
ECS Wireless F oundations 6.Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath
6: Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 1 6. Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity
6:Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser EECS Diversity Wireless oundations Fundamental Feature of Wireless Channels: Time Variation Channel Strength Time time-varying channel ·multipath fading large-scale channel variations time-varying interference Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 2
6: Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 2 Fundamental Feature of Wireless Channels: Time Variation • multipath fading • large-scale channel variations • time-varying interference
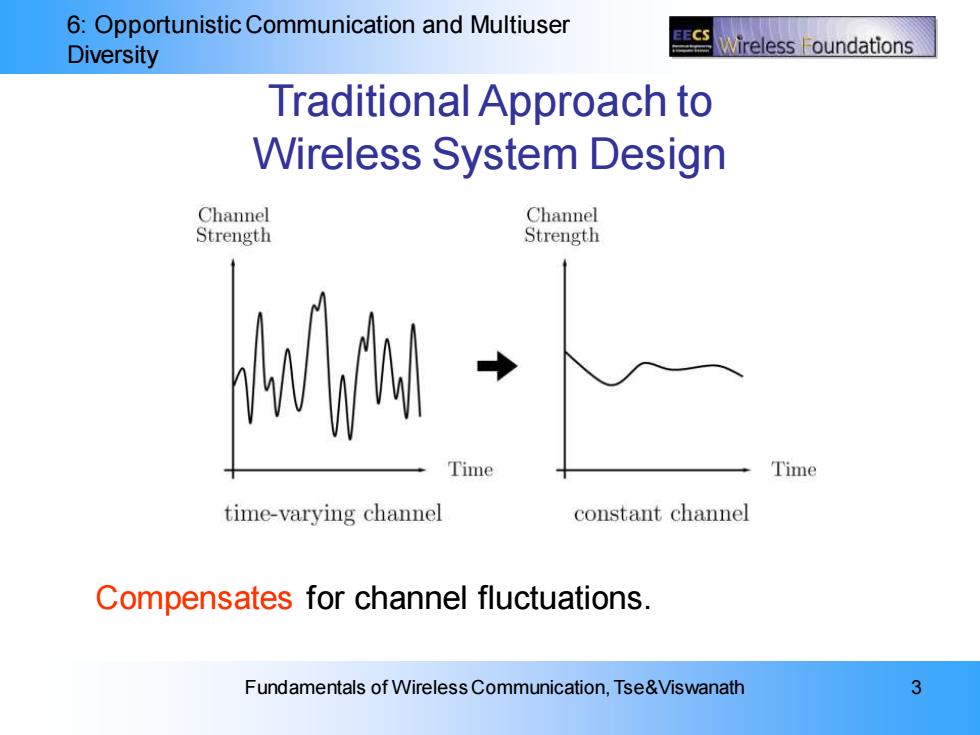
6:Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser ECS Diversity Wireless F oundations Traditional Approach to Wireless System Design Channel Channel Strength Strength Time Time time-varying channel constant channel Compensates for channel fluctuations. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 3
6: Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 3 Traditional Approach to Wireless System Design Compensates for channel fluctuations

6:Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser ECS Diversity vireless oundations Example:CDMA Systems Two main types of compensating mechanisms: 1.Channel diversity: frequency diversity via Rake combining time diversity via interleaving and coding macro-diversity via soft handoff transmit/receive antenna diversity 2.Interference management: 一 power control interference averaging Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 4
6: Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 4 Example: CDMA Systems Two main types of compensating mechanisms: 1. Channel diversity: – frequency diversity via Rake combining – time diversity via interleaving and coding – macro-diversity via soft handoff – transmit/receive antenna diversity 2. Interference management: – power control – interference averaging
6:Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser EECS Diversity Wireless F oundations What Drives this Approach? Channel Channel Strength Strength Time Time time-varying channel constant channel Main application is voice,with very tight latency requirements. Needs a consistent channel. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 5
6: Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 5 What Drives this Approach? Main application is voice, with very tight latency requirements. Needs a consistent channel

6:Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser EECS Diversity ireless oundations Opportunistic Communication: A Different View Transmit more when and where the channel is good. Exploits fading to achieve higher long-term throughput, but no guarantee that the "channel is always there". Appropriate for data with non-real-time latency requirements (file downloads,video streaming). Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 6
6: Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 6 Opportunistic Communication: A Different View Transmit more when and where the channel is good. Exploits fading to achieve higher long-term throughput, but no guarantee that the "channel is always there". Appropriate for data with non-real-time latency requirements (file downloads, video streaming)
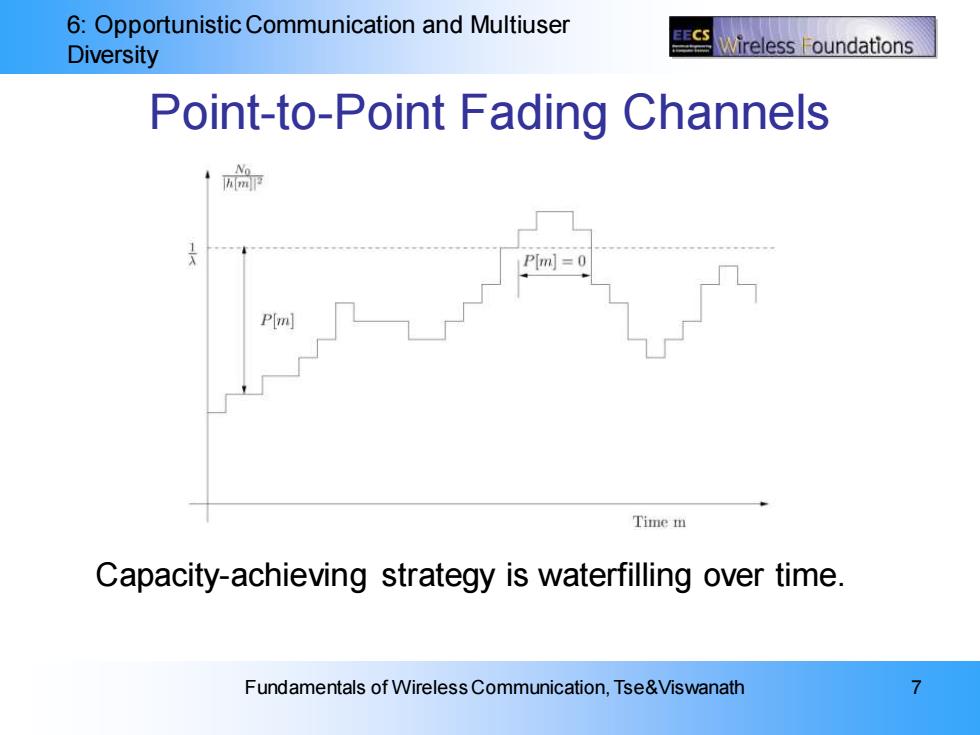
6:Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser EECS Diversity Wireless F oundations Point-to-Point Fading Channels P[m]=0 P(m Time m Capacity-achieving strategy is waterfilling over time. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath
6: Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 7 Point-to-Point Fading Channels Capacity-achieving strategy is waterfilling over time
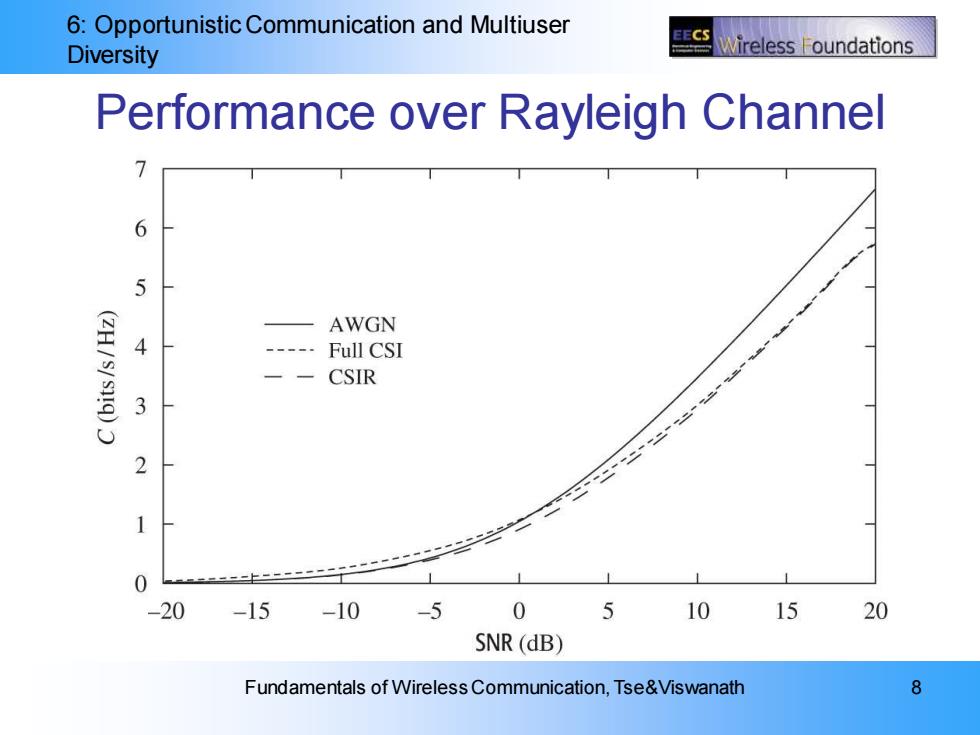
6:Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser ECS Diversity ireless oundations Performance over Rayleigh Channel 7 6 5 AWGN 4 Full CSI CSIR 3 2 1 0 -20 -15 -10 -5 0 10 15 20 SNR (dB) Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 8
6: Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 8 Performance over Rayleigh Channel

6:Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser ECS Diversity Wireless F oundations Performance:Low SNR 3 2.5 2 CSIR Full CSI.. 1.5 1 050 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 SNR [dB] At low SNR,capacity can be greater when there is fading. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 9
6: Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 9 Performance: Low SNR At low SNR, capacity can be greater when there is fading
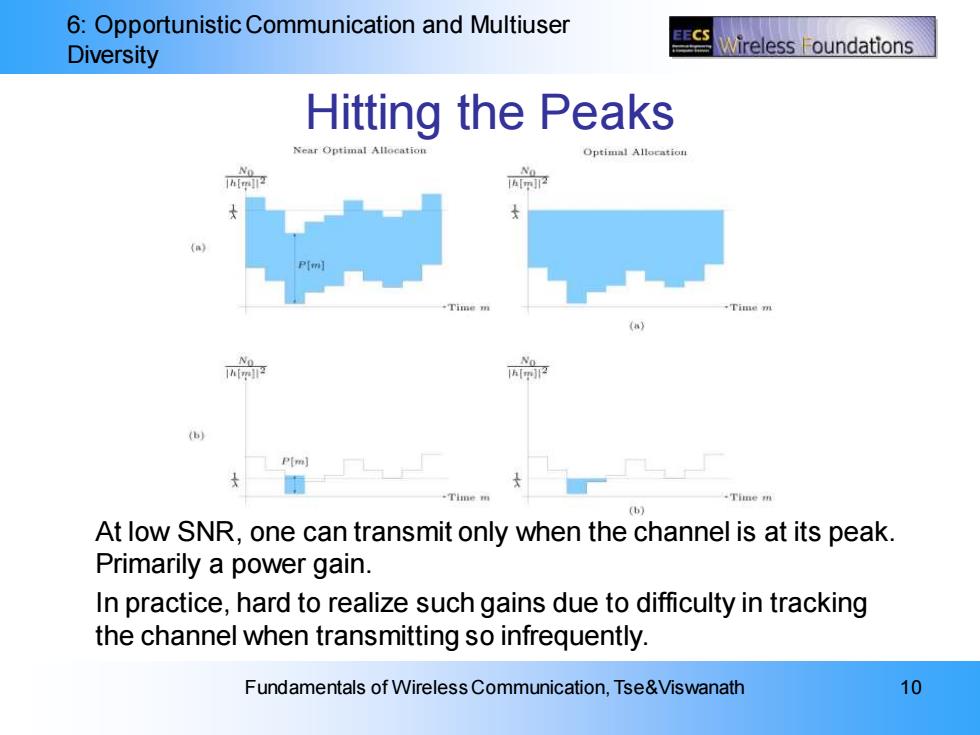
6:Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser EECS Diversity Nireless oundations Hitting the Peaks Near Optimal All Optimal Allocation Time (】 P(m] (b At low SNR,one can transmit only when the channel is at its peak. Primarily a power gain. In practice,hard to realize such gains due to difficulty in tracking the channel when transmitting so infrequently. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 10
6: Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 10 Hitting the Peaks At low SNR, one can transmit only when the channel is at its peak. Primarily a power gain. In practice, hard to realize such gains due to difficulty in tracking the channel when transmitting so infrequently