
Chapter 3 2 Chapter 3 Linear algebra Objectives: ·Mathematic review Concepts,laws and rules ·Linear algebra rol Theory Computation of exponential matrix
Chapter 3 Linear algebra Objectives: • Mathematic review • Concepts, laws and rules • Linear algebra • Computation of exponential matrix Chapter 3 2

Chapter 3 3 3.1 Mathematic review 1.Vector Space (or Linear Space )if it satisfies with 1)Sums "1+1=1+ for all&in V (:+;)=(+:)+T;for allv,vin V 1+(-)=(-)+1:0 1,-I inV 1+0:01:1 re V 2)Products (a)1(r:)=(n n1,"2 are real numbers,V (b)r ()=r+r:isareal number,:e V (c)(2)=+1,rare real numbers,V Subspace:Suppose andare subspace of V,then v2 is also a subspace of V +2 is also a subspace of V
1. Vector Space (or Linear Space ), if it satisfies with 1) Sums 1 2 2 1 v v v v 1 2 3 1 2 3 v ( v v ) ( v v ) v v ( v ) ( v ) v 0 v 0 0 v v for all & in v1 v2 V for all & in v1 , v 2 v3 V v , v in V v V 2) Products (a) r ( r v ) ( r r ) v are real numbers, 1 2 1 2 1 2 r , r v V (b) is a real number, 1 2 1 2 r ( v v ) r v r v v 1 , v 2 V r r v r v r v 1 2 1 2 (c) ( ) 1 2 are real numbers, r , r v V Subspace: Suppose and are subspace of , then v1 v2 V v 1 v 2 is also a subspace of V v 1 v 2 is also a subspace of V Chapter 3 3 3.1 Mathematic review

Chapter 3 4 2.Inner Products of 下&W Suppose =[2&w=, vw=W,w〉=[,2yn =w,+w2+ty,w,=∑,w, two vectors are orthogonal (or perpendicular)if=vw=0 3.Outer Product of V W V W2 … VWn V2 V2W1 V2W2 V2Wn VW = w,..- VnW2 vnwn
v & w 2. Inner Products of 3. Outer Product of v & w Suppose & , T n [ v , v , , v ] v 1 2 T w w w n [ , , , ] w 1 2 v V , w W n i n n i i n n T v w v w v w v w w w w v v v 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 2 ... ... v w v, w , ,... two vectors are orthogonal (or perpendicular) if v & w v , w v w 0 T n n n n n n n n v w v w v w v w v w v w v w v w v w w w w v v v T ... ... ... ... ... ... ... , ,... ... 1 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 v w Chapter 3 4

Chapter 3 5 4.Euclidean Norm of Vector where v=,Y The geometrical meaning 10,0,30) cory
4. Euclidean Norm of Vector 2 1 1 2 n i i v v v v 2 n 2 2 2 1 v v , v where . T n [ v , v , , v ] v 1 2 v V The geometrical meaning v1 v3 v2 v ( , , ) 1 0 2 0 3 0 v v v v Chapter 3 5

Chapter 3 6 5.The distance of x&y awg-小-区g-j月 I[x2,,i,]'&y=1J1,…,]',ieV,】eV SJTu cor Obviously,d(x,y)=0,if and only if =y
5. The distance of x & y 2 1 1 2 ( ) ( ) n i i i d x , y x y x - y , x - y x y x [ 1 , 2 , , ] & y [ 1 , 2 , , ] , x V , y V T n T n x x x y y y Obviously, d ( x , y ) 0 , i f a n d o n ly i f x y y d ( x , y ) Chapter 3 6

Chapter 3 7 6.Vector Function of Scalar f:R→R ( f5() f(t)= f(t) Furthermore,Vector Function of vector f:R"→R or (X) heory X X2 f(X)= (X) and X= L(x) m
6. Vector Function of Scalar n f : R R or ( ) ... ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 1 f t f t f t t n f Furthermore, Vector Function of vector m n f : R R or ( ) ... ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 1 X X X f X n f f f m x x x ... 2 1 and X Chapter 3 7

Chapter 3 8 7.Matrix Function of Scalar Pu(t) P12(t) Pi(t) P:R→Ra P(t)= P21(t) P22(t) or P2m() … Pa(t)Pn2(1) Pnn()J」 Furthermore,Matrix Function of Vector Pu(X) P12(X) Pi(X) P:R'→R or P(X)= P21(X) P22(X) p2m(X) X= … P(X) P2(X) P(X) Example 2x1+3x22+hx3 f(X)= sin x +cos x3 where log x2 f(X)=2x1+3x,2+hx; x f2 (X)=sim x+cosx; and X= 2 f;(X)=log x2 X3
7. Matrix Function of Scalar n m R R P : or ( ) ( ) ( ) ... ... ... ... ( ) ( ) ... ( ) ( ) ( ) ... ( ) ( ) 1 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 1 p t p t p t p t p t p t p t p t p t t n n n m m m P Furthermore, Matrix Function of Vector r n m R R P : or ( ) ( ) ... ( ) ... ... ... ... ( ) ( ) ... ( ) ( ) ( ) ... ( ) ( ) 1 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 1 X X X X X X X X X P X n n n m m m p p p p p p p p p r x x x ... 2 1 X Example 2 1 3 3 2 1 2 log sin cos 2 3 ln ( ) x x x x x x f X where 3 2 1 1 2 f ( X ) 2 x 3 x ln x 2 1 3 f ( X ) s in x c o s x 3 2 f ( X ) lo g x and 3 2 1 X x x x Chapter 3 8

Chapter 3 9 8.Derivative of Matrix Function p11(t) dP0=P(0≌ p2(0… pim(t) dt p.2(t) Pnm(t)】 In a similar way ) df()-f0= f5(0) dt U 9.The gradient of f(X)f:R"→R af(x) Ox f(x) af(x) OX Ox2 Notations:Vf(X)or grad f(X)or f(x) Ox Example: 7 2X1 f(X)=f(x2 )=x2+sin x,+e" Then VI= ar coSX2 OX
8. Derivative of Matrix Function ( ) ( ) ... ( ) ... ... ... ... ( ) ( ) ... ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 p t p t p t p t p t p t t d t d t n n n m m P P In a similar way ( ) ... ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 1 f t f t f t t dt d t n f f 9. The gradient of f ( X ) f R R n : n x f x f x f f ( ) ... ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 1 X X X X X Notations: or or f ( X ) g r a d f ( X ) X f Example: 3 2 2 1 3 2 1 ( ) ( ) sin x x x e x x x f f X Then 3 2 1 cos 2 x e x x f f X Chapter 3 9

Chapter 3 10 f(X1,x2,xm) (X) 10.Jacobian matrix of f(X)= f2(X1:X2...xm) f5(X) fn(x1,x2xm) L(x) of 所 x2 of(x) 8 站 aX 0x2 xm ● a前 8x1 x2 Example: 2 f(X)=f( +X2-X4 sin x2 -X3 cory the Jacobian matrix is of 0 -3x,2 OX 0 c0sx2-10
10. Jacobian matrix of ( ) ... ( ) ( ) ( , ,... ) ... ( , ,... ) ( , ,... ) ( ) 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 1 1 2 X X X f X n m n m m f f f f x x x f x x x f x x x m n m n n n m m x f x f x f x f x f x f x f x f x f ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ( ) 1 2 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 1 X f X Example: 2 3 3 2 4 2 1 4 3 2 1 sin ( ) ( ) x x x x x x x x x f X f 4 2 f : R R the Jacobian matrix is 0 cos 1 0 2 1 0 3 2 2 1 4 x x x X f Chapter 3 10
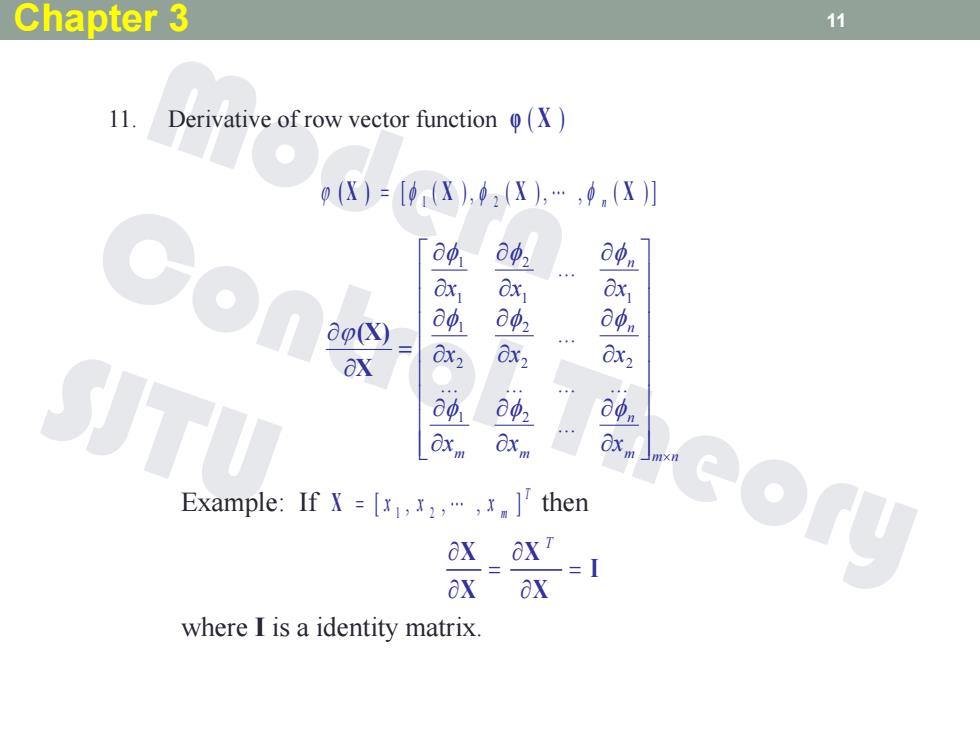
Chapter 3 11 11. Derivative of row vector function (X) 0(X)=[9(X),(X),…,0(X] 80 0p2 a中n x1 Ox1 O o(X) op 042 a中n OX 0x2 0x2 0x2 oo a4, op 0Xm xm Example:If X =[x.x]then OX OXT c⊙y -=I where I is a identity matrix
11. Derivative of row vector function φ ( X ) [ ( ) , ( ) , , ( ) ] ( X ) 1 X 2 X n X m m n n m m n n x x x x x x x x x ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 X (X) Example: If then T m [ x , x , , x ] X 1 2 I X X X X T where I is a identity matrix. Chapter 3 11