
EECS Wireless Foundations 4.Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath
4. Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 1 4. Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management

4.Cellular Systems:Multiple Access and EECS Interference Management Vireless oundations Cellular Systems So far we have focused on point-to-point communication. In a cellular system,additional issues come into forefront: Multiple access Inter-cell interference management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 2
4. Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 2 Cellular Systems • So far we have focused on point-to-point communication. • In a cellular system, additional issues come into forefront: – Multiple access – Inter-cell interference management

4.Cellular Systems:Multiple Access and EECS Interference Management Wireless F oundations Some History Cellular concept (Bell Labs,early 70's) AMPS (analog,early 80's) GSM(digital,narrowband,late 80's) IS-95(digital,wideband,early 90's) ·3G/4 G systems Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 3
4. Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 3 Some History • Cellular concept (Bell Labs, early 70’s) • AMPS (analog, early 80’s) • GSM (digital, narrowband, late 80’s) • IS-95 (digital, wideband, early 90’s) • 3G/4G systems

4.Cellular Systems:Multiple Access and Interference Management Wireless oundations Four Systems ·Narrowband(GSM) Wideband system:CDMA(IS-95) Wideband system:OFDM(Flash OFDM) Opportunistic Communication (1x EV-DO)(later) Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 4
4. Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 4 Four Systems • Narrowband (GSM) • Wideband system: CDMA (IS-95) • Wideband system: OFDM (Flash OFDM) • Opportunistic Communication (1x EV-DO) (later)

4.Cellular Systems:Multiple Access and Interference Management Wireless F oundations Narrowband (GSM) The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels.(200 kHz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel(8 users) Multiple access is orthogonal:users within the cell never interfere with each other. Interference between users on the same channel in different cells is minimized by reusing the same channel only in cells far apart. 。 Users operate at high SINR regime The price to pay is in reducing the overall available degrees of freedom. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 5
4. Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 5 Narrowband (GSM) • The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 kHz in GSM) • Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) • Multiple access is orthogonal: users within the cell never interfere with each other. • Interference between users on the same channel in different cells is minimized by reusing the same channel only in cells far apart. • Users operate at high SINR regime • The price to pay is in reducing the overall available degrees of freedom
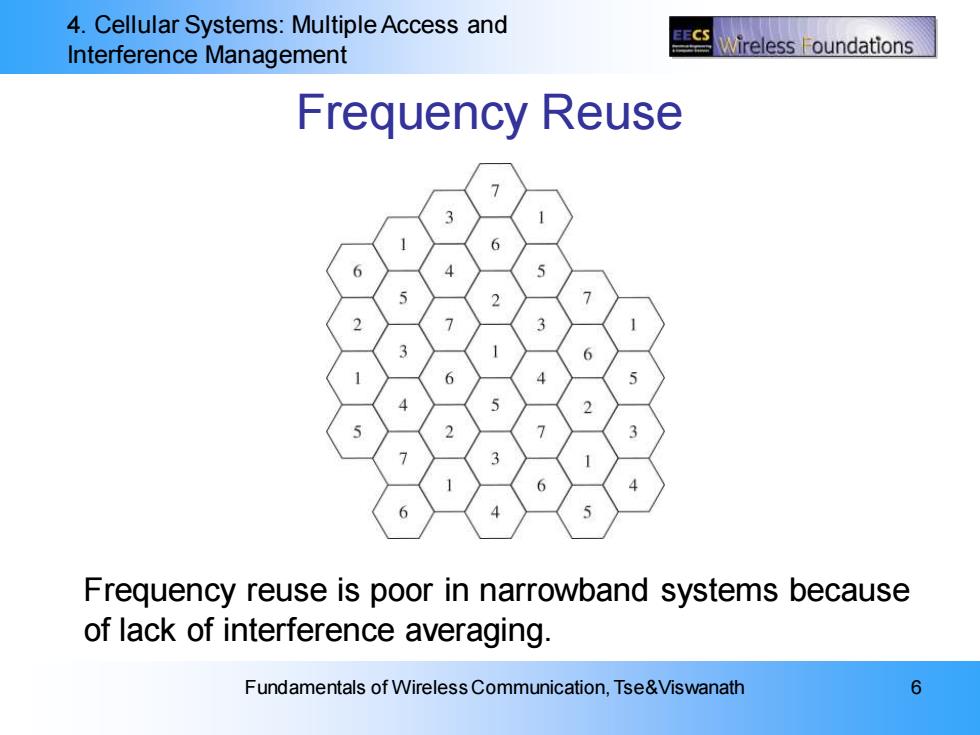
4.Cellular Systems:Multiple Access and Interference Management Vireless oundations Frequency Reuse Frequency reuse is poor in narrowband systems because of lack of interference averaging. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 6
4. Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 6 Frequency Reuse Frequency reuse is poor in narrowband systems because of lack of interference averaging

4.Cellular Systems:Multiple Access and EECS Interference Management Wireless F oundations Wideband System:CDMA ● Universal frequency reuse:all the users in all cells share the same bandwidth (1.25 MHz in IS-95 and 1x) ● Main advantages: Maximizes the degrees of freedom usage Allows interference averaging across many users. Soft capacity limit Allows soft handoff Simplify frequency planning 。 Challenges Very tight power control to solve the near-far problem. More sophisticated coding/signal processing to extract the information of each user in a very low SINR environment. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 7
4. Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 7 Wideband System: CDMA • Universal frequency reuse: all the users in all cells share the same bandwidth (1.25 MHz in IS-95 and 1x) • Main advantages: – Maximizes the degrees of freedom usage – Allows interference averaging across many users. – Soft capacity limit – Allows soft handoff – Simplify frequency planning • Challenges – Very tight power control to solve the near-far problem. – More sophisticated coding/signal processing to extract the information of each user in a very low SINR environment

4.Cellular Systems:Multiple Access and EECS Interference Management Vireless oundations Design Goals 1)make the interference look as much like a white Gaussian noise as possible: Spread each user's signal using a pseudonoise noise sequence Tight power control for managing interference within the cell Averaging interference from outside the cell as well as fluctuating voice activities of users. 2)apply point-to-point design for each link Extract all possible diversity in the channel Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 8
4. Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 8 Design Goals • 1) make the interference look as much like a white Gaussian noise as possible: – Spread each user’s signal using a pseudonoise noise sequence – Tight power control for managing interference within the cell – Averaging interference from outside the cell as well as fluctuating voice activities of users. • 2) apply point-to-point design for each link – Extract all possible diversity in the channel

4.Cellular Systems:Multiple Access and ECS Interference Management Wireless F oundations Point-to-Point Link Design Extracting maximal diversity is the name of the game. Time diversity is obtained by interleaving across different coherence time and convolutional coding. Frequency diversity is obtained by Rake combining of the multipaths. Transmit diversity in 3G CDMA systems Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 9
4. Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 9 Point-to-Point Link Design • Extracting maximal diversity is the name of the game. • Time diversity is obtained by interleaving across different coherence time and convolutional coding. • Frequency diversity is obtained by Rake combining of the multipaths. • Transmit diversity in 3G CDMA systems
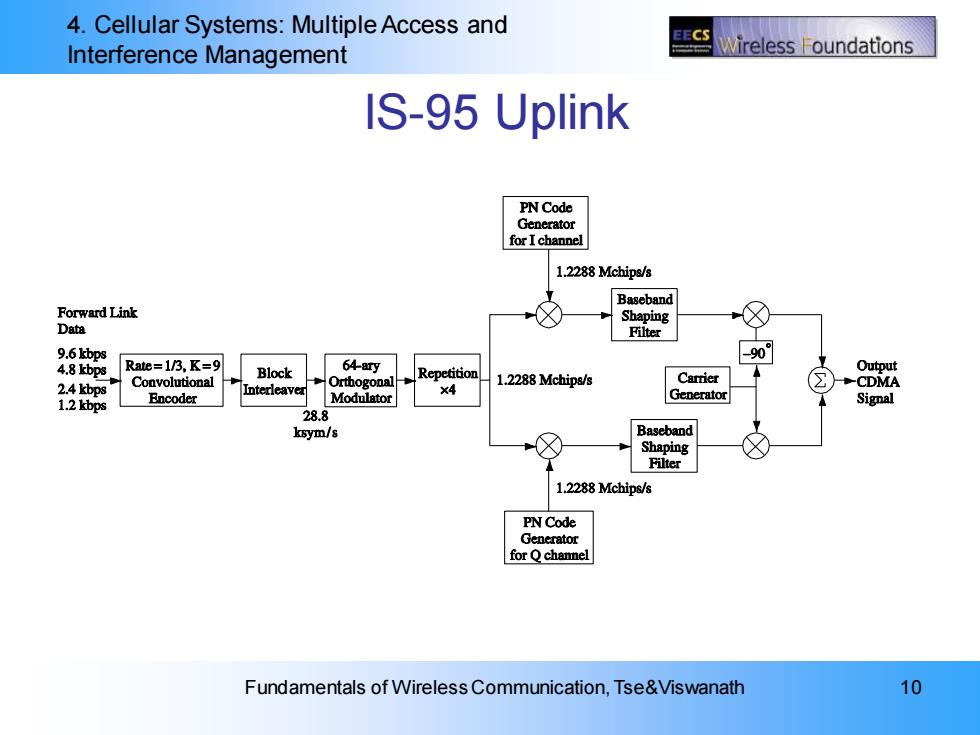
4.Cellular Systems:Multiple Access and ECS Interference Management ireless oundations IS-95 Uplink PN Code Generator for I channel 1.2288 Mchips/s Baseband Forward Link Shaping Data Filter 9.6bp8 -90 4.8 kbps Rate=1/3,K=9 Block 648ry Repetition Output 2.4 kbps Convolutional Orthogonal 1.2288 Mchips/s Carrier CDMA Encoder Interleaver 1.2 kbps Modulator ×4 Generator Signal 28.8 ksym/s Baseband Shaping Filter 1.2288 Mchips/s PN Code Generator for Q chanel Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 10
4. Cellular Systems: Multiple Access and Interference Management Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 10 IS-95 Uplink