
Lecture 2 Energy and Energy Transfer
Energy and Energy Transfer Lecture 2
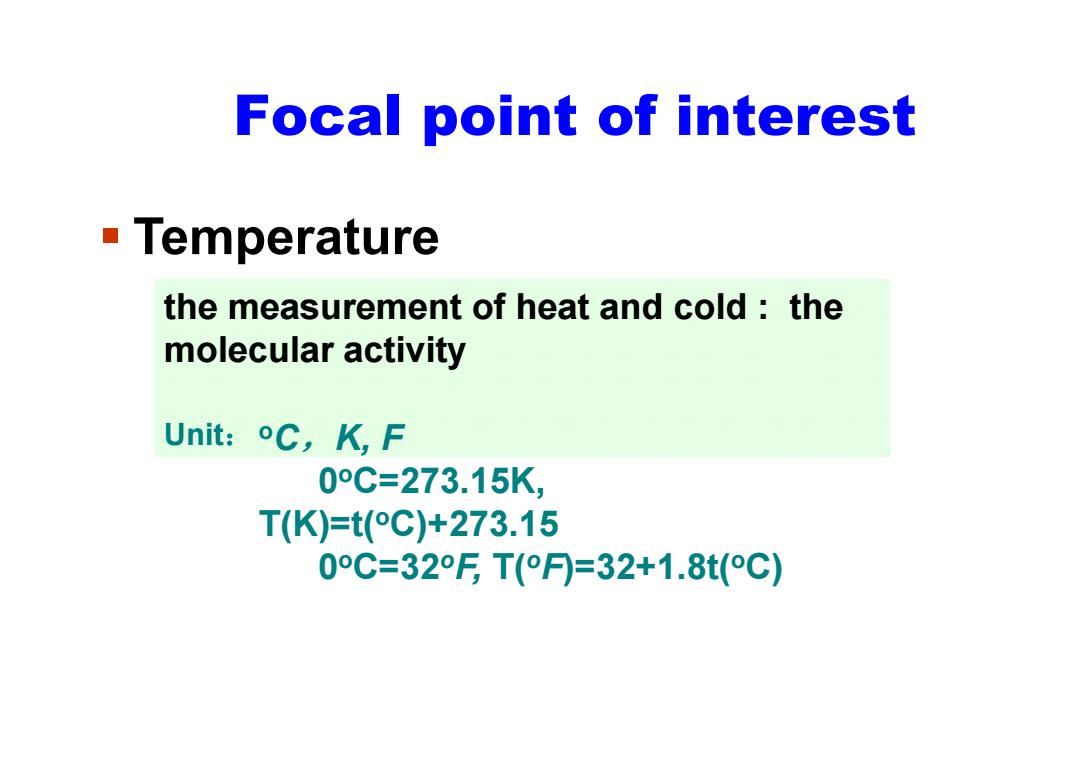
Focal point of interest Temperature the measurement of heat and cold:the molecular activity Unit:oC,K,F 0°C=273.15K, T(K)=t(°C)+273.15 0C=32FT(月=32+1.8t(°C)
Focal point of interest Temperature the measurement of heat and cold : the molecular activity Unit:o C ,K, F 0 oC=273.15K, T(K)=t( oC)+273.15 0 oC=32 oF, T( o F)=32+1.8t( oC)
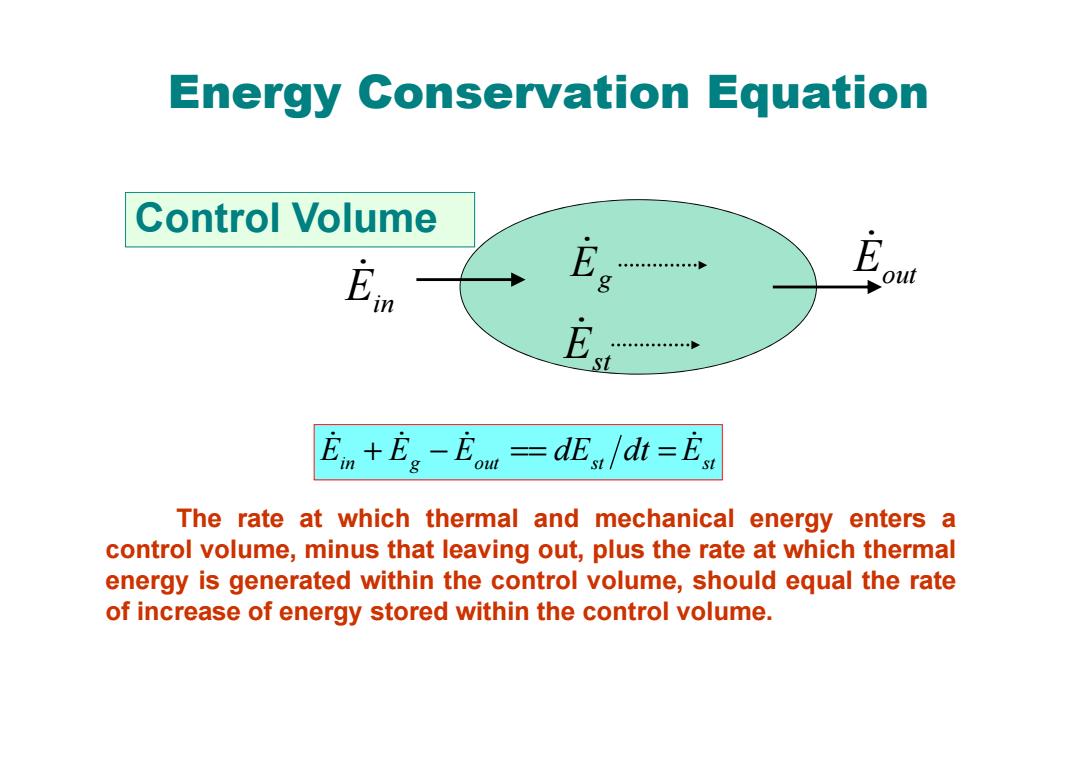
Energy Conservation Equation Control Volume 中年·”年… g out E t En+Eg-Eou =dEs /dt =Est The rate at which thermal and mechanical energy enters a control volume,minus that leaving out,plus the rate at which thermal energy is generated within the control volume,should equal the rate of increase of energy stored within the control volume
Energy Conservation Equation in g out st Est E E E dE dt + − == = The rate at which thermal and mechanical energy enters a control volume, minus that leaving out, plus the rate at which thermal energy is generated within the control volume, should equal the rate of increase of energy stored within the control volume. Control Volume Ein Eout E g Est

Energy inflow and outflow by conduction,convection,radiation Conduction across the surface: Rate equ. Ccond =-kAdI -Fourier's Law dx k--Thermal conductivity of the material [w/m-K]
Conduction across the surface: Rate equ. ——Fourier’s Law dT q A dx cond = − k k -- Thermal conductivity of the material [w/m·K] Energy inflow and outflow by conduction, convection, radiation

Conductivity for biological tissue: k,=0.419*(0.133+1.36mm)[wlmK)] m fraction of water mass in tissue k,(T)=k.x*[1+0.003(T-T】 Wdlch,1984
Conductivity for biological tissue: 0.419* (0.133 1.36 ) t w k m = + m w 0 , 0 ( ) *[1 0.003( )] t tT kT k T T =+ − fraction of water mass in tissue Wdlch, 1984 [w/(m·K)]
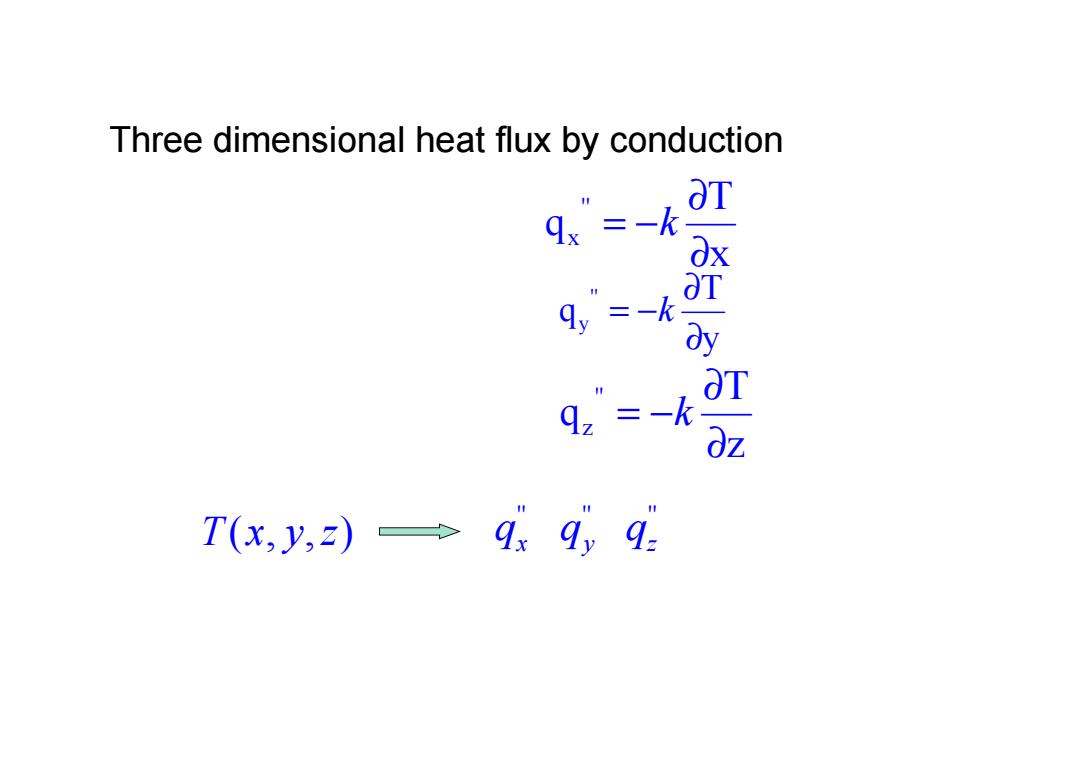
Three dimensional heat flux by conduction OT 9x =-k y =-k =-k r T(x,y,)→99,9
x T q '' x ∂ ∂ = −k y T q '' y ∂ ∂ = −k z T q '' z ∂ ∂ = −k Three dimensional heat flux by conduction T(x, y,z) '' qx '' qy '' qz
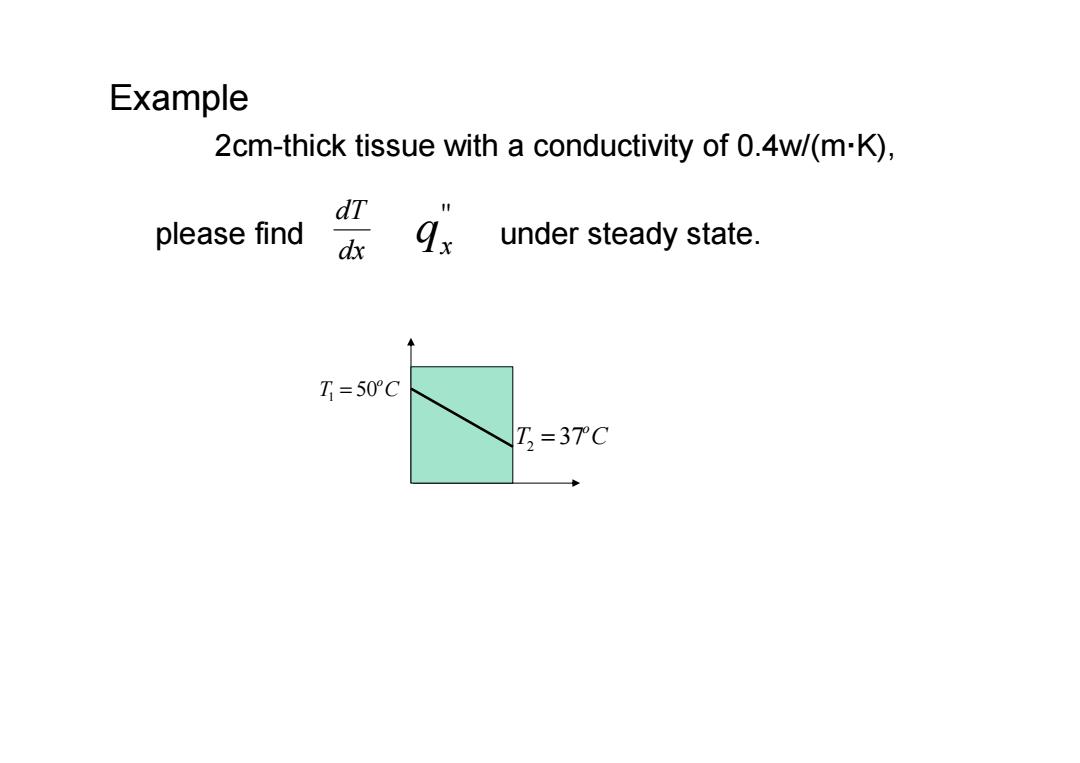
Example 2cm-thick tissue with a conductivity of 0.4w/(m-K) please find gx under steady state. T=50°C T,=37C
Example 2cm-thick tissue with a conductivity of 0.4w/(m·K), please find under steady state. T Co 1 = 50 '' qx T Co 2 = 37 dx dT
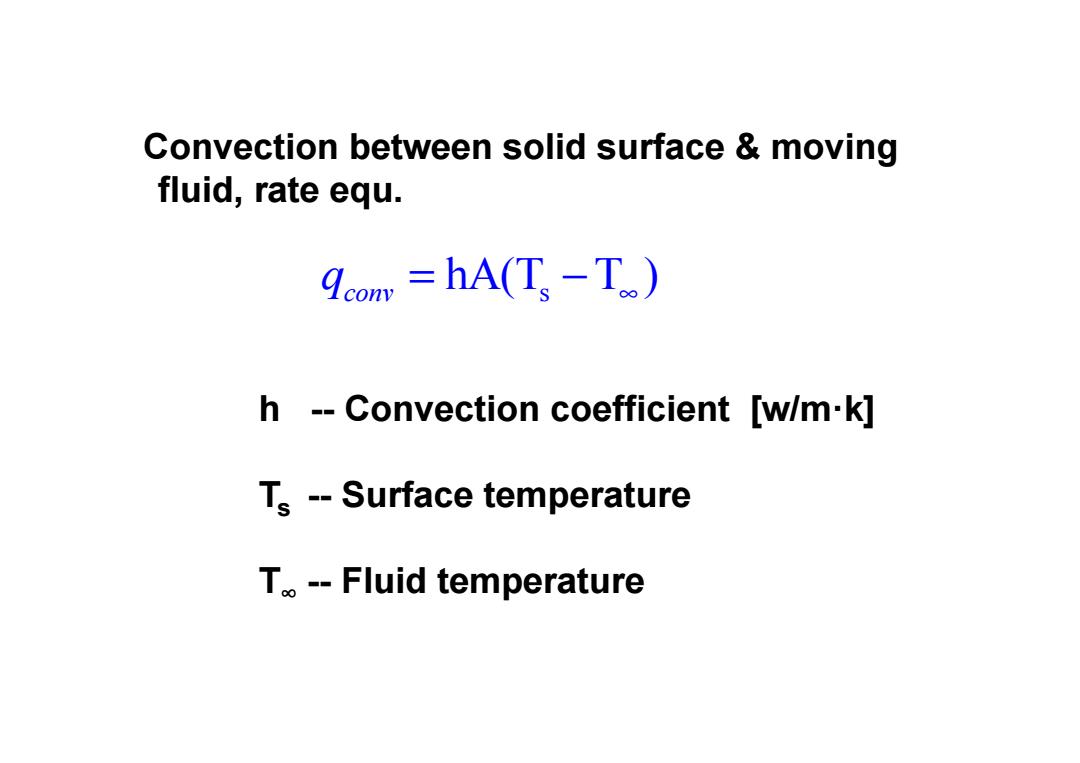
Convection between solid surface moving fluid,rate equ. com =hA(Ts -T) h --Convection coefficient [w/m-k] Ts --Surface temperature T。-Fluid temperature
Convection between solid surface & moving fluid, rate equ. s hA(T T ) conv q = − ∞ h -- Convection coefficient [w/m·k] Ts -- Surface temperature T ∞ -- Fluid temperature
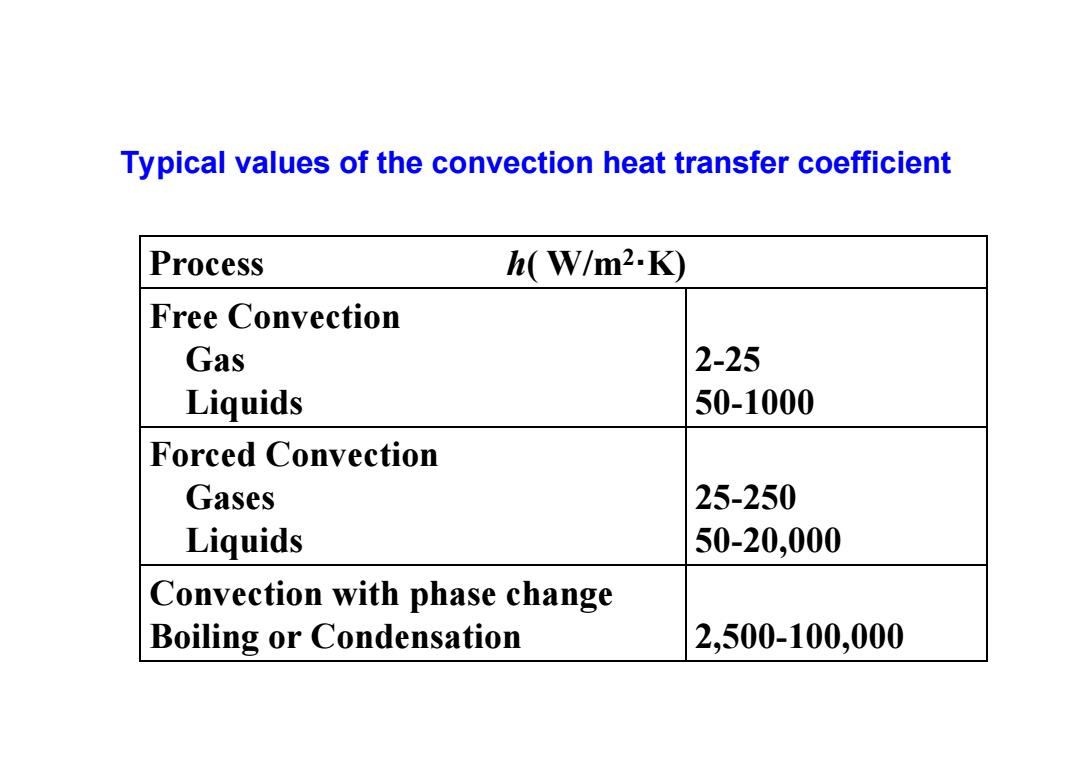
Typical values of the convection heat transfer coefficient Process h(W/m2.K) Free Convection Gas 2-25 Liquids 50-1000 Forced Convection Gases 25-250 Liquids 50-20,000 Convection with phase change Boiling or Condensation 2,500-100,000
Typical values of the convection heat transfer coefficient Process h( W/m 2·K) Free Convection Gas Liquids 2-25 50-1000 Forced Convection Gases Liquids 25-250 50-20,000 Convection with phase change Boiling or Condensation 2,500-100,000

net radiation exchange from the surface to the surrounding: 9=8o(T4-T4)A
net radiation exchange from the surface to the surrounding: 4 4 s sur εσ(T T )A rad s q = −