
Dynamic Vascular Response a)Structure Nerve of blood vessel Vata tasortm Adventitia External elastic lamina Tunica media Internal elastic lamina T'umica intima Endothelitom o可 【,a Lumen Lymphatic Ue结e Variable basal C打dothelum
a) Structure Dynamic Vascular Response
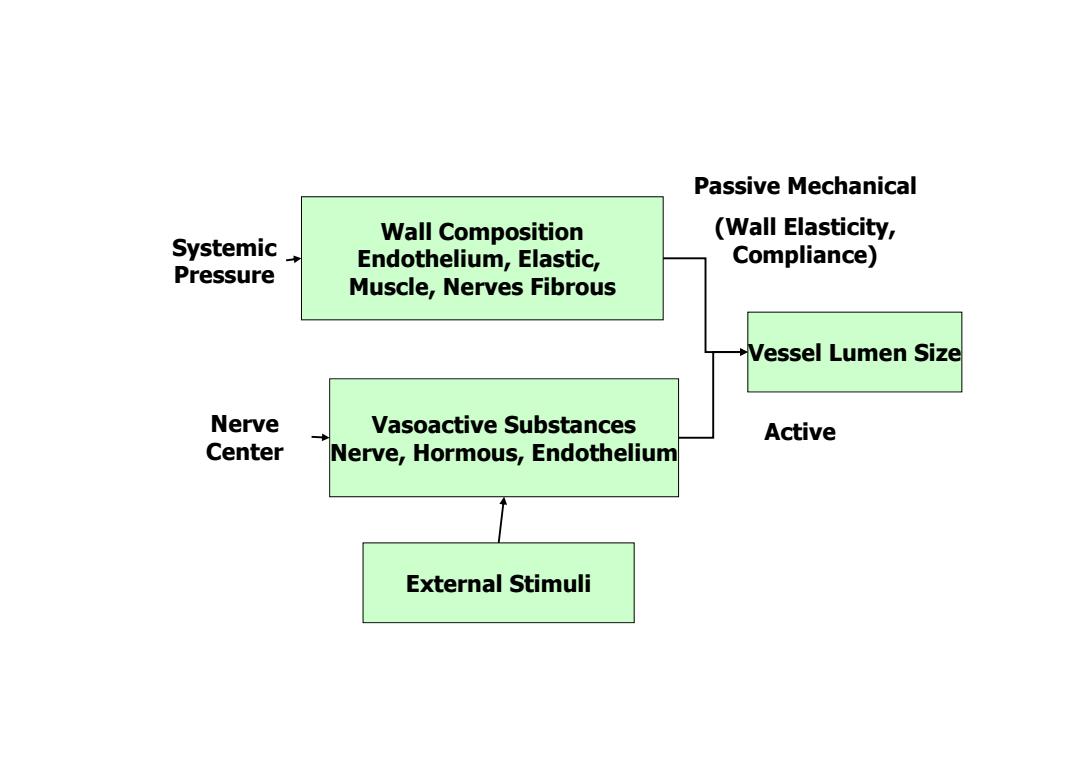
Passive Mechanical Wall Composition (Wall Elasticity, Systemic, Endothelium,Elastic, Compliance) Pressure Muscle,Nerves Fibrous Vessel Lumen Size Nerve Vasoactive Substances Active Center Nerve,Hormous,Endothelium External Stimuli
Vasoactive Substances Nerve, Hormous, Endothelium Wall Composition Endothelium, Elastic, Muscle, Nerves Fibrous Vessel Lumen Size Systemic Pressure Nerve Center Passive Mechanical (Wall Elasticity, Compliance) External Stimuli Active

b)Contractile apparatus -Smooth muscle cell: 。Spindle shaped 。Center diameter::3-8μm,length:15um-200μm
b) Contractile apparatus – Smooth muscle cell: • Spindle shaped • Center diameter:3‐8μm, length: 15 μm‐200μm
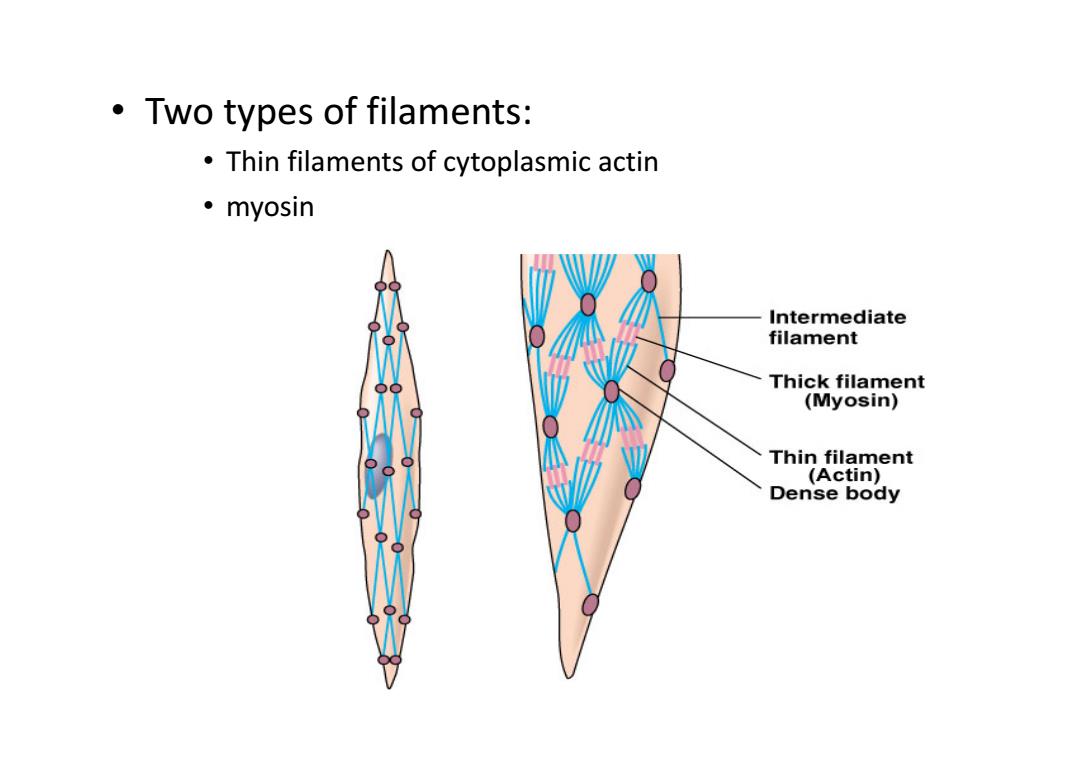
Two types of filaments: Thin filaments of cytoplasmic actin ·myosin Intermediate filament Thick filament (Myosin) Thin filament (Actin) Dense body
• Two types of filaments: • Thin filaments of cytoplasmic actin • myosin
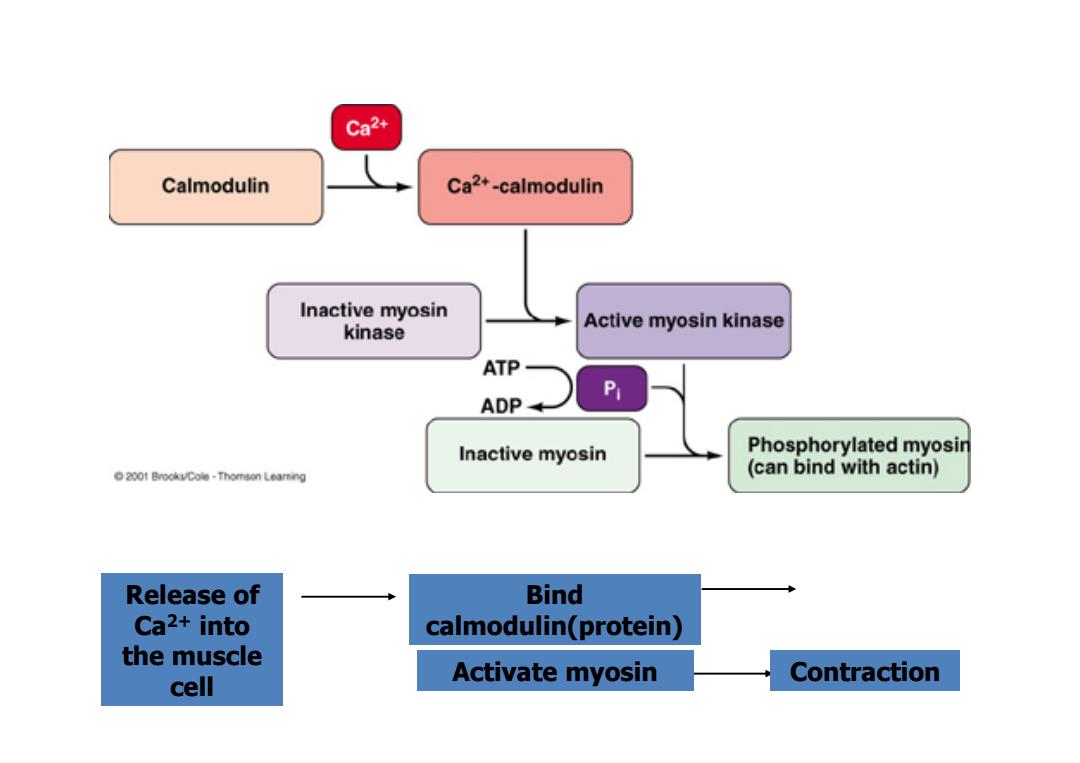
Ca2+ Calmodulin Ca2+-calmodulin Inactive myosin kinase Active myosin kinase ATP- ADP Inactive myosin Phosphorylated myosin 2001 BrockuCole-Thomson Leaming (can bind with actin) Release of Bind Ca2+into calmodulin(protein) the muscle cell Activate myosin Contraction
Release of Ca2+ into the muscle cell Bind calmodulin(protein) Activate myosin Contraction
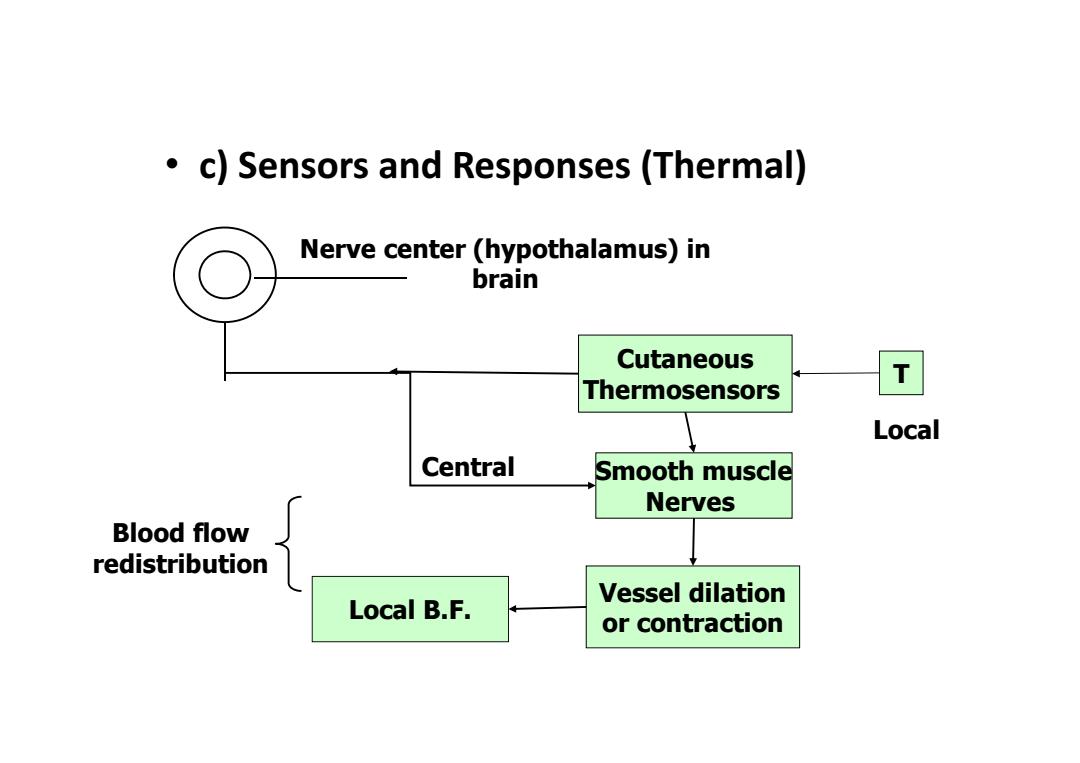
c)Sensors and Responses (Thermal) Nerve center (hypothalamus)in brain Cutaneous Thermosensors T Local Central Smooth muscle Nerves Blood flow redistribution Vessel dilation Local B.F. or contraction
Cutaneous Thermosensors Smooth muscle Nerves Vessel dilation or contraction Local B.F. T Local Nerve center (hypothalamus) in brain Blood flow redistribution Central • c) Sensors and Responses (Thermal)
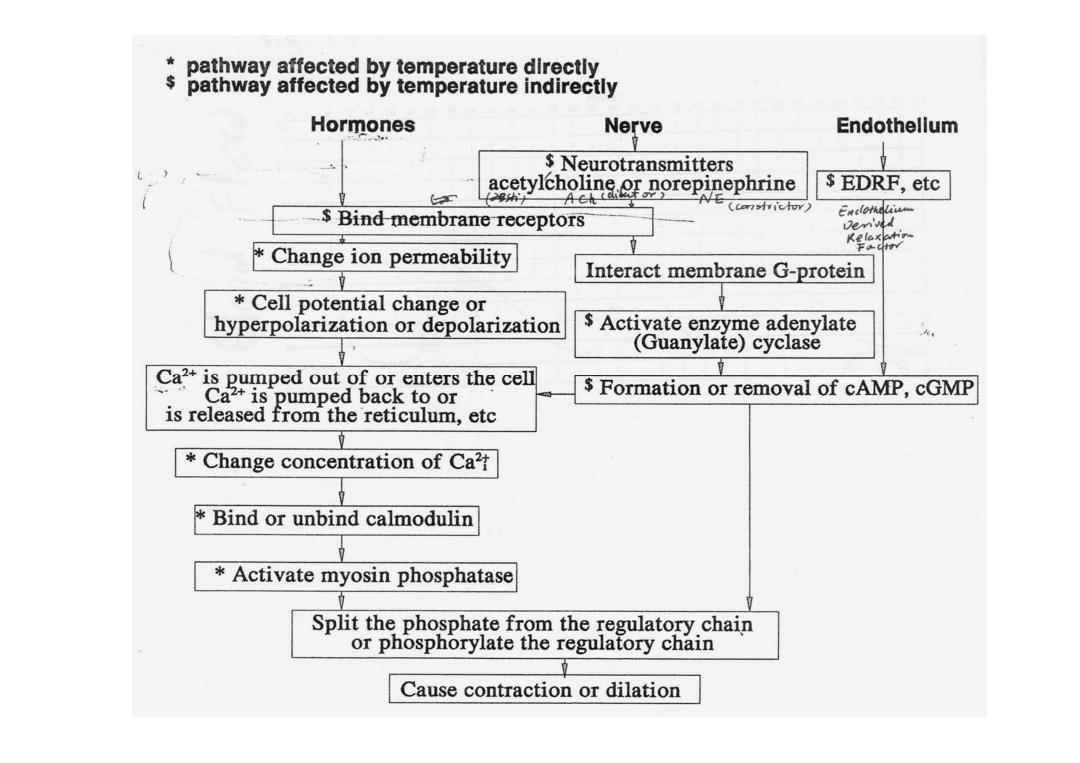
pathway affected by temperature directly $ pathway affected by temperature indirectly Hormones Nerve Endothellum Neurotransmitters acetylcholine.or norepinephrine EDRF,etc h为 .Bind-membrane receptors AE (oonshichor) Enclothaliwm Change ion permeability Interact membrane G-protein Cell potential change or hyperpolarization or depolarization Activate enzyme adenylate (Guanylate)cyclase Ca2is pumped out of or enters the cell Ca2+is pumped back to or Formation or removal of cAMP,cGMP is released from the reticulum,etc Change concentration of Ca Bind or unbind calmodulin Activate myosin phosphatase Split the phosphate from the regulatory chain or phosphorylate the regulatory chain Cause contraction or dilation
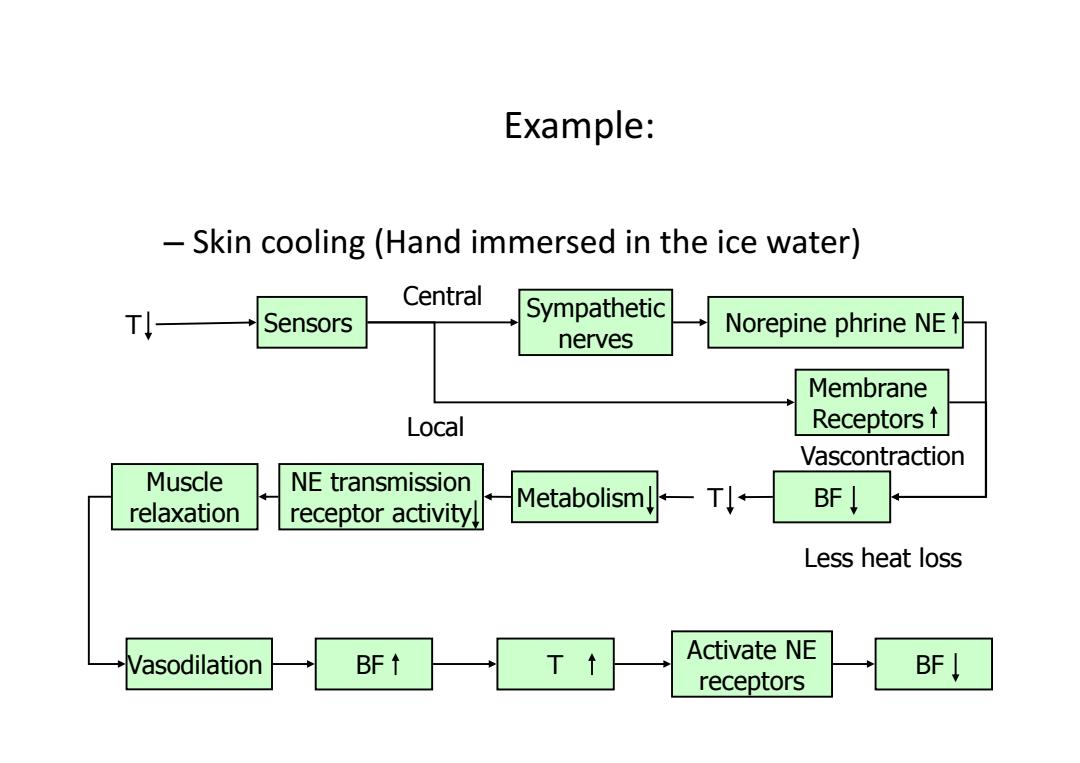
Example: -Skin cooling(Hand immersed in the ice water) Central T↓ Sensors Sympathetic Norepine phrine NE t nerves Membrane Local Receptors t Vascontraction Muscle NE transmission relaxation receptor activity. MetabolismlT BF Less heat loss Activate NE Vasodilation BF↑ T↑ receptors BF↓
Example: – Skin cooling (Hand immersed in the ice water) Metabolism Sympathetic nerves Norepine phrine NE Membrane Receptors BF NE transmission receptor activity Muscle relaxation Vasodilation BF T Activate NE receptors BF T T Sensors Local Central Vascontraction Less heat loss

MINUTES 4026202483236404485256606d6第72704B29610004082i610124 R.T.17'C

Tt→Sensors Central Nerves Exercise Ach Cardio Redistribution Local output 1 of BF NE receptors↓ Ca2+ Vasodilation active PHI Metabolic ratet BF t Passive Permeability of vessel wall f T↓ Local heating NE Blood viscosityt receptors t BF T↑
Local heating T Sensors Nerves NE receptors Ach Ca2+ Cardio output Redistribution of BF BF T NE receptors PH Metabolic rate Permeability of vessel wall Blood viscosity BF T Central Local Exercise Vasodilation active Passive CO2