
ECS Wireless oundations 5.Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 1 5. Capacity of Wireless Channels

5:Capacity of Wireless Channels EECS Vireless oundations Information Theory So far we have only looked at specific communication schemes. Information theory provides a fundamental limit to(coded) performance. It succinctly identifies the impact of channel resources on performance as well as suggests new and cool ways to communicate over the wireless channel. It provides the basis for the modern development of wireless communication. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 2
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 2 Information Theory • So far we have only looked at specific communication schemes. • Information theory provides a fundamental limit to (coded) performance. • It succinctly identifies the impact of channel resources on performance as well as suggests new and cool ways to communicate over the wireless channel. • It provides the basis for the modern development of wireless communication

5:Capacity of Wireless Channels EECS Wireless Foundations Historical Perspective Gugliemo Marconi Claude Shannon 1901 1948 Wireless communication .Information theory says every has been around since channel has a capacity. 1900's. Many recent advances based Ingenious but somewhat on understanding wireless adhoc design techniques channel capacity. New points of views arise. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 3
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 3 Historical Perspective • Wireless communication has been around since 1900’s. • Ingenious but somewhat adhoc design techniques Gugliemo Marconi Claude Shannon •Information theory says every channel has a capacity. • Many recent advances based on understanding wireless channel capacity. New points of views arise. 1901 1948
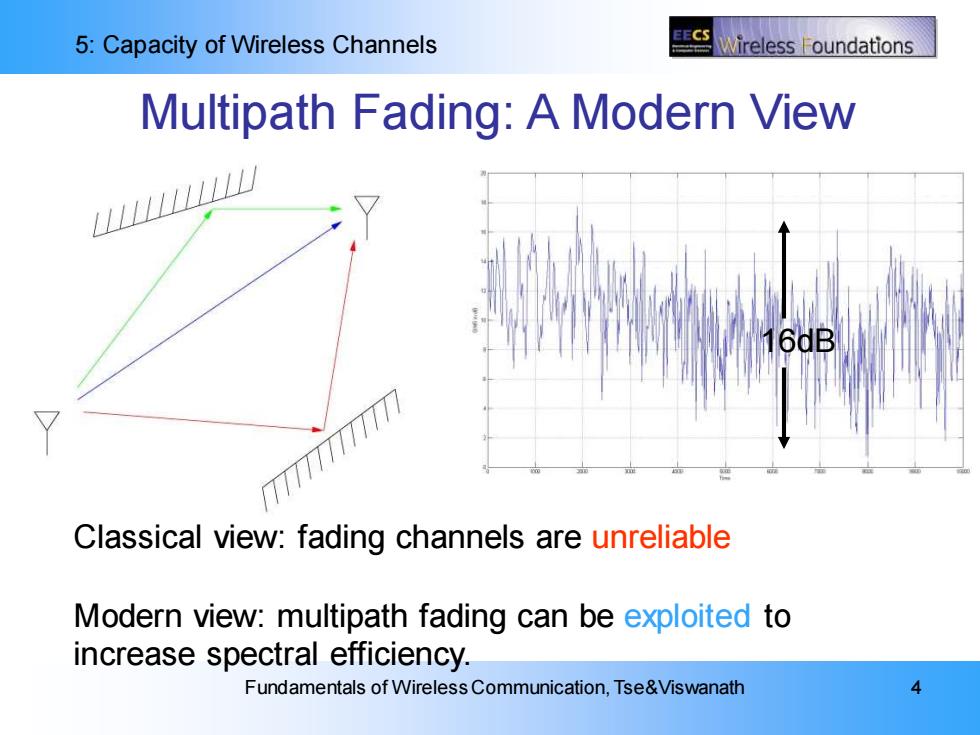
5:Capacity of Wireless Channels EECS Wireless oundations Multipath Fading:A Modern View LLL7777177777 6dB Classical view:fading channels are unreliable Modern view:multipath fading can be exploited to increase spectral efficiency. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 4
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 4 Multipath Fading: A Modern View Classical view: fading channels are unreliable Modern view: multipath fading can be exploited to increase spectral efficiency. 16dB
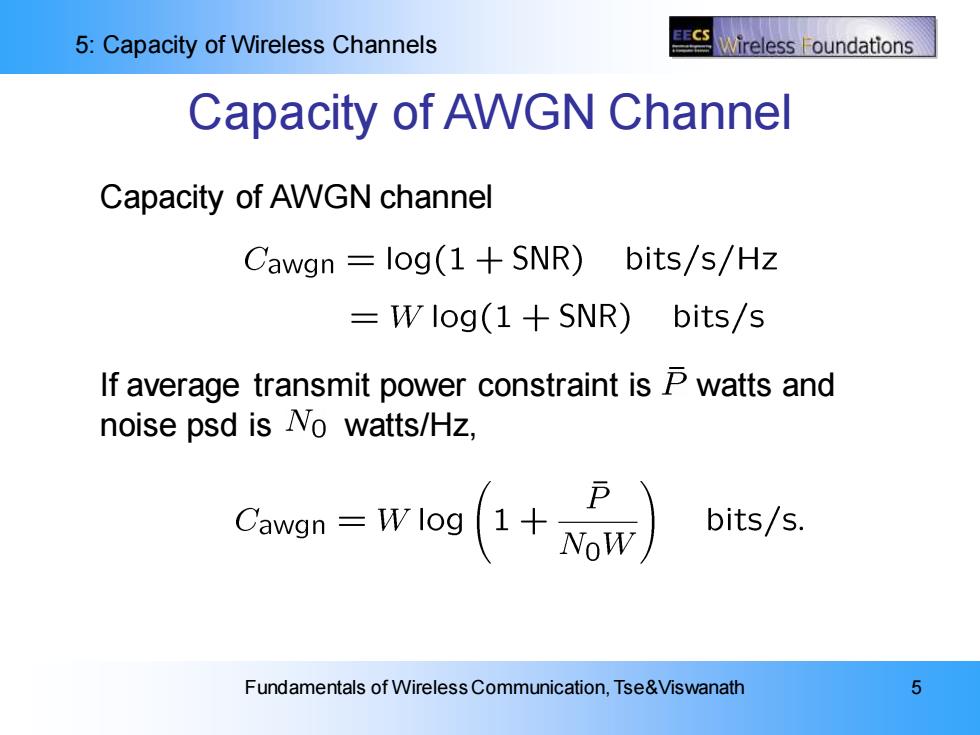
5:Capacity of Wireless Channels Vireless F oundations Capacity of AWGN Channel Capacity of AWGN channel Cawgn log(1+SNR) bits/s/HZ =Wlog(1+SNR)bits/s If average transmit power constraint is P watts and noise psd is No watts/Hz, bits/s. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 5
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 5 Capacity of AWGN Channel Capacity of AWGN channel If average transmit power constraint is watts and noise psd is watts/Hz
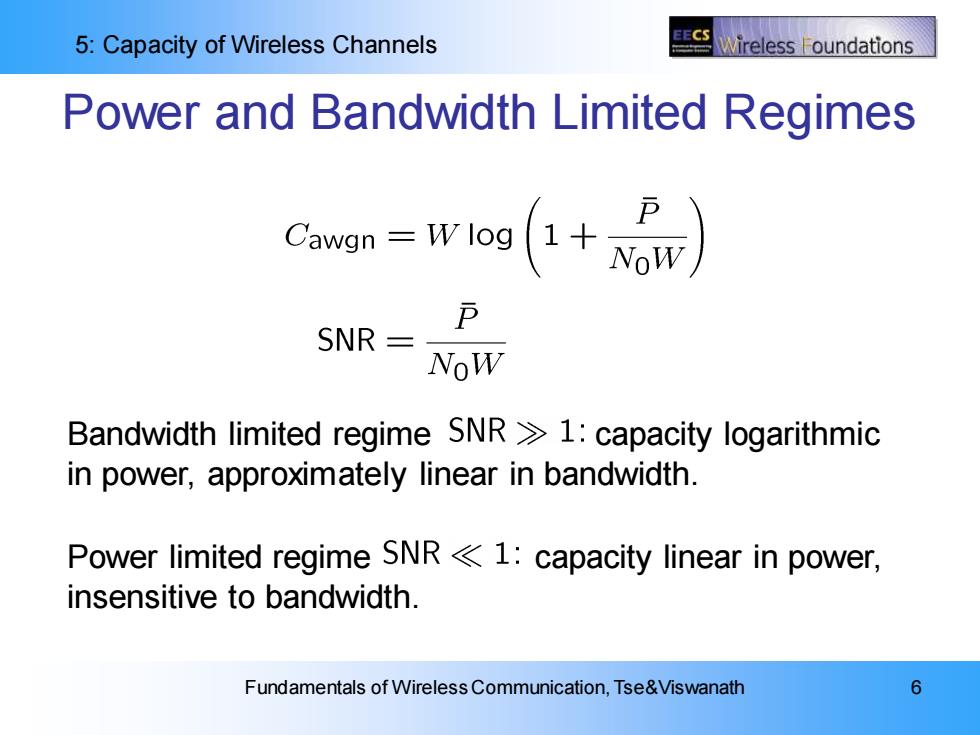
5:Capacity of Wireless Channels Vireless oundations Power and Bandwidth Limited Regimes SNR= NoW Bandwidth limited regime SNR1:capacity logarithmic in power,approximately linear in bandwidth. Power limited regime SNR<1:capacity linear in power, insensitive to bandwidth. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 6
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 6 Power and Bandwidth Limited Regimes Bandwidth limited regime capacity logarithmic in power, approximately linear in bandwidth. Power limited regime capacity linear in power, insensitive to bandwidth
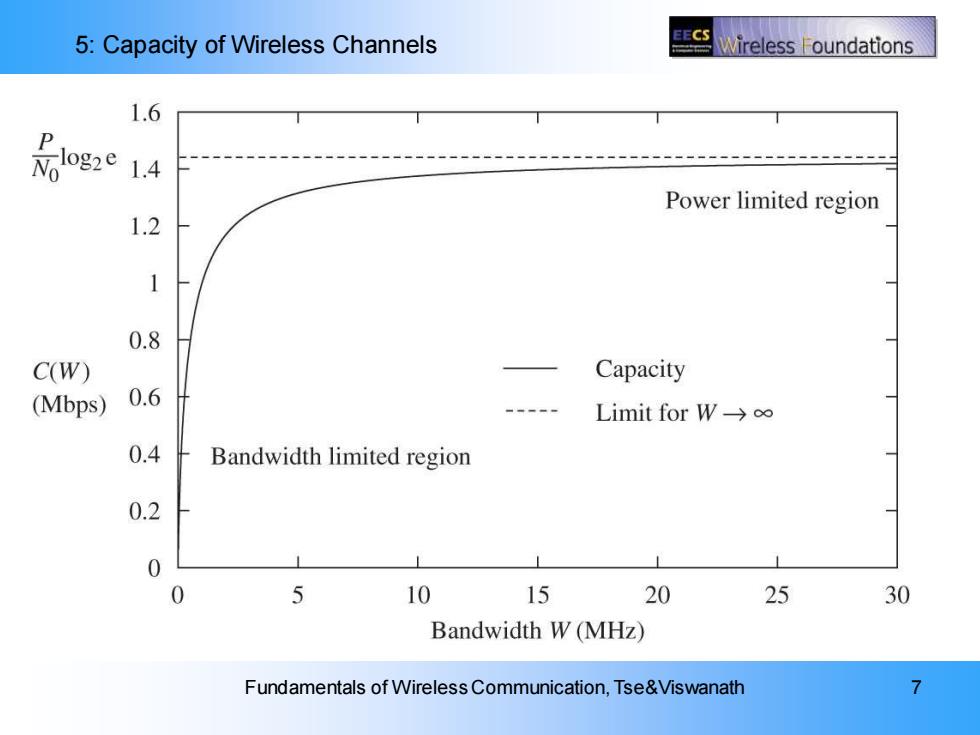
5:Capacity of Wireless Channels CS Wireless F oundations 1.6 P 1.4 Power limited region 1.2 0.8 C(W) Capacity (Mbps) 0.6 Limit for W→o∞ 0.4 Bandwidth limited region 0.2 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Bandwidth W(MHz) Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 7
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 7

5:Capacity of Wireless Channels Vireless oundations Example 1:Impact of Frequency Reuse Different degree of frequency reuse allows a tradeoff between SINR and degrees of freedom per user. Users in narrowband systems have high link SINR but small fraction of system bandwidth. Users in wideband systems have low link SINR but full system bandwidth. 。 Capacity depends on both SINR and d.o.f.and can provide a guideline for optimal reuse. Optimal reuse depends on how the out-of-cell interference fraction f(p)depends on the reuse factor p. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 8
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 8 Example 1: Impact of Frequency Reuse • Different degree of frequency reuse allows a tradeoff between SINR and degrees of freedom per user. • Users in narrowband systems have high link SINR but small fraction of system bandwidth. • Users in wideband systems have low link SINR but full system bandwidth. • Capacity depends on both SINR and d.o.f. and can provide a guideline for optimal reuse. • Optimal reuse depends on how the out-of-cell interference fraction f() depends on the reuse factor

5:Capacity of Wireless Channels EECS Wireless F oundations Numerical Examples Linear cellular system Hexagonal system 14 12 Rate bite//H 0.6 Frequency reuse factor 1 0.4 0. 12 Prequency reuse factor 1 0.2 /2… 04 51015 2025 30 -10 5 0 51015 202530 Cell edge SNR(dB) Cell edge SNR (dB) Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 9
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 9 Numerical Examples Linear cellular system Hexagonal system
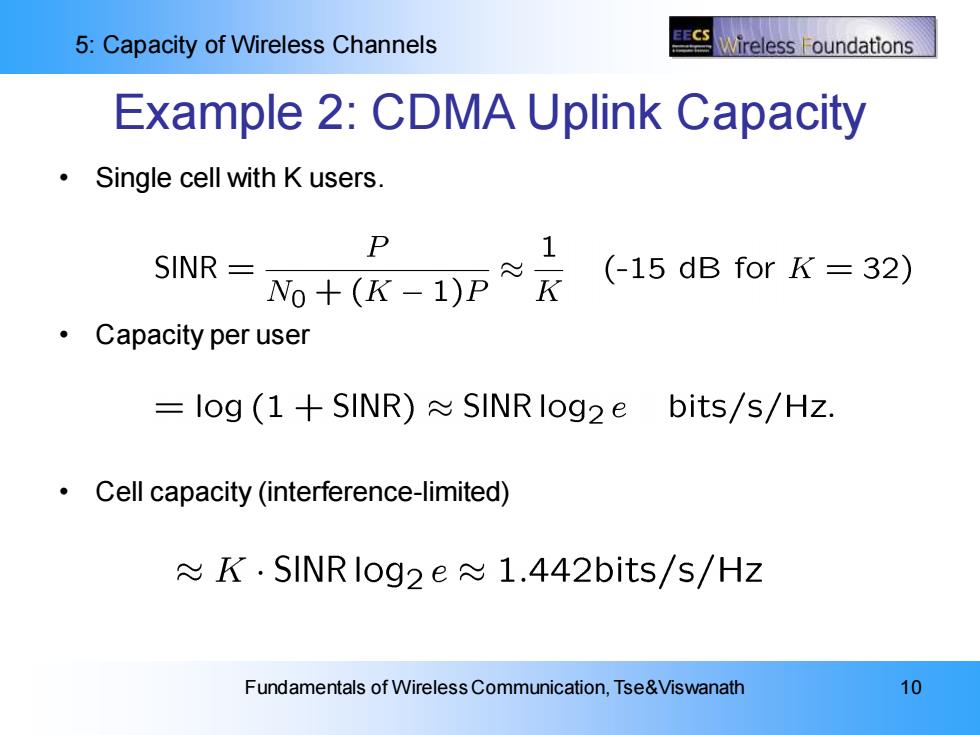
EECS 5:Capacity of Wireless Channels Wireless oundations Example 2:CDMA Uplink Capacity 。 Single cell with K users. P 1 SINR o+(K-1)P≈ (-15 dB for K=32) ·Capacity per user =log (1+SINR)SINRlog2e bits/s/Hz. Cell capacity (interference-limited) K.SINRlog2e 1.442bits/s/Hz Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 10
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 10 Example 2: CDMA Uplink Capacity • Single cell with K users. • Capacity per user • Cell capacity (interference-limited)