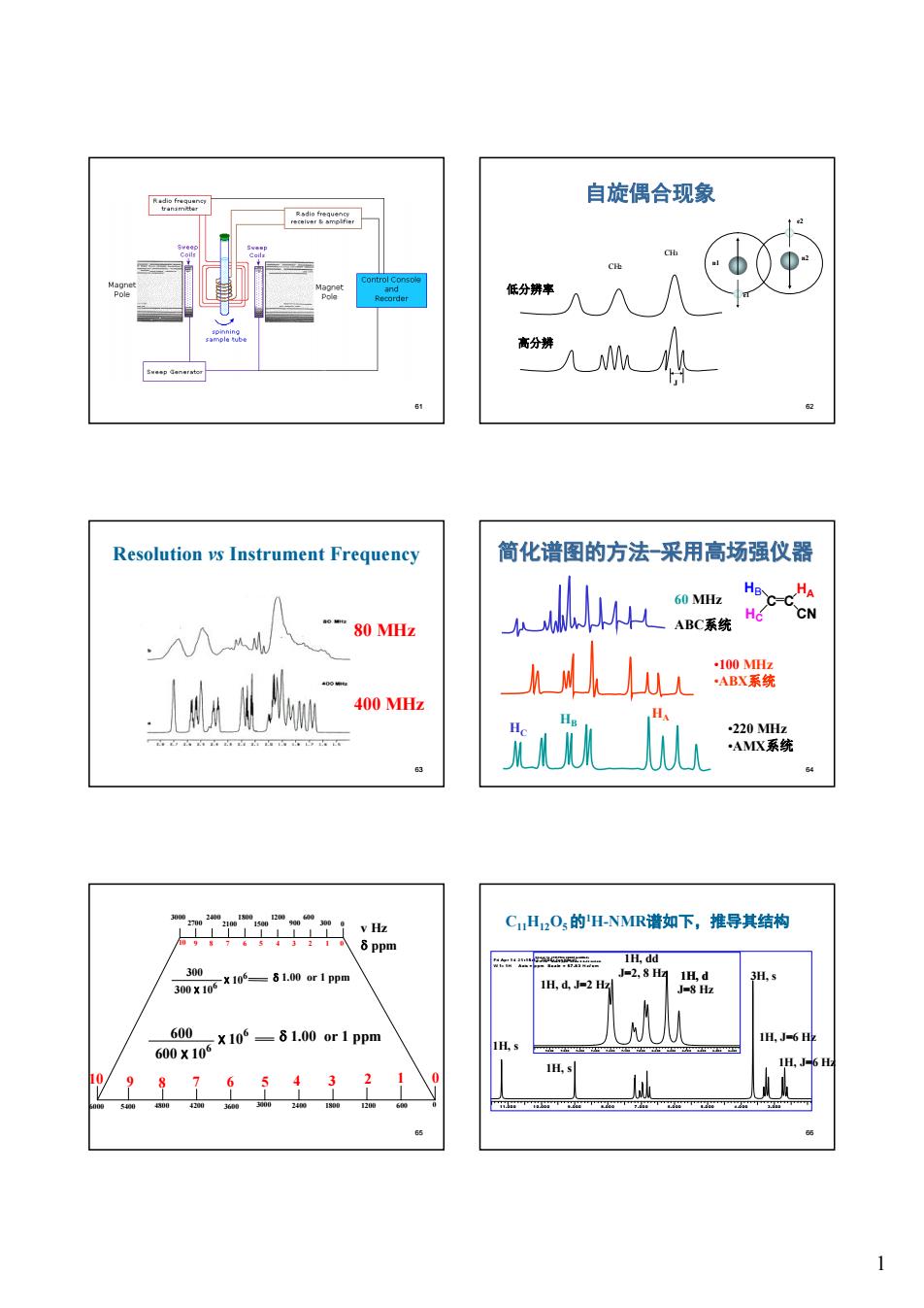
自旋偶合现象 . "人UM公 Resolution vs Instrument Frequency 简化谱图的方法一采用高场强仪器 -80 MHz kL2心 深铁 400Mz Tiii CH2O,的H-NMR谱如下,推导其结构 H.dd 3n00X1-61a0r1pp
1 61 62 自旋偶合现象 e1 n1 n2 e2 CH2 CH3 高分辨 J 低分辨率 63 Resolution vs Instrument Frequency 80 MHz 400 MHz 64 简化谱图的方法-采用高场强仪器 HC HB HA C C HA CN HB HC 60 MHz ABC系统 •100 MHz •ABX系统 •220 MHz •AMX系统 65 300 0 600 900 1200 1500 3000 6000 600 0 2700 2400 2100 1800 5400 4800 4200 3600 3000 2400 1800 1200 300 300 x 106 x 106 d 1.00 or 1 ppm 600 600 x 10 6 x 106 d 1.00 or 1 ppm 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 4 3 2 1 0 10 9 8 7 6 5 v Hz d ppm 66 C11H12O5 的1H-NMR谱如下,推导其结构 Fri A p r 1 4 2 1 :1 5 :1 2 2 0 0 0 : (u n title d ) W 1 : 1 H A xis = p p m S c a le = 5 7 .8 3 H z/ c m 1 1 .0 0 0 1 0 .0 0 0 9 .0 0 0 8 .0 0 0 7 .0 0 0 6 .0 0 0 5 .0 0 0 4 .0 0 0 3 .0 0 0 Fri A p r 1 4 2 1 : 1 7 :3 9 2 0 0 0 : (u n t itle d ) W 1 : 1 H A xis = p p m S c a le = 8 .1 2 H z/ c m 7 .6 0 0 7 .5 0 0 7 . 4 0 0 7 .3 0 0 7 .2 0 0 7 . 1 0 0 7 .0 0 0 6 .9 0 0 6 .8 0 0 6 .7 0 0 6 .6 0 0 6 .5 0 0 6 .4 0 0 1H, d, J=2 Hz J=2, 8 Hz J=8 Hz 1H, J=6 Hz 1H, d 3H, s 1H, dd 1H, s 1H, s 1H, J=6 Hz

Informative NMR Parameters 自旋-自旋偶合 Chemical shift 自旋核与自旋核之间的相互作用(干扰) Spin-spin Linewidths 偶合的结果造成谱线增多,称之裂分。 The nuclear Overhauser effect 偶合的程度用偶合常数(J)表示,单位 Chemical exchange. Abbreviations for proton multiplicities NMR Spectrum s=singlet,d=doublet,t=triplet, q-quartet,m-multiplet. Higher multiplicities are given in fulli quintet,hextet,heptet,etc. 出 "oneover one millionth"isparts-per-milio or ppm. 乙醇 向心原则 1连出盖去发现乙幕的八MR值号及与结构的关系 向心原则 HCH,CH,厂 7 2
2 67 Chemical shift Spin-spin splitting Linewidths The nuclear Overhauser effect Chemical exchange. Informative NMR Parameters 68 自旋-自旋偶合 自旋核与自旋核之间的相互作用(干扰) 偶合的结果 造成谱线增多,称之裂分。 偶合的程度用偶合常数(J)表示,单位: Hz 69 Abbreviations for proton multiplicities: s = singlet, d = doublet, t = triplet, q = quartet, m = multiplet. Higher multiplicities are given in full i.e. quintet, hextet, heptet, etc. 70 The X-axis of the spectrum is called the delta scale (δ) with units of ppm and the Y-axis is an intensity scale. The height of the peak on the Y-axis is proportional to the number of 1H nuclei in the molecule with the same chemical shift. δ is a ratio of Hz/MHz, the result is a ratio without units (1/1ⅹ106) or one over one million. A better term for "one over one millionth" is parts-per-million or ppm. NMR Spectrum 71 W e d A p r 1 2 1 0 :1 6 :3 5 2 0 0 0 : (u n title d ) W 1 : 1 H A xis = p p m S c a le = 4 1 .3 8 H z/ c m 6 .5 0 0 6 .0 0 0 5 .5 0 0 5 .0 0 0 4 .5 0 0 4 .0 0 0 3 .5 0 0 3.0 0 0 2 .5 0 0 2 .0 0 0 1 .5 0 0 1 .0 0 0 0.5 0 0 乙 醇 向心原则 HOCH2CH3 1951年Arnold首先发现乙醇的NMR信号及与结构的关系。 In 1951, the proton spectrum of ethanol with three distinct resonances showed the potential of NMR for structure elucidation of organic compounds. 72 CH2CH3 向心原则
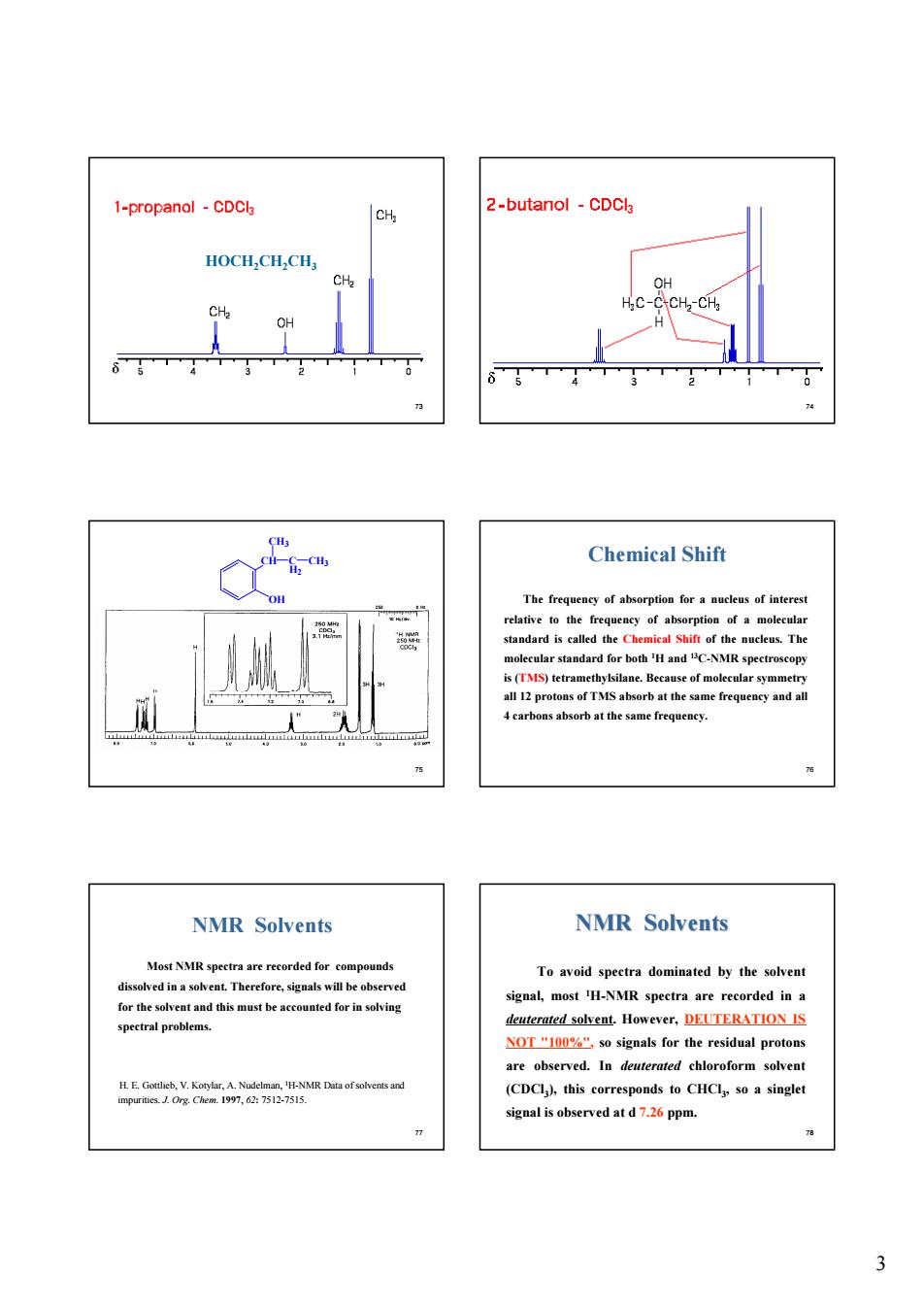
-propanol-CDCl CH 2-butanol-CDCl HOCH.CH.CH CH Chemical Shift The frequeney of absorption fora nucleus of interest elative to the fre ncy of absorption of a molecula ucleus.Th of mol NMR Solvents NMR Solvents Most NMR spestra are reserded for comp unds To avoid spectra dominated by the solven dissolved ina sove Therefore,signalswill beed signal,most H-NMR spectra are recorded in leuterated solvent.However,DEUTERATION IS NOT"so signals for the residual protons are observed.In deuterated chloroform solvent (CDCl),this corresponds to CHCl so a singlet signal is observed at d7.2 ppm
3 73 HOCH2CH2CH3 74 75 OH CH CH3 C CH3 H2 76 The frequency of absorption for a nucleus of interest relative to the frequency of absorption of a molecular standard is called the Chemical Shift of the nucleus. The molecular standard for both 1H and 13C-NMR spectroscopy is (TMS) tetramethylsilane. Because of molecular symmetry all 12 protons of TMS absorb at the same frequency and all 4 carbons absorb at the same frequency. Chemical Shift 77 NMR Solvents Most NMR spectra are recorded for compounds dissolved in a solvent. Therefore, signals will be observed for the solvent and this must be accounted for in solving spectral problems. H. E. Gottlieb, V. Kotylar, A. Nudelman, 1H-NMR Data of solvents and impurities. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62: 7512-7515. 78 NMR Solvents NMR Solvents To avoid spectra dominated by the solvent signal, most 1H-NMR spectra are recorded in a deuterated solvent. However, DEUTERATION IS NOT "100%", so signals for the residual protons are observed. In deuterated chloroform solvent (CDCl3), this corresponds to CHCl3, so a singlet signal is observed at d 7.26 ppm
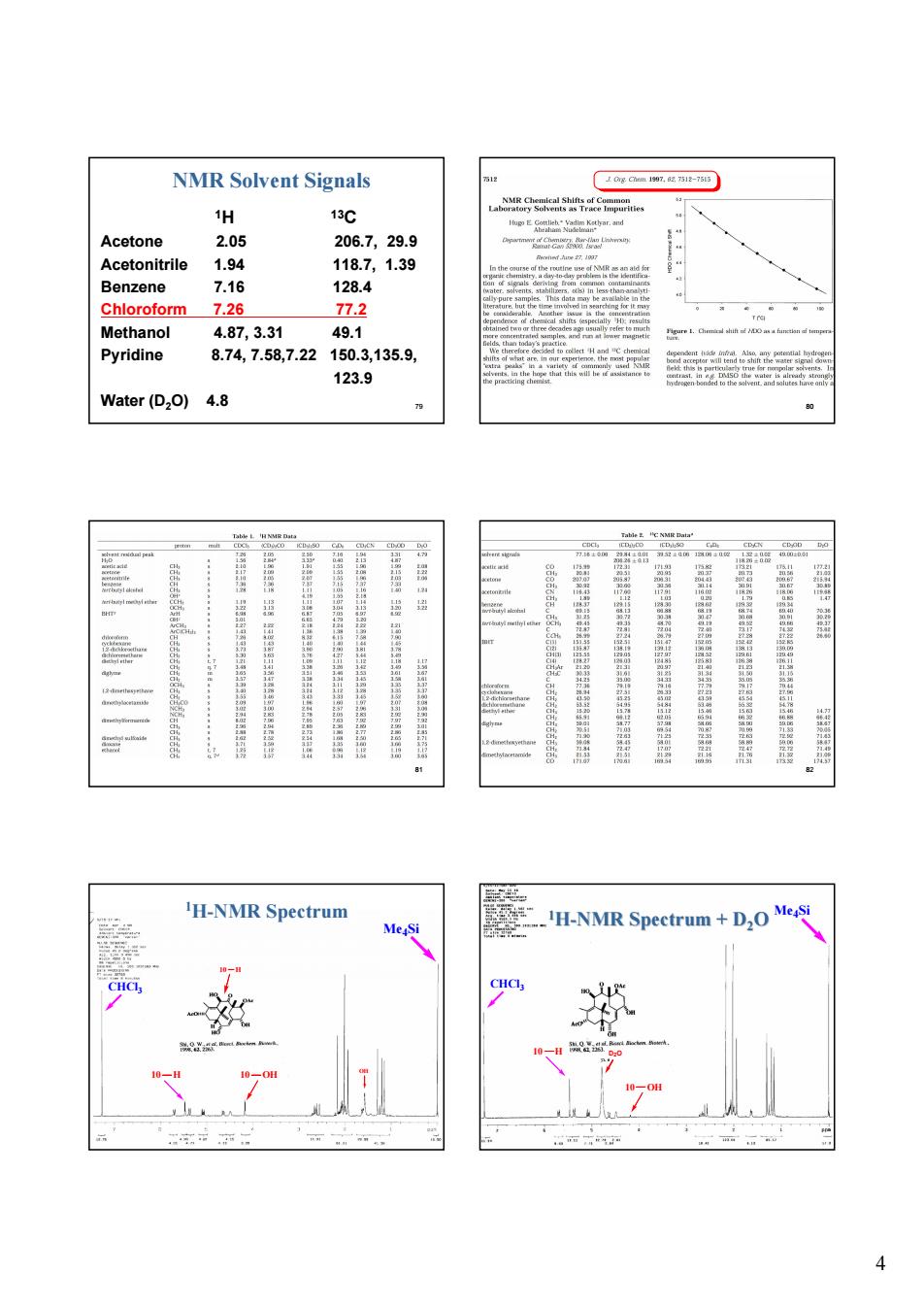
NMR Solvent Signals 上0好Owg间 H 13℃ Acetone 205 2067 29.9 Acetonitrile 1.94 118.7, 1.39 Benzene 7.16 128.4 Chloroform 7.26 77.2 Methanol 4.87,3.31 49.1 Pyridine 8.74,7.58,7.22150.3,135.9, 123.9 Water(D2O)4.8 . 'H-NMR Spectrum H-NMR Spectrum+D,O
4 79 NMR Solvent Signals 1H 13C Acetone 2.05 206.7, 29.9 Acetonitrile 1.94 118.7, 1.39 Benzene 7.16 128.4 Chloroform 7.26 77.2 Methanol 4.87, 3.31 49.1 Pyridine 8.74, 7.58,7.22 150.3,135.9, 123.9 Water (D2O) 4.8 80 81 82 83 Me4Si CHCl3 10 H 10 OH OH 10 H 1H-NMR Spectrum 84 D2O Me4Si CHCl3 10 OH 10 H 1H-NMR Spectrum + D2O

H-NMR Spectrum/D,O TMS , 3 ,T5中 H-NMR TMS In the NMR spestrum of an It ased to be comm practice toadd related NMR spectrum.However,modern spectrometers can "lock"on solvent signals,so addition of internal CDCl 7.26 ppm for H and 77.7 ppm for C. 化学位移 Chemical shift 边8为负值,地大部分有机物中的室核成碳镇的化学位 Chemical shift is defined as 愁邮是正值。 nuclear shielding /applied magnetic ◆当外融场强度自左至右扫精逐渐增大时,植却自左至右 field. 逐南减小 ◆凡是5值较小的楼,就说它处于高场。 Chemical shift is a function of the ◆不列的同位素枝因严藏常数变化幅度不尊,值变化的 nucleus and its environment
5 85 OH 10 H 10 OH 10 OH 1H-NMR Spectrum/D2O 86 TMS 在化学位移测定时,常用的标准物是四甲基硅烷(CH3)4Si,简称 TMS。TMS 用作标准物质的优点是: 1. TMS 化学性质不活泼,与样品之间不发生化学反应和分子间缔合; 2. TMS 是一个对称结构,四个甲基有相同的化学环境,因此无论在氢谱 还是在碳谱中都只有一个吸收峰; 3. 因为 Si的电负性(1.9)比 C 的电负性(2.5)小,TMS 中的氢核和碳 核处在高电子密度区,产生大的屏蔽效应,它产生 NMR 信号所需的 磁场强度比一般有机物中的氢核和碳核产生 NMR 信号所需的磁场强 度都大得多,与绝大部分样品信号之间不会互相重叠干扰; 4. TMS 沸点很低(27度),容易去除,有利于回收样品。 5. 但 TMS 是非极性溶剂,不溶于水。对于那些强极性试样,必须用重 水为溶剂测谱时要用其它标准物。 87 It used to be common practice to add Me4Si, or related compounds, as an internal reference standard for 1H and 13C NMR spectra with the proton signal occurring at 0.0 ppm and the carbon signal occurring at 0.0 ppm in the 13C NMR spectrum. However, modern spectrometers can "lock" on solvent signals, so addition of internal reference standards is not usually required. CDCl3, 7.26 ppm for H and 77.7 ppm for C. TMS 88 In the NMR spectrum of an organic compound, peaks appear at the positions of absorption, also called the positions of resonance or precession frequencies, for different nuclei in the molecule. The exact chemical shift of a particular nucleus in a molecule gives us information about how the atom with that nucleus is bonded in the molecule. 89 化学位移 u 在1H 谱和13C 谱中都规定标准物 TMS 的化学位移值 d = 0,位于图谱的右边。在它的左边 d 为正值,在它的右 边 d为负值,绝大部分有机物中的氢核或碳核的化学位 移都是正值。 u 当外磁场强度自左至右扫描逐渐增大时,d值却自左至右 逐渐减小。 u 凡是 d 值较小的核,就说它处于高场。 u 不同的同位素核因屏蔽常数变化幅度不等, d值变化的 幅度也不同,如1H 的 d值小于 20,13C 的 d大部分在 0- 250,而195Pt的 d 可达 13000。 90 Chemical shift is defined as nuclear shielding / applied magnetic field. Chemical shift is a function of the nucleus and its environment. Chemical shift