
第四章外场中的原子 4.1塞曼效应 *4.2磁共振技术 *4.3原子频标 4.4斯塔克效应
第四章 外场中的原子 4.1 塞曼效应 *4.2 磁共振技术 *4.3 原子频标 4.4 斯塔克效应
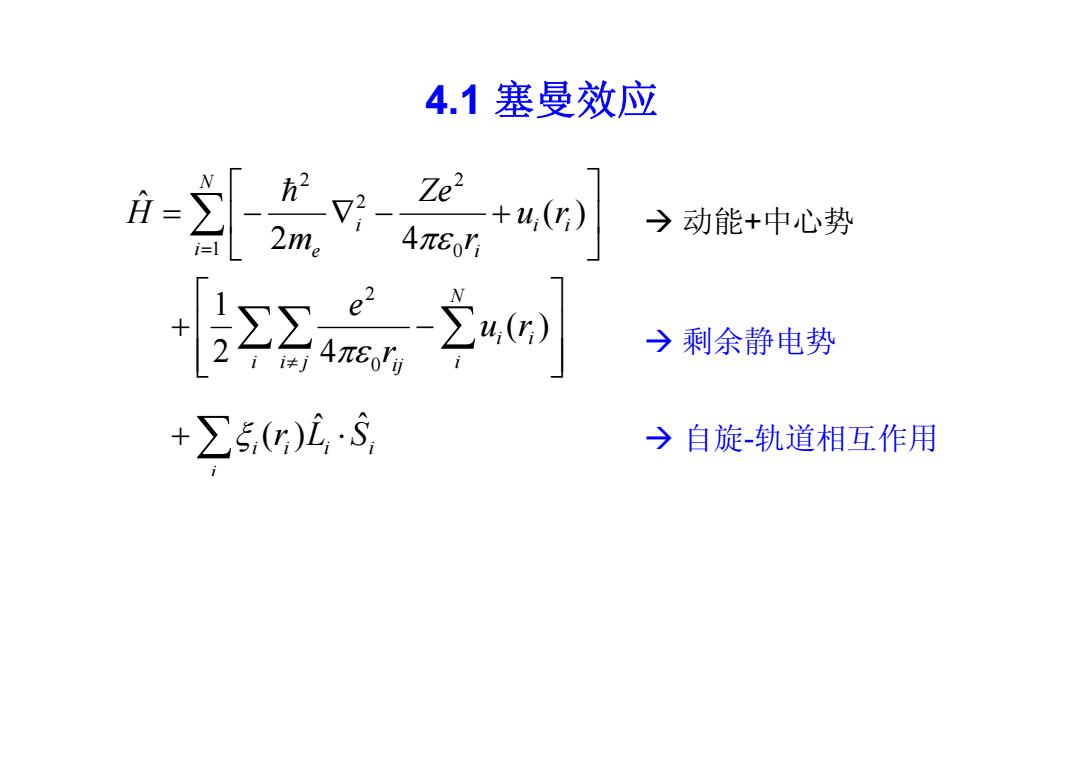
4.1塞曼效应 -含编 →动能+中心势 -2 →剩余静电势 +∑5G)L,S →自旋-轨道相互作用
4.1 塞曼效应 B r L S u r r e u r r Ze m H i i i i i N i i i i j i ij N i i i i i e ˆ ˆ ( ) ( ) 2 4 1 ( ) 2 4 ˆ 0 2 1 0 2 2 2 动能+中心势 剩余静电势 自旋-轨道相互作用 原子磁矩与外场作用 原子总磁矩 外磁场
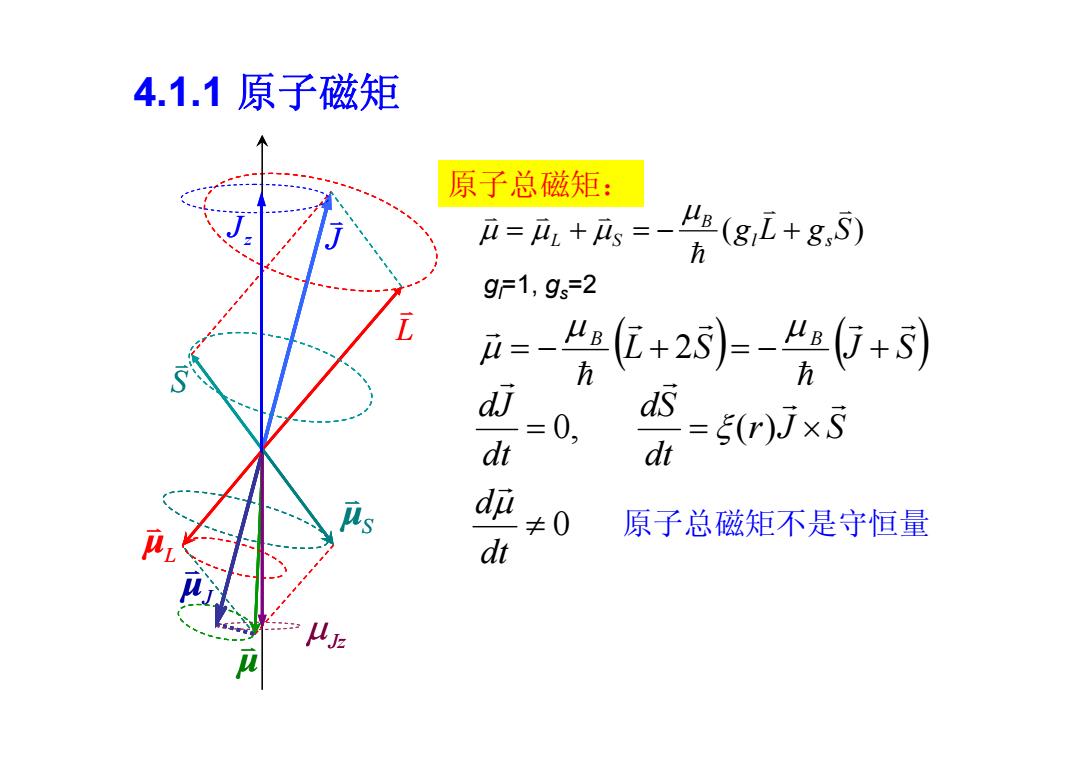
4.1.1原子磁矩 原子总磁矩: =m,+,=-号 Hn(g L+g,S) 9F1,9s=2 i=、 6+2=-片0+到 dJ 0, dt dS =g(r)Jx5 ds dt d ≠0 原子总磁矩不是守恒量 dt 八
4.1.1 原子磁矩 L S J L μ S μ μ J μ z J Jz L S J L μ S μ μ J μ z J Jz 原子总磁矩: (g L g S) l s B L S gl=1, gs=2 L S J S B B 2 r J S dt dS dt dJ 0, ( ) 0 dt d 原子总磁矩不是守恒量
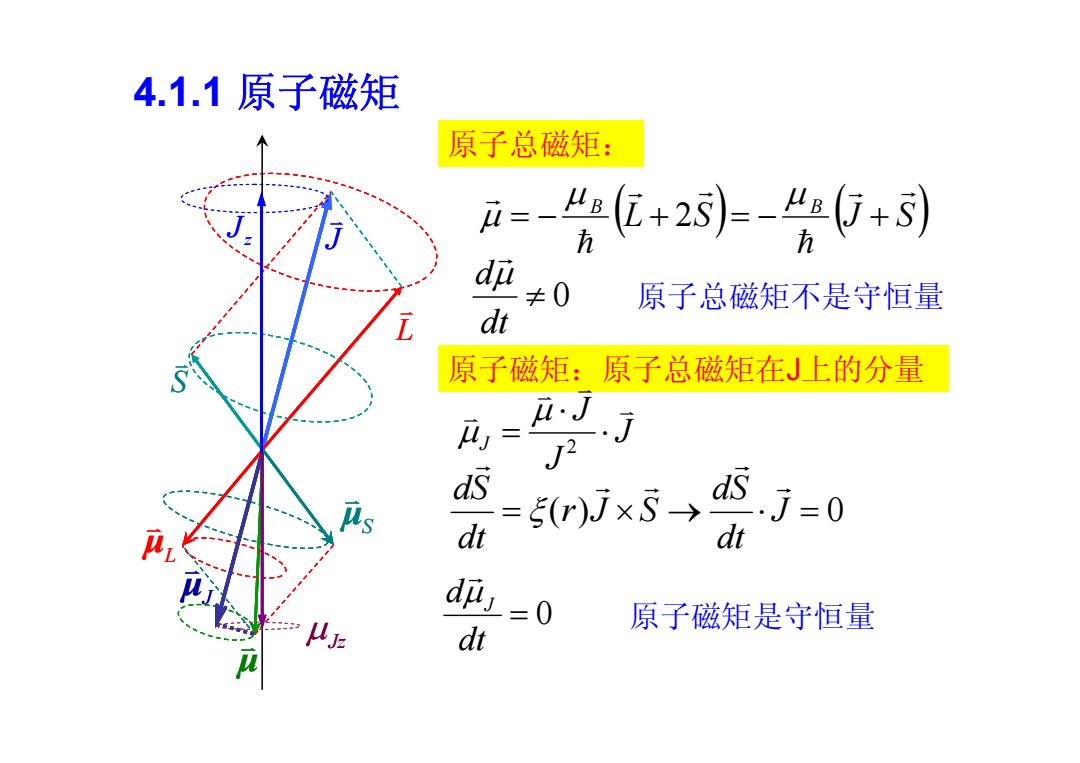
4.1.1原子磁矩 原子总磁矩: 及=-片+2列=-会0+到 d+0 原子总磁矩不是守恒量 dt 原子磁矩:原子总磁矩在」上的分量 J. 2 ds .j=0 dt 5Wx5, dt d =0 原子磁矩是守恒量 dt
4.1.1 原子磁矩 L S J L μ S μ μ J μ z J Jz L S J L μ S μ μ J μ z J Jz 原子总磁矩: L S J S B B 2 ( ) J 0 dt dS r J S dt dS 0 dt d 原子总磁矩不是守恒量 原子磁矩:原子总磁矩在 J上的分量 J J J J 2 0 dt d J 原子磁矩是守恒量

应=-i+25)=-(0+5) a-)7=-402+5八小J 2=-5=j2+52-2j.5 7.5=)2+52-E) 了2+2-正)J=-8九 + LBJ 2h 2J2 8y=1+ J(J+1)+S(S+1)-L(L+1) 朗德因子 2J(J+1)
J J J S J J L S J S B B B 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 J S J S L L J S J S J S J J B J S L J ) 2 ( 1 2 2 2 2 2 g J B J 2 ( 1 ) ( 1 ) ( 1 ) ( 1 ) 1 J J J J S S L L g J 朗德因子

J =一8」h 4=-8VJ(J+1)4E L=-mjgjMB m=-J,-J+1,…,J-1,J 上述推导是在假设外磁场远远小于原子内部磁场的情况下获得的,也 即外磁场很弱,并不破坏自旋轨道耦合的情况。因此朗德因子只适 用于弱外磁场的情形。 LS耦合的最后一步也是自旋-轨道相互作用,所以上述公式对于 LS耦合也适用
g J B J J J J B g J (J 1) Jz J J B m g m J J J J J , 1,, 1, 上述推导是在假设外磁场远远小于原子内部磁场的情况下获得的,也 即外磁场很弱,并不破坏自旋-轨道耦合的情况。因此朗德因子只适 用于弱外磁场的情形。 LS耦合的最后一步也是自旋轨道相互作用,所以上述公式对于 LS耦合也适用

4.1.2塞曼效应 896年,塞曼在研究磁场对光的影响实验时发现 One of the items in the Zeeman archive is a laboratory notebook that contains the first recorded observation of the Zeeman effect [8].The entry is dated 2 September 1896 and is preceded by many pages of notes on totally unrelated experimental work.It opens with the words: 'Influence of magnetization on flame.'The notes that follow describe a very simple experiment:a piece of asbestos,soaked in a solution of kitchen salt,is put in a flame placed between the poles of a magnet.With the help of a grating,a spectrum is created.The vellow sodium D-lines appear as narrow and sharp lines.'When the magnet is switched on',the description continues, the lines become wider until they are two to three times 塞曼(P.Zeeman, as wide'.This simple sentence describes the discovery 1865-1943),荷兰 something new. A publication describing his 人,1902年诺贝尔 experiments was presented by Kamerlingh Onnes at the 物理学奖获得者 monthly meeting of Saturday 31 October of the Section "in recognition of the of Sciences of the Dutch Academy of Sciences.In it Zeeman concluded: extraordinary service they rendered by their researches The experiments have made it increasingly probable that into the influence of magnetism absorption and thus also emission lines of a gaseous upon radiation phenomena" substance are widened by magnetic forces.[4] A.J.Kox,Euro.J.Phys.18(1997)139-144
4.1.2 塞曼效应 塞曼(P. Zeeman, 1865-1943),荷兰 人,1902年诺贝尔 物理学奖获得者 "in recognition of the extraordinary service they rendered by their researches into the influence of magnetism upon radiation phenomena" 1896年,塞曼在研究磁场对光的影响实验时发现 A. J. Kox, Euro. J. Phys. 18 (1997) 139-144

9 Ba起hhth6k1以 di lyju in it wrvul t tny wimin tal hritit e2么3efu人wk wi化hh+化i6af atdoo以do’oA Atesdept.wuuriti t pting.synilmalii ia 么hkt hm五gekw4 ohghaian,防wa2z 2网 k浴以 va.le-tt mh总 1rh认. 木cdwf vir Beeh Tnil hiau h aw fut l元kn1: s/-u/ra,公 Figure 3.Two pages from Zeeman's notebook with the first recorded observation of the Zeeman effect

洛伦兹的解释 According to Zeeman's reminiscences [11],the Monday following the Saturday on which Zeeman's paper was submitted,a theor The general solution of the last equation is: effect was proposed by Lorent at the Academy meeting.The =acos(@ot+p) (4) the following model.Atoms harmonically bound to a centr with a and p constants and wo =2(k/m).For the The frequencies of their vibr and y motions two sets of solutions are found: frequencies of the spectral li question.When a magnetic fiel x=a1c0s(ω1t+p1) (5) particles will experience a Lor the harmonic force.For a fie y=-a1S1n(ω1t+p1) (6) equations of motion take the f and d2x eH dy 171 dt2 =-kx十 c dr x a2 cos(@2t+p2) (7) d2y eH dx n y a2 sin(@2t +p2) (8) dr2 三一ky一 c dt d2z The new frequencies w and @z are found from: m ar =-kz. 、 eH on=0 (9) mc ,2 eH (10 mc
洛伦兹的解释

塞曼在1896-1897年几个月的时间里: 1.发现了谱线在磁场中被展宽 2.被展宽的谱线边界上的光有偏振,验证了洛伦兹的解释 3.测量了原子中谐振子的荷质比,比氢离子大1000倍 ●进一步的实验研究发现,展宽的谱线包含三条分裂的谱线, 正如洛伦兹的理论预言。 。再进一步的实验研究发现,光谱线在外磁场中分裂会出现多 于或少于三条的情形,而这无法由洛仑兹的理论予以解释。 光谱线在外磁场中分裂为三条的现象就称为正常塞曼效应, 否则就称为反常塞曼效应
塞曼在1896-1897年几个月的时间里: 1. 发现了谱线在磁场中被展宽 2. 被展宽的谱线边界上的光有偏振,验证了洛伦兹的解释 3. 测量了原子中谐振子的荷质比,比氢离子大1000倍 进一步的实验研究发现,展宽的谱线包含三条分裂的谱线, 正如洛伦兹的理论预言。 再进一步的实验研究发现,光谱线在外磁场中分裂会出现多 于或少于三条的情形,而这无法由洛仑兹的理论予以解释。 光谱线在外磁场中分裂为三条的现象就称为正常塞曼效应, 否则就称为反常塞曼效应