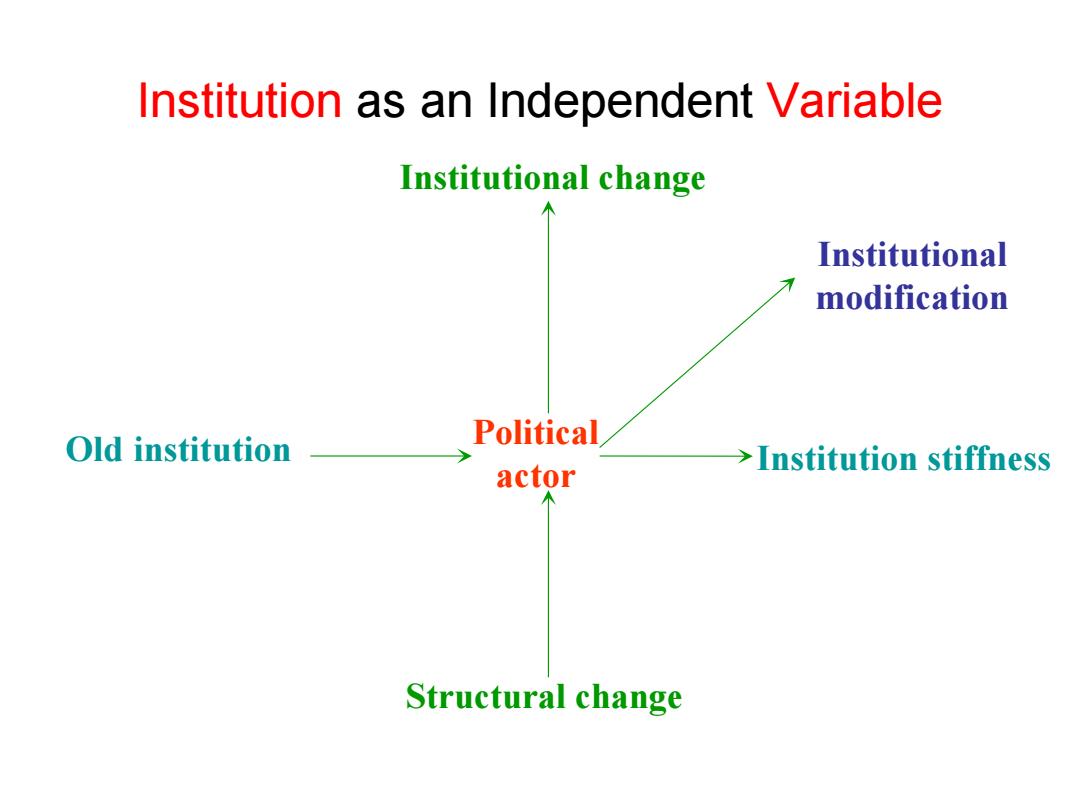
Institution as an Independent Variable Institutional change Institutional modification Old institution Political >Institution stiffness actor Structural change
Institution as an Independent Variable Structural change Old institution Political actor Institutional change Institutional modification Institution stiffness