
河北医科大学药学院 ●河止医件女罩 天然药物化学 天然药物化学 生物活性结构特在 Medicinal Natural Product Chemistry 学分 理化性 史清文 004689726 http:/202.206.48.213:8091/ 第10章海洋药物 Biodiversity《生物多样性公约》12 第11章天然药物的研究开发 6 第12章天然产物的结构修饰 from the natoral world is permane 史清文 天然药物化学教研宝405宝 http:/202.206.48.213:8091/ 天然药物化学 地球只有 速壶天热产物的共用排成?天然产物有率姿表型? 限多物种还没来及和我们人类见面从 。热 盒、型 1 天然药化教研室史清文教授
河北医科大学药学院 天然药化教研室史清文教授 1 史清文 天 然 药 物 化 学 Medicinal Natural Product Chemistry http://202.206.48.213:8091/ QQ 46897262 天 然 药 物 化 学 1. 总 论 2. 糖和苷 3. 苯丙素类 4. 醌类化合物 5. 黄酮类化合物 6. 萜类和挥发油 7. 三萜及其苷类 8. 甾体及其苷类 9. 生物碱 化学成分 主要类型 结构特征 理化性质 结构测定 提取分离 生物合成 生物活性 第10章 海洋药物 第11章 天然药物的研究开发 第12章 天然产物的结构修饰 史 清 文 天然药物化学教研室-405室 http://202.206.48.213:8091/ • ~ 100 species/day is lost • Loss potential of medicines Biodiversity《生物多样性公约》1992 Human health is inseparable from the health of the natural world. A species that seemed unimportant to us today may become an extremely valuable economic resource tomorrow. The loss of a species from the natural world is permanent 保护环境,保护生物的多样性,就是保护我们人类自己 物种的消失不仅会使人类永远失去 一种自然资源-基因,还会通过食物 链引起其他物种的消失。 Earth of 21th Century 地球只有一个——停止自己的贪婪 很多物种还没来得及和我们人类见面就从地球上消失了 How much is nature worth? The loss of our forests and biodiversity in general could cost us between 1.2-2.8 trillion a year . Qinghaosu? Taxol ? 天 然 药 物 化 学 这些天然产物的共同特点? 天然产物有哪些类型? O O O O H CH3 H CH3 O H H3C 15 Artemisinin O N MeO Me HO H 3 Galantamine HO AcO OBz H OAc OH O O O OH Ph NH O O HO O HO N H CH3 N N H H HO H3CO H 1 Quinine 12 Morphine 10 Taxol N N O O O 11 Camptothecin O O OH HO 13 Daidzein HO O O HO 14 Esculetin HO OH H O O 9 Digitoxigenin H Glc-O H H H 8 Ginsenoside Rg3 H OH OH Glc O O O 2 Tanshinoe IIA O O OH OH OH OH OHOH OH O 6 Sucrose OH 4 Borneol OH 5 Menthol 7 Parthenolide O O O OH

河北医科大学药学院 海洋中天然产物的类型?特点?活性? 数 之26et 钙的连 2016.59日智利 Drugs From The Sea 赤潮爆发 Why Marine? What in Sea? 已是海洋的世纪 向大海要药 Red Tide?Why? 第十章 海洋药物 Marine Natural Medicine(MNM) 海洋药物 What are they? Why do we care MNM? What/How do we study? http:/202.206,48.23 天然药化教研室史清文教授 2
河北医科大学药学院 天然药化教研室史清文教授 2 海洋中天然产物的类型? 特点? 活性? O Br Cl Br HO O O O O O O O O O O O O O O OH O O O OH O O O O HO OH O OH S O O ONa HO OH OH OH OH OH O S O ONa HO OH O H H H H H H H HO H H H H H H H H OH OHH H H H H H OH H OH HO OH H H OH H H OH OH H H HO H H H H H O O O O O O O H OH H H H H H H H H HO H A O O O O HO OH H H H H H H O O O HO OH H H O O Br H H O H OH OH H H HO H OH O O HO OH OH CO2H O H H HO N O H N O N O N O HN O S N H O H H H Br H OAc AcO OAc OH H H O I Sessile Organisms What in Sea? Will next anti-cancer drug come from Ocean? 2016-5-9日 智利 赤潮爆发 Red Tide? Why? Drugs From The Sea ? Why Marine? What in Sea? 21世纪是海洋的世纪 向大海要药 第 十 章 MARINE NATURAL MEDICINE 海 洋 药 物 史 清 文 2018-6-14 http://202.206.48.213:8091/ Marine Natural Medicine (MNM) What are they? Why do we care MNM? What/How do we study? 海 洋 药 物

河北医科大学药学院 海洋药物 海洋药物 Purpose and Aim 「a 2道物完的主对 】家提大环内雕臭的结构特点、分是,丁解其生物活性: 家担表能表化合物的站构精点、分先,了解其生物活性 了解晨夹的蜂构种流、分臭和生物活性: 6 掌植前列味素奏化合尚灿构特点:丁解共生编浴性: Recommended References 5业t D g19T2-19 2.David J.Newman and Gordon M.Cragg Marine Natural 、 http:/202.206.48.213:8091/ marine drug 天然药化教研室史清文教授 3
河北医科大学药学院 天然药化教研室史清文教授 3 Purpose and Aim 1 了解开展海洋药物研究的现状和意义; 2 知道海洋药物研究的主要对象; 3 掌握大环内酯类的结构特点、分类,了解其生物活性; 4 掌握聚醚类化合物的结构特点、分类,了解其生物活性; 5 了解肽类的结构特点、分类和生物活性; 6 掌握前列腺素类化合物结构特点;了解其生物活性; 7 了解C15乙酸原类化合物的结构特点; 海 洋 药 物 海 洋 药 物 研究海洋天然产物化学的意义 1. 概 述 海洋天然产物化学研究的历史和现状 2. 海 洋天然产物主要的结构类型 大环内酯类化合物 聚醚类化合物 肽类化合物 前列腺素类化合物 C15乙酸原类化合物 生物碱及其它类化合物 海洋天然产物化学研究的对象 萜类化合物 生物碱类化合物 甾体类化合物 3. 海 洋天然产物主要的生物活性 抗癌、海洋毒素 1. D. John Faulkner. Highlights of Marine Natural Products Chemistry (1972–1999). Nat. Prod. Rep., 2000, 17, 1-6. 2. David J. Newman and Gordon M. Cragg. Marine Natural Products and Related Compounds in Clinical and Advanced Preclinical Trials. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1216- 1238. 3. Ana Martins, Helena Vieira, Helena Gaspar and Susana Santos. Marketed Marine Natural Products in the Pharmaceutical and Cosmeceutical Industries: Tips for Success. Mar. Drugs, 2014, 12, 1066-1101. Recommended References http://202.206.48.213:8091/ D. John Faulkner. Highlights of Marine Natural Products Chemistry (1972–1999). Nat. Prod. Rep., 2000, 17, 1-6. Newman David J. National Cancer Institute Gordon M. Cragg National Institutes of Health, USA Newman D. J

河北医科大学药学院 Marine Drugs Approved by the FDAor EMEA 推荐参考书:《中华洋本)2009 《降洋天产】 于广利,弹科季出港06 推荐参考书 海洋天然产物 海洋天然学 课外读物 第一节概述 。海洋天然产物化学研究的历史回顾 INTRODUCTION 中華药,2009.4011上1687-1695 一、 海洋知多少How much have you learn? 中海洋天然产物化学研究概速 二、海洋生物的转点Characteristics of MNP 中苹药,2010,41(7八:1031-1047. 三、海洋天然产物的研究概况Outline of MNP 。天然药物化学史活来白海洋的药物 四、海洋天然产物研究的意义Meaning of MNF 中苹药,2016,410时1629-1642 五、海洋天热产物研究的对象Objects of MNP http:/202.206.48.213:8091/ 天然药化教研室史清文教授 4
河北医科大学药学院 天然药化教研室史清文教授 4 Marine Drugs Approved by the FDA or EMEA 《现代海洋药物学》 易杨华 科学出版社,2006 《海洋药物导论》 易杨华 上海科学技术出版社,2004 《海洋天然产物》 林文翰 化学工业出版社,2006 《功能海洋生物分子—发现与应用》 谭仁祥 科学出版社, 2007 《海洋天然产物的分离纯化与结构鉴定》 邓松之 化学工业出版社,2007 《海洋天然产物与药物研究开发》 于广利,谭仁祥 科学出版社, 2016 推荐参考书: 《中华海洋本草》2009 管华诗 院士 谭仁祥 林文翰 于广利 易杨华 推荐参考书 课 外 读 物 ☞ 海洋天然产物化学研究的历史回顾 中草药,2009,40(11): 1687-1695. ☞ 海洋天然产物化学研究概述 中草药,2010,41(7): 1031-1047. http://202.206.48.213:8091/ ☞ 天然药物化学史话-来自海洋的药物 中草药,2016,47(10): 1629-1642. 第一节 概 述 INTRODUCTION 一、海洋知多少 How much have you learn? 二、海洋生物的特点 Characteristics of MNP 三、海洋天然产物的研究概况 Outline of MNP 四、海洋天然产物研究的意义 Meaning of MNP 五、海洋天然产物研究的对象 Objects of MNP

河北医科大学药学院 第一节概述 Ocean Is A Desert of Organisms? INTRODUCTION 海洋知多少?H0 much have you learn ab 61 Ocean Habitat Diversity 开启海洋之旅 湾洋一2】世纪的药库和精仓 霜潮一世界上最长寿的生物之 天然药化教研室史清文教授 5
河北医科大学药学院 天然药化教研室史清文教授 5 INTRODUCTION 一、海洋知多少?How much have you learn about ocean? Northern Hemisphere Southern Hemisphere Equator 61% 81% 第一节 概 述 Ocean Is A Desert of Organisms? Life on earth has its origin in the sea 海洋占地球表面积的71.2%,占地球生物圈体积的95%,生物 总量占地球总生物量的87% with a wide variety of chemicals. 海洋——最大的生命栖息地 In harsh conditions and hostile environment 开启海洋之旅 海洋——21世纪的药库和粮仓 Caves Polar Coral Reef Kelp Forest Deep Sea Volcano Ocean Habitat Diversity 珊瑚—世界上最长寿的生物之一 4265岁 "“ Rainforests of the Sea” Marine world is a very competitive and hostile environment

河北医科大学药学院 Life from Sea Peaceful coexistenc In competitive and hostile environment 生活在地球缘洋中的搬生畅种是可能比人是目前传计的数量 。海洋3.6亿多平方公里 A Rich Treasure Chest of New Medicinal Produ 毫洋生种是:34门阳 平生物量占地味感生物:87 线14000K可 心洛输的海洋将是人是未来的“大南喜”? 梦神者牛轻的许编安并父程不空剂 海洋生物有哪些? 海洋植物 1。海洋技物 等的 2海洋动物类 3.海洋微生物 天然药化教研室史清文教授
河北医科大学药学院 天然药化教研室史清文教授 6 • 生活在地球海洋中的微生物种类可能比人类目前估计的数量 多100倍,达到500-1000万种。这也就意味着,如果一名泳者 不小心吞下了一口海水,他同时也会吞下1000种微生物。 Life from Sea Peaceful coexistence In competitive and hostile environment 海洋3.6亿多平方公里 海洋生物种类: 34门(32 Phyla occur in the sea and 17 on land) 100万种 海洋生物量占地球总生物量: 87% , 利用率 2% 我国海岸线: 18000 Km, 岛屿海岸线14000 Km 我国海域面积: 470 多万平方公里 浩瀚的海洋将是人类未来的“大药房”? A Rich Treasure Chest of New Medicinal Products 海洋中有丰富多样的生物物种,其品种是陆地上的数倍以上,无论 大小、软硬、抑或速度快慢,都能生存下来,这说明它们有天然自卫、 抵抗疾病的能力。特别是那些身上充满生物活性分子、利用化学方式保 护自己的海洋物种,很可能蕴含丰富的药物资源,开发价值不可估量。 “silent world” 海洋生物有哪些? 1. 海洋植物 2. 海洋动物类 3. 海洋微生物 海 洋 植 物 Plants in Ocean 低等的藻类植物:Algae 高等的种子植物:红树林 (Mangrove) 藻类(Algae)植物的大小极为悬殊。最小的单细胞藻类个体很小很小, 只有在显微镜下才能看到它们;而最大的巨藻身长可达二三百米,完全可 以称得上是庞然大物。海洋中的种子植物,如大叶藻、红树等,种类很少。 木果楝

河北医科大学药学院 Drugs from the Sea:Invertebrates 然二 天照 海洋微生物 Why Produce Marine Natural Products? Marine Microorganisms Marine world is a Allelochemical mediated interactions in spatial competition Defense Against Predators As a weapon for prey capture acquirs and maintain space? 天然药化教研室史清文教授
河北医科大学药学院 天然药化教研室史清文教授 7 海洋动物类 海绵动物 Sponges 腔肠动物 Coelenterates 软体动物 Molluscs 棘皮动物 Echinoderms 环节动物 Annelida 节肢动物 Arthropoda 脊椎动物门 Vertebrates 无脊椎动物门 Invertebrates Animals in Ocean 地球上的无脊椎动物是脊椎动物的20多倍。 Sponges!! Cnidarians (e.g. Corals) Microorganisms Tunicates Echinoderms Mollusca Red Algae Brown Algae Green Algae 38% 21% 7% 3% 7% 6% 2% 1% 15% Drugs from the Sea: Invertebrates Sponges Cnidarian e.g. Corals Microorganisms Green Algae Brown Algae Red Algae Tunicates Echinoderms Mollus 刺胞动物 棘皮动物 软体动物 被囊动物 海 洋 微 生 物 Marine Microorganisms 细 菌 真 菌 Actinomycetes Fungi 放线菌 微藻 Bacteria Microalgae Why so many biologically active compounds from invertebrates? Communication Competition between species Defense against pathogens Defense against predators Marine world is a very competitive and hostile environment Why Produce Marine Natural Products? Allelochemical mediated interactions in spatial competition Examples of sponge-derived cytotoxic compounds is trying to prevent a coral from invading its space, it may produce a chemical to prevent the coral cells from growing and dividing in competition for space in natural environment. How do the sponges acquire and maintain space? Defense Against Predators Hunting behaviour of Conus geographus 杀 手 芋 螺 . Venom components of the nirvana cabal are believed to be released into the water to disorient and impair the swimming behaviour of prey. As a weapon for prey capture

河北医科大学药学院 二、Features of Metabolites of Marine 1.Unique Environment of Marine Living Thing Marine ore survive in the terrestrially Unsually high or low/constant Sea Has Higher Biodiversity Than Land “海魔” 059 5065m t 2007年8月26日美国生活科学:英科学家从深度达到的 5和采的连提中新发现了一选非者专特的降洋季物, 最新海洋生物普查 天然药化教研室史清文教授 8
河北医科大学药学院 天然药化教研室史清文教授 8 二、Features of Metabolites of Marine What’s difference in Metabolites between marine organism and terrestrial organisms? Sea Has Higher Biodiversity Than Land 1. Unique Environment of Marine Living Things Marine organisms survive in the terrestrially unusual conditions Higher salt content (High salinity) Low or zero light and limited oxygen Poor nutrition High pressure Unusually high or low/constant temperatures 海洋卤化过程:卤离子,特别是溴离子诱导作用产生的分子环化或重排 的过程。海洋卤化过程产生了大量结构独特的萜类,如仅凹顶藻一属就分 离出26种骨架类型的400多种萜类化合物。 HN O NH O 1 HN O NH O 2 Gram-positive bacterium obtained from 5065 m deep ocean sediment from the Central Pacific Basin, the deepest reported sample from which a new natural product has been isolated. Both exhibit significant cytotoxicity against human tumour cell lines, as well as moderate antiviral activity against Herpes simplex virus-II (HSV-II). B. S. Davidson and R. W. Schumacher, Tetrahedron, 1993, 49, 6569. 5065 m “海魔” 一种只能在2700米以下水域 找到的怪异生物 A deep-sea fungus, Phialocephala sp., obtained at a depth of 5059 m, has yielded the novel metabolite trisorbicillinone A, bearing a unique trimeric sorbicillin skeleton, and exhibiting significant cytotoxicity towards murine P388 and HL60 cells (IC50=9.10 and 3.14 mM, respectively). The same group identified a further two new antineoplastic antibiotic bisorbicillinoids from the same sample, designated oxosorbiquinol and dihydrooxosorbiquinol. D. Li, F. Wang, X. Xiao, et al. Tetrahedron Lett., 2007, 48, 8083 and 5235. 5059 m 2007年8月26日美国生活科学网: 英国科学家从深度达到约 3500米的海域中新发现了一些非常奇特的海洋生物。 “The Deep-Sea Biodiversity holds major promise for the treatment of human diseases” ---Dr. Sara Maxell, Medicines from the Deep, 2005 • 历时10年的全球“海洋生物普查”项目2011年10月4日在伦敦发布最终 报告: 根据普查得出的统计数据,海洋生物物种总计约100万多种,其中 25万种是人类已知的海洋物种,其他75多万种海洋物种人类知之甚少,这 些人类不甚了解的物种大多生活在北冰洋、南极和东太平洋未被深入考察 的海域。丰富的海洋生物蕴藏着巨大的开发潜力,海洋是人类未来的大药房。 透 明 海 参 透 明 无 壳 海 蜗 牛 南 极 海 底 生 物 最新海洋生物普查
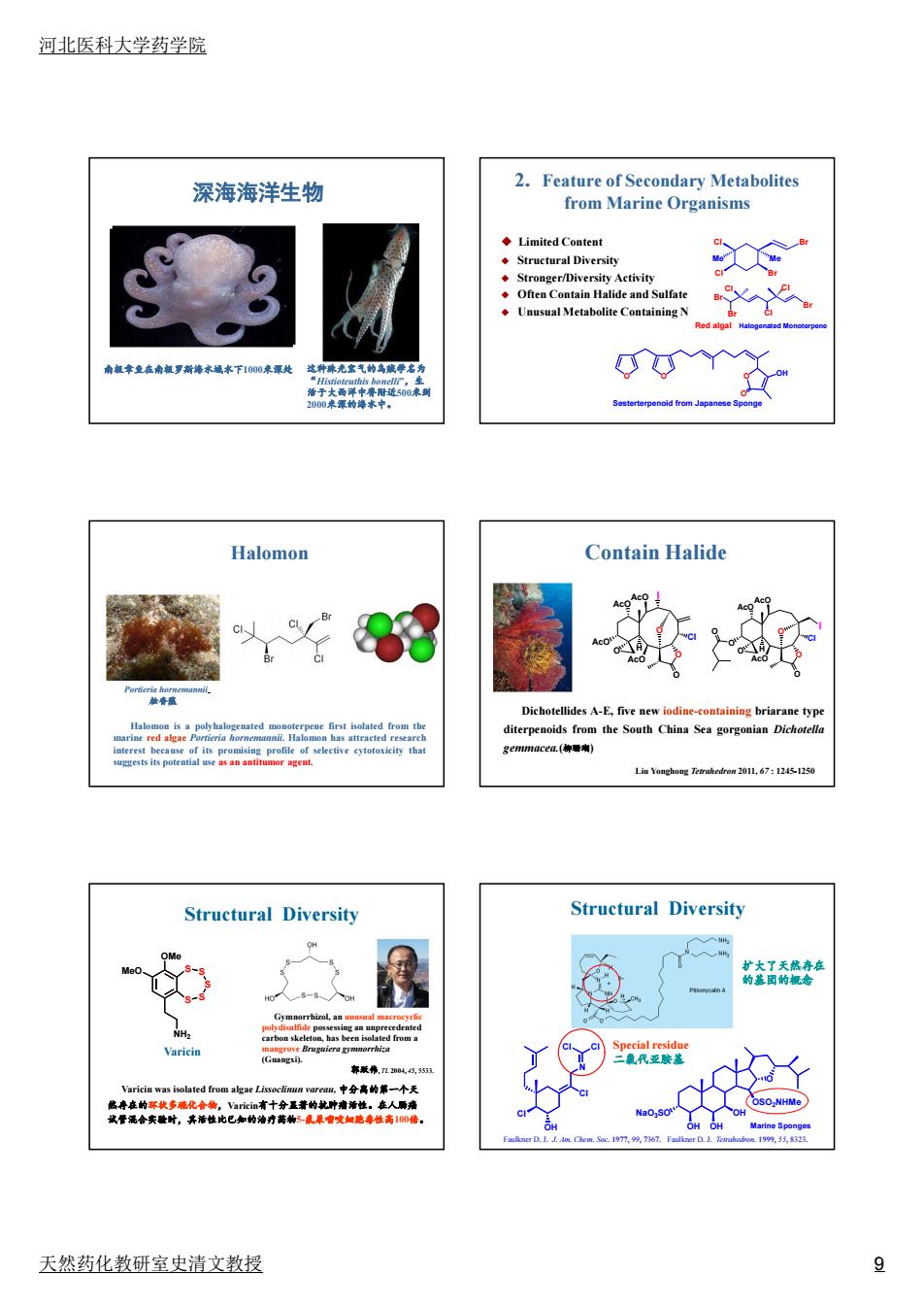
河北医科大学药学院 深海海洋生物 2.Feature of Secondary Metabolites from Marine Organisms miedCoaiea Halomon Contain Halide 实 Structural Diversity Structural Diversity 天然药化教研室史清文教授 9
河北医科大学药学院 天然药化教研室史清文教授 9 南极章鱼在南极罗斯海水域水下1000米深处 这种珠光宝气的乌贼学名为 “Histioteuthis bonelli”,生 活于大西洋中脊附近500米到 2000米深的海水中。 深海海洋生物 2. Feature of Secondary Metabolites from Marine Organisms Limited Content Structural Diversity Stronger/Diversity Activity Often Contain Halide and Sulfate Unusual Metabolite Containing N O O O OH O Sesterterpenoid from Japanese Sponge Br Cl Br Br Cl Cl Halogenated Monoterpene Cl Cl Me Br Br Me Red algal Halomon is a polyhalogenated monoterpene first isolated from the marine red algae Portieria hornemannii. Halomon has attracted research interest because of its promising profile of selective cytotoxicity that suggests its potential use as an antitumor agent. Halomon Portieria hornemannii 松香藻 O AcO AcO AcO AcO I Cl O O O H O O AcO AcO AcO Cl O O O H I O Dichotellides A-E, five new iodine-containing briarane type diterpenoids from the South China Sea gorgonian Dichotella gemmacea.(柳珊瑚) Liu Yonghong Tetrahedron 2011, 67 : 1245-1250 Contain Halide S S S S S NH2 OMe MeO Varicin was isolated from algae Lissoclinun vareau, 中分离的第一个天 然存在的环状多硫化合物,Varicin有十分显著的抗肿瘤活性。在人肠癌 试管混合实验时,其活性比已知的治疗药物5-氟尿嘧啶细胞毒性高100倍。 Varicin Gymnorrhizol, an unusual macrocyclic polydisulfide possessing an unprecedented carbon skeleton, has been isolated from a mangrove Bruguiera gymnorrhiza (Guangxi). 郭跃伟, TL 2004, 45, 5533. Structural Diversity O OH Cl N Cl Cl Cl OH NaO3SO OH OH OSO2NHMe Faulkner D. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 7367. Faulkner D. J. Tetrahedron. 1999, 55, 8323. Structural Diversity Marine Sponges Special residue 二氯代亚胺基 扩大了天然存在 的基团的概念
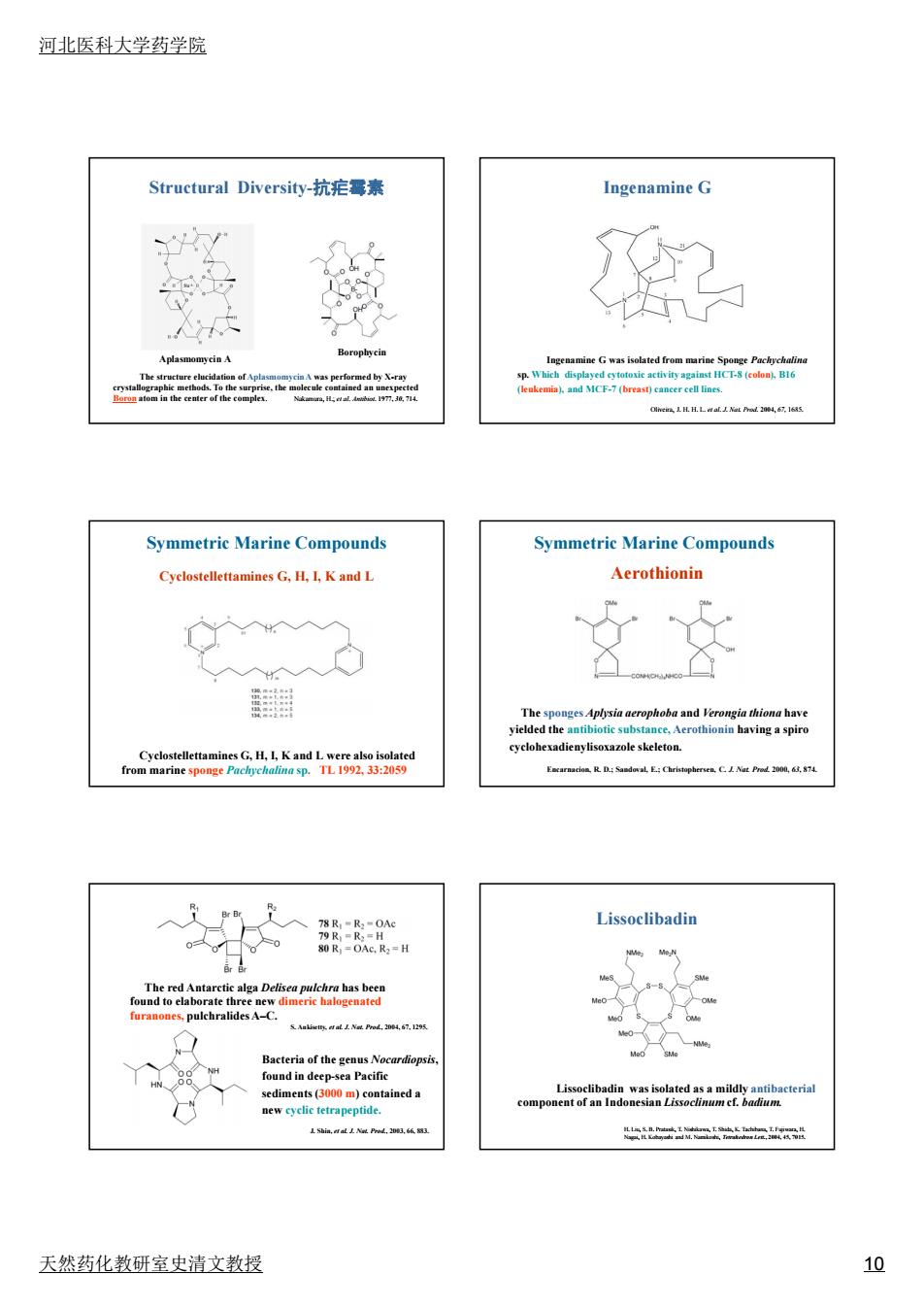
河北医科大学药学院 Structural Diversity-抗疟霉素 Ingenamine G 7 plasmomy cin A G was iveladm Symmetric Marine Compounds Svmmetric Marine Compounds CyclostellettaminesG.H.I.K and L Aerothionin nSwGK Lissoclibadin omet oa Indo 13n工4 天然药化教研室史清文教授 10
河北医科大学药学院 天然药化教研室史清文教授 10 Structural Diversity-抗疟霉素 The structure elucidation of Aplasmomycin A was performed by X-ray crystallographic methods. To the surprise, the molecule contained an unexpected Boron atom in the center of the complex. Nakamura, H.; et al. Antibiot. 1977, 30, 714. Aplasmomycin A Borophycin Ingenamine G Ingenamine G was isolated from marine Sponge Pachychalina sp. Which displayed cytotoxic activity against HCT-8 (colon), B16 (leukemia), and MCF-7 (breast) cancer cell lines. Oliveira, J. H. H. L. et al. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1685. Cyclostellettamines G, H, I, K and L Cyclostellettamines G, H, I, K and L were also isolated from marine sponge Pachychalina sp. TL 1992, 33:2059 Symmetric Marine Compounds Aerothionin The sponges Aplysia aerophoba and Verongia thiona have yielded the antibiotic substance, Aerothionin having a spiro cyclohexadienylisoxazole skeleton. Encarnacion, R. D.; Sandoval, E.; Christophersen, C. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 874. Symmetric Marine Compounds The red Antarctic alga Delisea pulchra has been found to elaborate three new dimeric halogenated furanones, pulchralides A–C. S. Ankisetty, et al. J. Nat. Prod., 2004, 67, 1295. Bacteria of the genus Nocardiopsis, found in deep-sea Pacific sediments (3000 m) contained a new cyclic tetrapeptide. J. Shin, et al. J. Nat. Prod., 2003, 66, 883. Lissoclibadin was isolated as a mildly antibacterial component of an Indonesian Lissoclinum cf. badium. Lissoclibadin H. Liu, S. B. Pratasik, T. Nishikawa, T. Shida, K. Tachibana, T. Fujiwara, H. Nagai, H. Kobayashi and M. Namikoshi, Tetrahedron Lett., 2004, 45, 7015