
生物分子模拟简介 雷鸣博士 北京化工大学理学院化学系 物理化学教研室
雷鸣 博士 北京化工大学理学院化学系 物理化学教研室 生物分子模拟简介
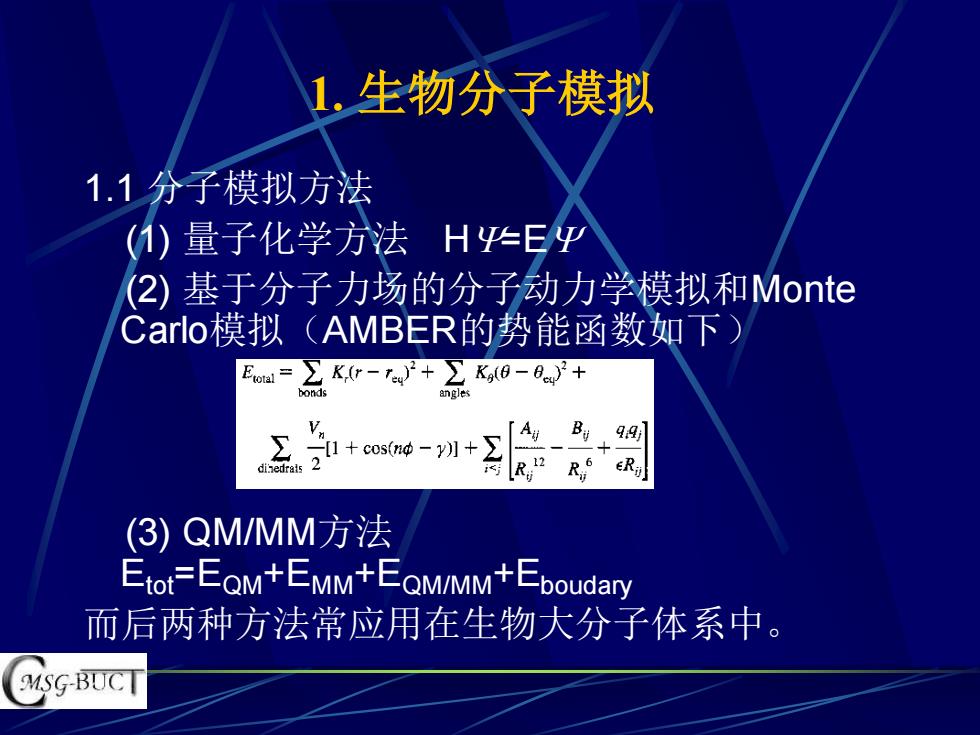
1.生物分子模拟 1.1分子模拟方法 ()量子化学法H华E平 (2)基于分子力场的分子动力学模拟和Monte Carlo模拟(AMBER的势能函数如下) +cosm中一 A、 B+9] (3)QM/MM方法 Etot=EQM+EMM+EQM/MM+Eboudary 而后两种方法常应用在生物大分子体系中。 MSG-BUCT
1. 生物分子模拟 1.1 分子模拟方法 (1) 量子化学方法 H=E (2) 基于分子力场的分子动力学模拟和Monte Carlo模拟(AMBER的势能函数如下) (3) QM/MM方法 Etot=EQM+EMM+EQM/MM+Eboudary 而后两种方法常应用在生物大分子体系中
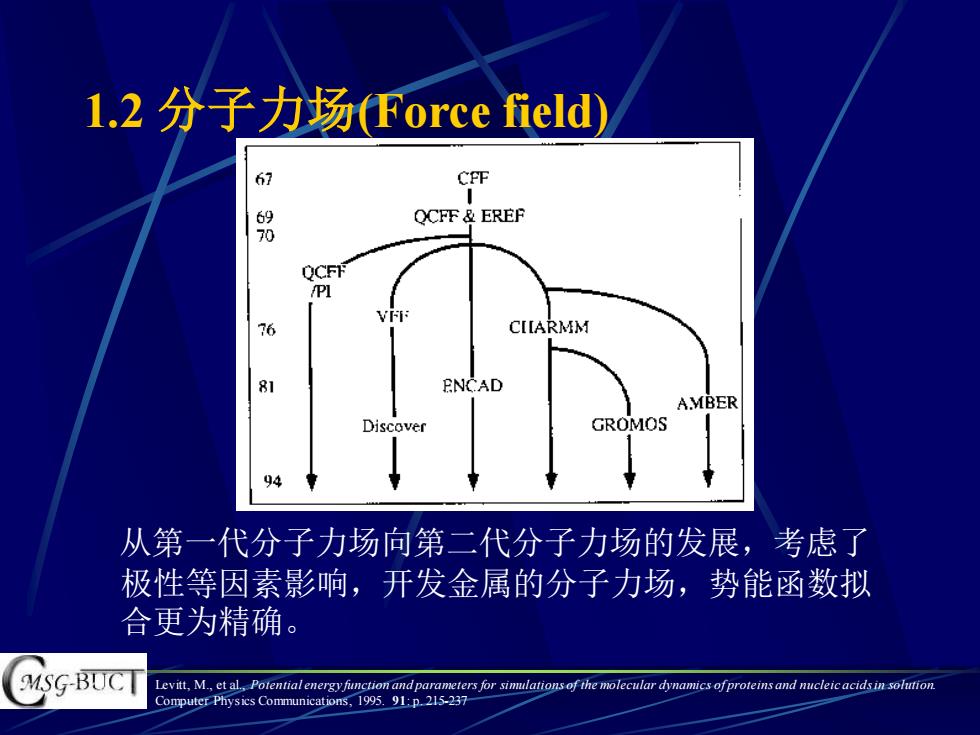
1.2分子力场Force field) 67 CP℉ 8 QCFF&EREF QCFF /Pl 76 CIARMM 8 ENCAD A.MBER Discove GROMOS 94 从第一代分子力场向第二代分子力场的发展,考虑了 极性等因素影响,开发金属的分子力场,势能函数拟 合更为精确。 MSG-BUCT Levitt,M.,et al,Potential energy function and parameters for sinuulations of the molecular dynamics ofproteins and nucleic acids in solution Computer Physics Communications,1995.91:p.215-23
1.2 分子力场(Force field) 从第一代分子力场向第二代分子力场的发展,考虑了 极性等因素影响,开发金属的分子力场,势能函数拟 合更为精确。 Levitt, M., et al., Potential energy function and parameters for simulations of the molecular dynamics of proteins and nucleic acids in solution. Computer Physics Communications, 1995. 91: p. 215-237

1.3生物分子模拟力图解决的问题 (1)蛋白质折叠和解折叠过程 (2)大尺度的生物分子构型变化及构型搜寻 (3)蛋白质,RNA/DNA及膜蛋白结构动力学特征与其功 能之间关系 (4)配体分子与生物分子的结合能力、生物大分子的结 合能力,即分子识别问题 (⑤)离子通道传递离子机理 (⑥)生物酶催化机理 (7)自由能计算 (8)蛋白质结构推测 MSG-BUC
1.3 生物分子模拟力图解决的问题 (1) 蛋白质折叠和解折叠过程 (2) 大尺度的生物分子构型变化及构型搜寻 (3) 蛋白质,RNA/DNA及膜蛋白结构动力学特征与其功 能之间关系 (4) 配体分子与生物分子的结合能力、生物大分子的结 合能力,即分子识别问题 (5) 离子通道传递离子机理 (6) 生物酶催化机理 (7) 自由能计算 (8) 蛋白质结构推测

1.4 Target Molecular Dynamics (TMD) Periplasmic side Periplasmic side C MI SI-MI a123 Leul9 N Cytoplasmic side S1-MI linker Phe10 S Phe 7 N Cytoplasmic side Fig.2.Schematic illustration of the tandem layers of hydrophobic lining of the gate that form the hydrophobic constrictions of the inner pore of the channel.For clarity,only two subunits are shown,and the M1 helices are drawn in parallel although they are packed at an angle in real structure.All other structural elements are omitted. Closed Open Fg.1.Overall architecture of modeled EcoMscL.Both the closed (Left)and open(Right)forms are showninside vlew(Upper)andtopvlew (Lower).Majo secondary structural elements are color-coded:yellow for M1,green for M2, blue for s1,red for 52,and orange for S3.The figures are made by graphic software MOLSCRIPT (28)and rendered by RASTE3D (29). Moy-bU八I Yifei Kong,Yufeng Shen,Tiffany E.Warth and Jianpeng Ma(2002).Conformational Pathways in the Gating of E.colt Mechanosensitive Channel.Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA.99:5999-6004
1.4 Target Molecular Dynamics(TMD) Yifei Kong, Yufeng Shen, Tiffany E. Warth and Jianpeng Ma (2002). Conformational Pathways in the Gating of E.coli Mechanosensitive Channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99: 5999-6004
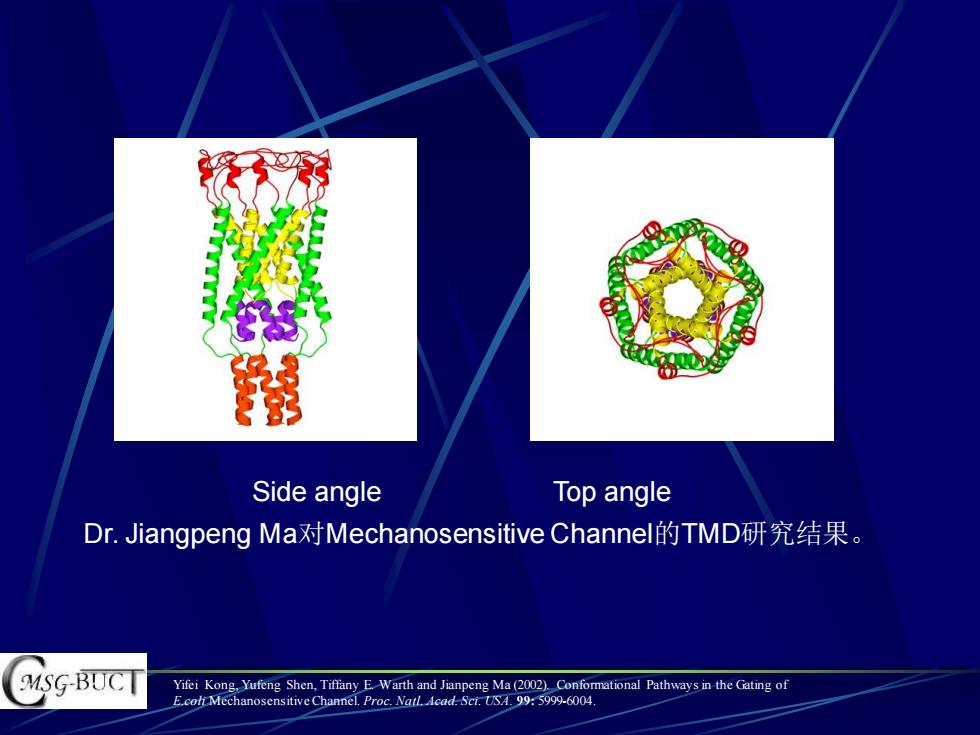
Side angle Top angle Dr.Jiangpeng Ma对Mechanosensitive Channell的TMD研究结果。 MSG-BUC] Yifei Kong,Yufeng Shen,Tiffany E Warth and Jianpeng Ma (2002).Conformational Pathways in the Gating of E.colt Mec hanosensitive Channel.Proc.Natl Acad.Sci.USA.99:5999-6004
Side angle Top angle Dr. Jiangpeng Ma对Mechanosensitive Channel的TMD研究结果。 Yifei Kong, Yufeng Shen, Tiffany E. Warth and Jianpeng Ma (2002). Conformational Pathways in the Gating of E.coli Mechanosensitive Channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99: 5999-6004

分子伴侣(Chaperonin) GROEL的动力 学行为 I.Conformational transition for single GroEL subunit. ll.Conformational transition for entire GroEL heptamer. MSG-BUCT Jianpeng Ma,Paul B.Sigler,Zhaohui Xu and Martin Karplus (2000).A Dyna Model for the Allosteric Mechanism of GroEL J.Mol.Biol.302,303-313
分子伴侣(Chaperonin) GROEL的动力 学行为 I. Conformational transition for single GroEL subunit. II. Conformational transition for entire GroEL heptamer. Jianpeng Ma, Paul B. Sigler, Zhaohui Xu and Martin Karplus (2000). A Dynamic Model for the Allosteric Mechanism of GroEL. J. Mol. Biol. 302, 303-313

1.5 Normal Mode Analysis (NMA) AAAATPase p97振动模式 Dr.Ma在NMA做的工作有助于研究蛋白分子的动力学特 征行为和功能的关系。 MSG-BUC http://sigler.bioch.bcm.tmc.edu/MaLab/gallery.php
1.5 Normal Mode Analysis(NMA) AAA ATPase p97 振动模式 Dr. Ma在NMA做的工作有助于研究蛋白分子的动力学特 征行为和功能的关系。 http://sigler.bioch.bcm.tmc.edu/MaLab/gallery.php
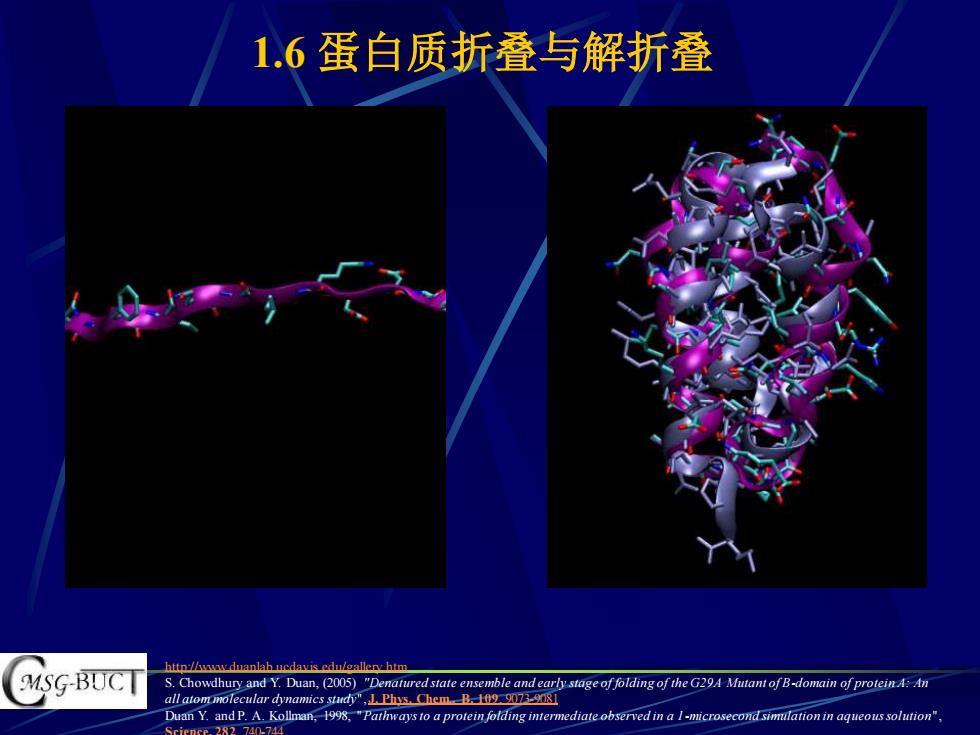
1.6蛋白质折叠与解折叠 http:/hww duanlab ucdavis edu/eallery htm MSG-BUCT S.Chowdhury and Y.Duan,(2005)"Denatured state ensemble and early stage of folding of the G29A Mutant of B-domain of protein A:An all atom molecular dynamics study",1.Phys.Chem B. Duan Y.and P.A.Kollman,1998,"Pathways to a protein folding intermediate observed in a I-microsecond simulation in aqueous solution", Sciener.282 740-744
1.6 蛋白质折叠与解折叠 http://www.duanlab.ucdavis.edu/gallery.htm S. Chowdhury and Y. Duan, (2005) "Denatured state ensemble and early stage of folding of the G29A Mutant of B-domain of protein A: An all atom molecular dynamics study", J. Phys. Chem., B, 109, 9073-9081 Duan Y. and P. A. Kollman, 1998, "Pathways to a protein folding intermediate observed in a 1-microsecond simulation in aqueous solution", Science, 282, 740-744
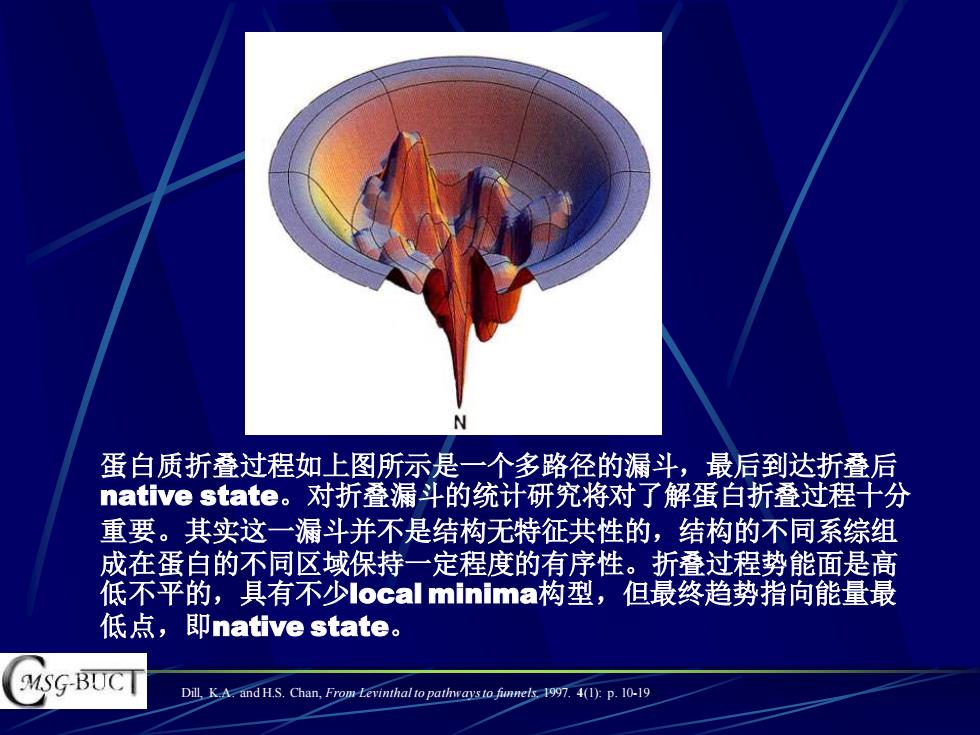
W 蛋白质折叠过程如上图所示是一个多路径的漏斗,最后到达折叠后 native state。对折叠漏斗的统计研究将对了解蛋白折叠过程十分 重要。其实这一漏斗并不是结构无特征共性的,结构的不同系综组 成在蛋白的不同区域保持一定程度的有序性。折叠过程势能面是高 低不平的,具有不少local minima构型,但最终趋势指向能量最 低点,即native state。 MSG-BUCT Dill,K A.and H.S.Chan,From-Levinthal to pathways to fimneis.1997.4(1):p.10-19
Dill, K.A. and H.S. Chan, From Levinthal to pathways to funnels. 1997. 4(1): p. 10-19 蛋白质折叠过程如上图所示是一个多路径的漏斗,最后到达折叠后 native state。对折叠漏斗的统计研究将对了解蛋白折叠过程十分 重要。其实这一漏斗并不是结构无特征共性的,结构的不同系综组 成在蛋白的不同区域保持一定程度的有序性。折叠过程势能面是高 低不平的,具有不少local minima构型,但最终趋势指向能量最 低点,即native state