
Chapter 2 2 Chapter 2 Mathematic Description of Systems Objectives: Classification of systems State variable description State space model of linear systems Linear-time-invariant systems 。Linearization Transfer function and state space model Theory
Chapter 2 Mathematic Description of Systems Objectives: • Classification of systems • State variable description • State space model of linear systems • Linear-time-invariant systems • Linearization • Transfer function and state space model Chapter 2 2
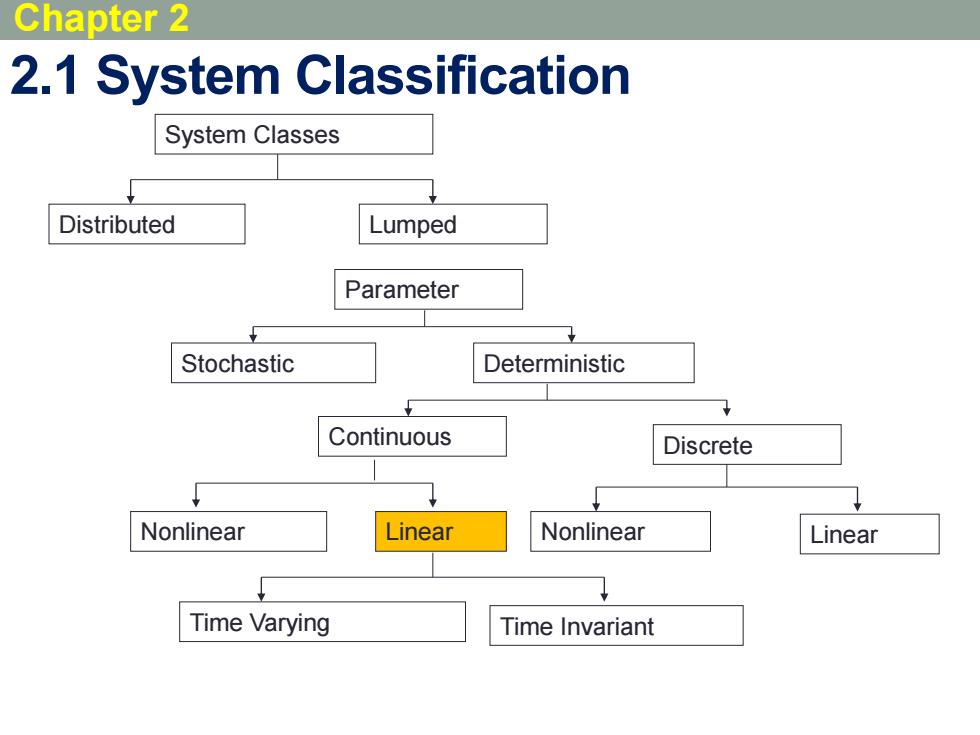
Chapter 2 2.1 System Classification System Classes Distributed Lumped Parameter Stochastic Deterministic Continuous Discrete Nonlinear Linear Nonlinear Linear Time Varying Time Invariant
2.1 System Classification System Classes Distributed Lumped Parameter Deterministic Time Invariant Linear Discrete Stochastic Continuous Time Varying Nonlinear Linear Nonlinear 3 Chapter 2
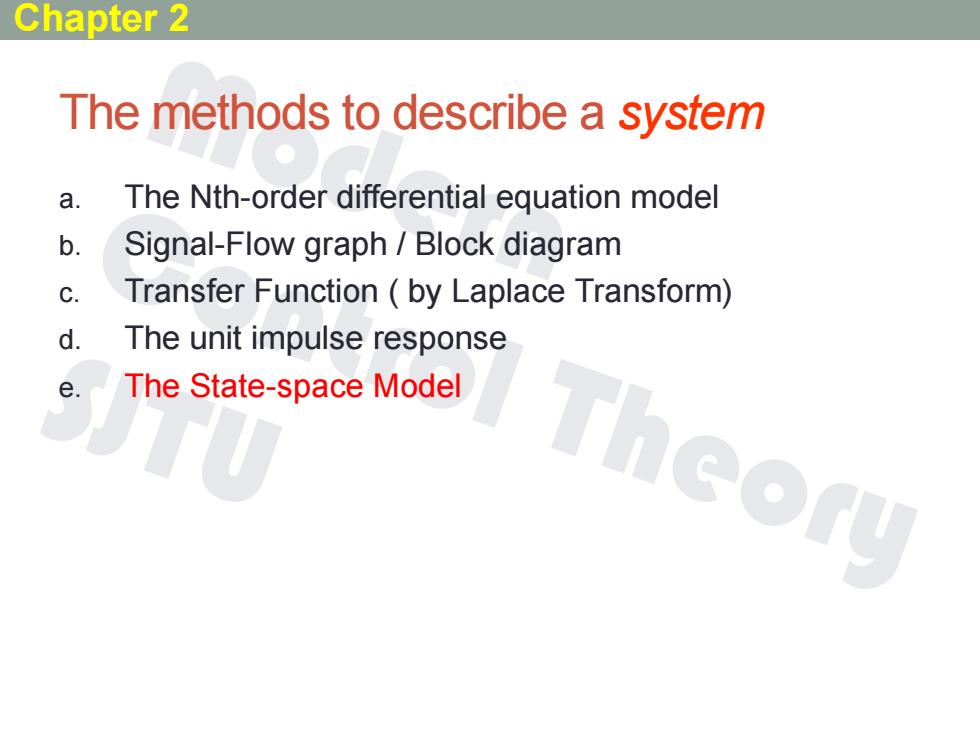
Chapter 2 The methods to describe a system a. The Nth-order differential equation model b. Signal-Flow graph Block diagram C. Transfer Function by Laplace Transform) d. The unit impulse response e The State-space Model Theory
The methods to describe a system a. The Nth-order differential equation model b. Signal-Flow graph / Block diagram c. Transfer Function ( by Laplace Transform) d. The unit impulse response e. The State-space Model Chapter 2

Chapter 2 Signal flowgraph/ Differential Equations State Equations Block diagram Impulse response Transfer function SJTU Theory Frequency response
Differential Equations State Equations Signal flowgraph/ Block diagram Impulse response Transfer function Frequency response Chapter 2

Chapter 2 6 2.2 State variable description Vhat is the“state"?e Consider some phrases: 。STATE of the Union STATE of mind。 Q:What describes the "state"? Q:Why are we interested in the state?
6 2.2 State variable description What is the “state”? Consider some phrases: • STATE of the Union • STATE of mind Q: What describes the “state”? Q: Why are we interested in the state? Chapter 2

Chapter 2 7 Definition of“state Set of variables,with 2 properties: 1. Represent complete system info 2. If state is known at time to,it is possible to compute state for all future time. "Theory
7 Definition of “state” Set of variables, with 2 properties: 1. Represent complete system info 2. If state is known at time t0 , it is possible to compute state for all future time. Chapter 2

Chapter 2 8 Example:Differential Equation 3rd order system++3y=u 3 state variables (write as a vector): W≡ W2 ,w= W3 Theory
8 Example: Differential Equation • 3rd order system • 3 state variables (write as a vector): y y y y u 3 3 1 2 3 , w y w w w y w y Chapter 2
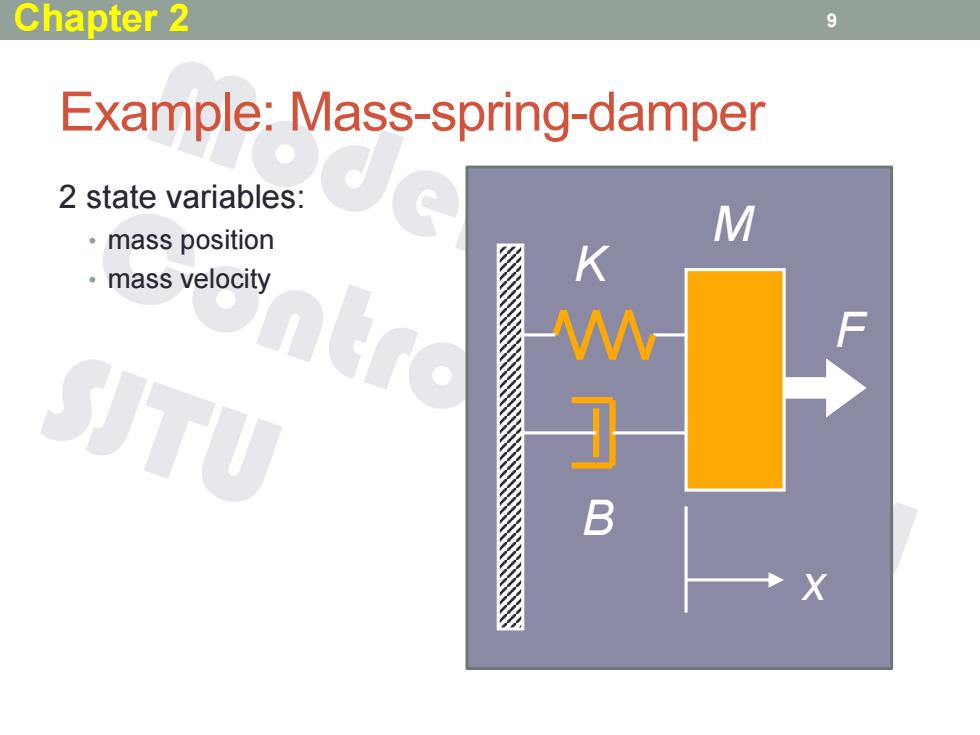
Chapter 2 9 Example:Mass-spring-damper 2 state variables: mass position M 。mass velocity K W SJTU B
9 Example: Mass-spring-damper B K M x F 2 state variables: • mass position • mass velocity Chapter 2

Chapter 2 10 Example:Mass-spring-damper 。2nd-order model M K M优+Bx+Kx=F SJTU B X
10 Example: Mass-spring-damper • 2nd-order model Mx Bx Kx F B K M x F Chapter 2
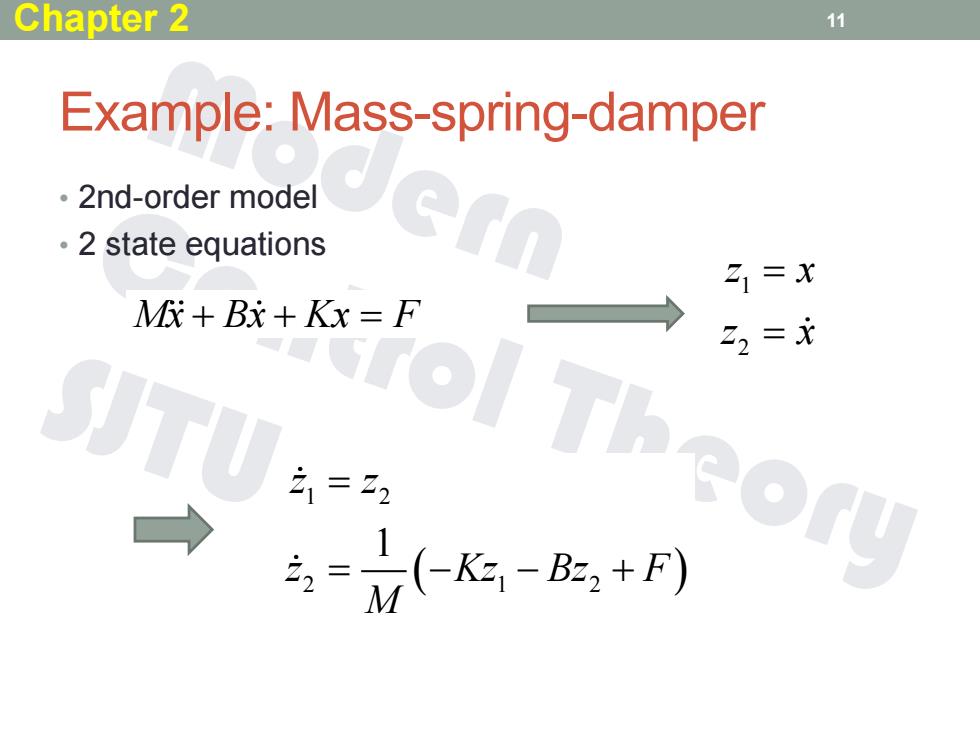
Chapter 2 11 Example:Mass-spring-damper 。2nd-order model 。2 state equations 21=X M优+Bx+Kx=F 22=X T 21=22 → ol Theory -人k-:+)
11 Example: Mass-spring-damper • 2nd-order model • 2 state equations 1 2 2 1 2 1 z z z Kz Bz F M 1 2 z x z x Mx Bx Kx F Chapter 2