
统计学习理论及应用 第九讲 数据表示-不含参模型 编写:文泉、陈娟 电子科技大学 计机科学与工程学院
统计学习理论及应用 第九讲 数据表示-不含参模型 编写:文泉、陈娟 电子科技大学 计算机科学与工程学院

目录 概率密度估计 ②直方图方法 Parzen窗 ④K近邻密度估计 ·k近邻分类器 1/27
目录 1 概率密度估计 2 直方图方法 3 Parzen 窗 4 K 近邻密度估计 k 近邻分类器 1 / 27

9.1.概率密度估计(Density Estimation) 一些基本概念 Density estimation:estimating the probability density function p(x)based on a given set of training samples D={x1,x2,,Xw}. Estimated density:denoted by p(x). Training samples are i.i.d.and distributed according to p(x): Parametric estimation:parameter vector 0 of p(x; Non-parametric estimation:a function p:F->R O Finite number of training samples meaning that there will be some errors in the function (density)estimation 2/27
9.1. 概率密度估计 (Density Estimation) 一些基本概念 1 Density estimation: estimating the probability density function p(x) based on a given set of training samples D = {x1, x2, ..., xN}. 2 Estimated density: denoted by pˆ(x). 3 Training samples are i.i.d. and distributed according to p(x). 4 Parametric estimation: parameter vector θ of p(x; θ) 5 Non-parametric estimation: a function p : F −→ R 6 Finite number of training samples meaning that there will be some errors in the function (density) estimation. 2 / 27

含参模型估计概率是已知总体分布形式(即函数形式) ·但实际情况,我们对分布其实是一无所知的,不含参模 型可以应用于任何概率分布的场合,无需假定概率分布的 形式是已知。 3/27
▶ 含参模型估计概率是已知总体分布形式 (即函数形式) ▶ 但实际情况,我们对分布其实是一无所知的,不含参模 型可以应用于任何概率分布的场合,无需假定概率分布的 形式是已知。 3 / 27

假定n个样本x1,2,,xn,采样自分布p(x),则一个向量 x在一个区域R的概率P为: P-p(. ·那么n个样本中,有k个样本在区域R的概率,由二项 式分布(binomial distribution)有: p(1-P)-. ·由随机变量k的期望和方差: Ek=nP var(k)nP(1-P) 有:E[月=E[因/n=P,var[]=var[/=P(1-P)/n 4/27
▶假定 n 个样本 x1, x2, ..., xn,采样自分布 p(x),则一个向量 x 在一个区域 R 的概率 P 为: P = ∫ R p(x ′ )dx′ . ▶ 那么 n 个样本中,有 k 个样本在区域 R 的概率,由二项 式分布 (binomial distribution) 有: Pk = ( n k ) P k (1 − P) n−k . ▶ 由随机变量 k 的期望和方差: E[k] = nP var(k) = nP(1 − P) 有:E[ k n ] = E[k]/n = P, var[ k n ] = var[k]/n 2 = P(1 − P)/n 4 / 27
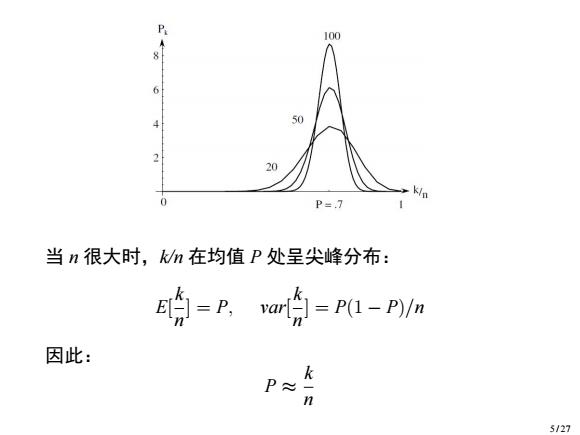
P 100 50 20 K/p 0 P=.7 当n很大时,kn在均值P处呈尖峰分布: 的=P,an哈=Pl-P/n 因此: P≈ 5/27
当 n 很大时,k/n 在均值 P 处呈尖峰分布: E[ k n ] = P, var[ k n ] = P(1 − P)/n 因此: P ≈ k n 5 / 27

·如果假定p(x)连续,且区域R足够小,使得p(x)在R这 个区域几乎没有变化,那么我们可以得到如下的一个近似: P=p)≈p) 其中,x是R中的一个点,V是R这个区域的体积(二维情 况下V为面积)。 由P≈k/n,R区域的概率密度函数可以近似估计为: P。k/n 6/27
▶ 如果假定 p(x) 连续,且区域 R 足够小,使得 p(x) 在 R 这 个区域几乎没有变化,那么我们可以得到如下的一个近似: P = ∫ R p(x ′ )dx′ ≈ p(x)V 其中,x 是 R 中的一个点,V 是 R 这个区域的体积(二维情 况下 V 为面积)。 ▶ 由 P ≈ k/n,R 区域的概率密度函数可以近似估计为: p(x) ≈ P V ≈ k/n V 6 / 27
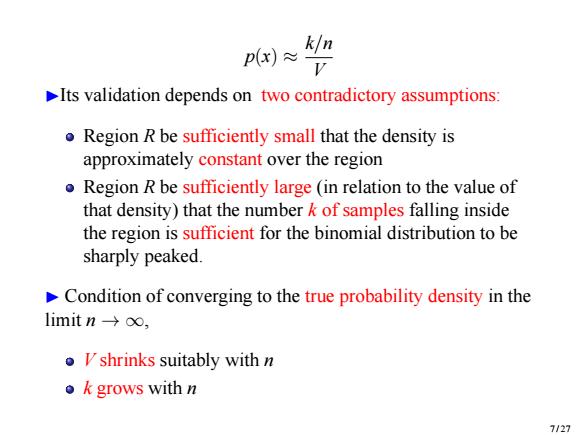
p(x)≈ kn Its validation depends on two contradictory assumptions: o Region R be sufficiently small that the density is approximately constant over the region o Region R be sufficiently large (in relation to the value of that density)that the number k of samples falling inside the region is sufficient for the binomial distribution to be sharply peaked. Condition of converging to the true probability density in the limit n→o, o Ishrinks suitably with n ●k grows with n 7/27
p(x) ≈ k/n V ▶Its validation depends on two contradictory assumptions: Region R be sufficiently small that the density is approximately constant over the region Region R be sufficiently large (in relation to the value of that density) that the number k of samples falling inside the region is sufficient for the binomial distribution to be sharply peaked. ▶ Condition of converging to the true probability density in the limit n → ∞, V shrinks suitably with n k grows with n 7 / 27

k/n p(x)≈ In practice,we will have to find a compromise for V: o Large enough to include enough examples within R o Small enough to support the assumption that is constant within R Two ways to calculate p(x): o fix Iand determine k from the data,giving rise to the kernel approach,such as histogram,Parzen window ofix k and determine /from the data,which gives rise to the k-nearest-neighbor 8/27
p(x) ≃ k/n V ▶ In practice, we will have to find a compromise for V: Large enough to include enough examples within R Small enough to support the assumption that is constant within R ▶ Two ways to calculate p(x): fix V and determine k from the data, giving rise to the kernel approach, such as histogram, Parzen window fix k and determine V from the data, which gives rise to the k-nearest-neighbor 8 / 27
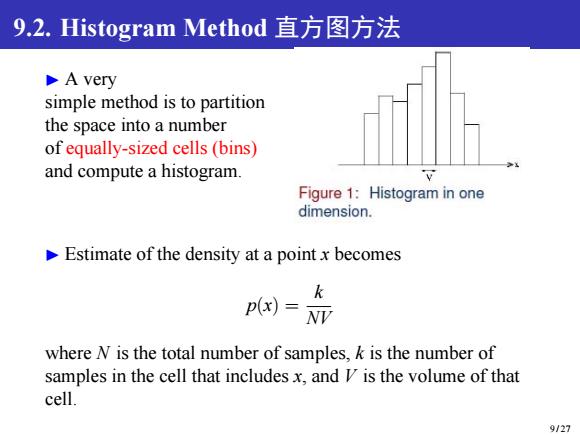
9.2.Histogram Method直方图方法 A very simple method is to partition the space into a number of equally-sized cells(bins) and compute a histogram. Figure 1:Histogram in one dimension. Estimate of the density at a point x becomes k p(x)= WN亚 where N is the total number of samples,k is the number of samples in the cell that includes x,and I is the volume of that cell. 9/27
9.2. Histogram Method 直方图方法 ▶ A very simple method is to partition the space into a number of equally-sized cells (bins) and compute a histogram. ▶ Estimate of the density at a point x becomes p(x) = k NV where N is the total number of samples, k is the number of samples in the cell that includes x, and V is the volume of that cell. 9 / 27