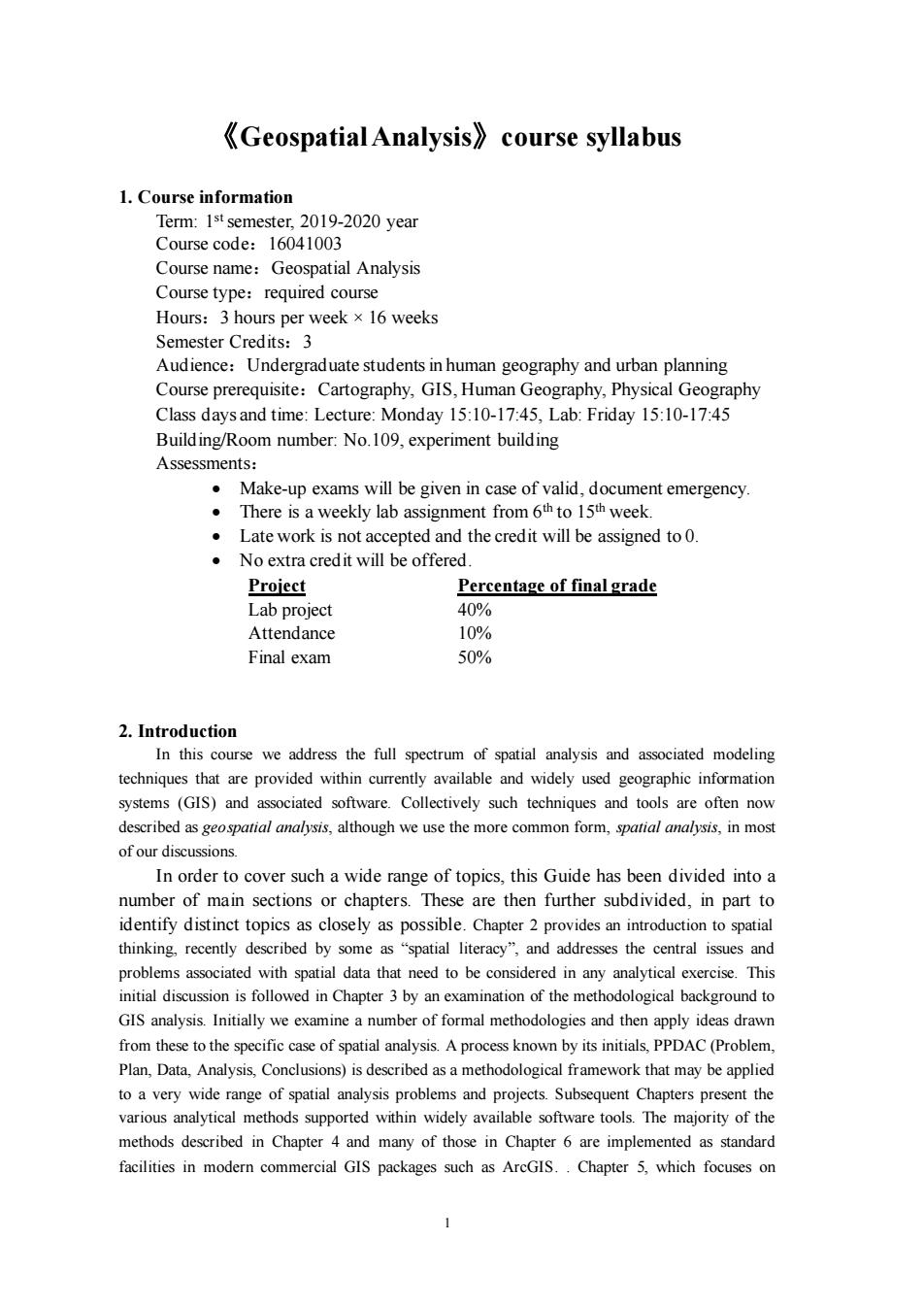
《Geospatial Analysis》course syllabus 1.Course information Term:1st semester,2019-2020 year Course code:16041003 Course name:Geospatial Analysis Course type:required course Hours:3 hou rs per week×l6 weeks Semester Credits:3 Audience:Undergraduate students in human geography and urban planning Course prerequisite:Cartography,GIS,Human Geography,Physical Geography Class daysand time:Lecture:Monday 15:10-1745 Lab:Friday 15:10-17:45 Building/Room number:No.109,experiment building Assessments. Make-up exams will be given in case of valid,document emergency. There is a weekly lab assignment from 6th to 15th week. Late work is not accepted and the credit will be assigned to 0. No extra credit will be offered Project Percentage of final grade Lab project 40% Attendance 106 Final exam 50% 2.Introduction In this course we address the full spectrum of spatial analysis and associated modeling techniques that are provided within currently available and widely used geographic information systems (GIS)and associated software.Collectively such techniques and tools are ofen now ibed as geopatial we use the alysis,in mos of our discussions In order to cover such a wide range of topics.this Guide has been divided into a number of main sections or chapters.These are then further subdivided,in part to identify distinct topics as closely as possible.Chapter 2 provides an introduction to spatial thinking.recently de as the c tral is ciated ith spatial data that need to b e con in any analytic exercise n is followed in Chapter 3 by an examination of the methodological background to GIS analysis.Initially we examine a number of formal methodologies and then apply ideas drawn from these to the specific case of spatial analysis.A process known by its initials.PPDAC (Problem. Plan,Data,Analysis,Conclusions)is described asa m ethodolo gical framework that may be applied to a very ange of spatial analysis proble and pters present t various anaytical methods supported within widely available sofware tools .The majority of the methods described in Chapter 4 and many of those in Chapter 6 are implemented as standard facilities in modern commercial GIS packages such as AreGIS..Chapter 5,which focuses on
1 《Geospatial Analysis》course syllabus 1. Course information Term: 1 stsemester, 2019-2020 year Course code:16041003 Course name:Geospatial Analysis Course type:required course Hours:3 hours per week ×16 weeks Semester Credits:3 Audience:Undergraduate students in human geography and urban planning Course prerequisite:Cartography, GIS, Human Geography, Physical Geography Class days and time: Lecture: Monday 15:10-17:45, Lab: Friday 15:10-17:45 Building/Room number: No.109, experiment building Assessments: • Make-up exams will be given in case of valid, document emergency. • There is a weekly lab assignment from 6th to 15th week. • Late work is not accepted and the credit will be assigned to 0. • No extra credit will be offered. Project Percentage of final grade Lab project 40% Attendance 10% Final exam 50% 2. Introduction In this course we address the full spectrum of spatial analysis and associated modeling techniques that are provided within currently available and widely used geographic information systems (GIS) and associated software. Collectively such techniques and tools are often now described as geospatial analysis, although we use the more common form, spatial analysis, in most of our discussions. In order to cover such a wide range of topics, this Guide has been divided into a number of main sections or chapters. These are then further subdivided, in part to identify distinct topics as closely as possible. Chapter 2 provides an introduction to spatial thinking, recently described by some as “spatial literacy”, and addresses the central issues and problems associated with spatial data that need to be considered in any analytical exercise. This initial discussion is followed in Chapter 3 by an examination of the methodological background to GIS analysis. Initially we examine a number of formal methodologies and then apply ideas drawn from these to the specific case of spatial analysis. A process known by its initials, PPDAC (Problem, Plan, Data, Analysis, Conclusions) is described as a methodological framework that may be applied to a very wide range of spatial analysis problems and projects. Subsequent Chapters present the various analytical methods supported within widely available software tools. The majority of the methods described in Chapter 4 and many of those in Chapter 6 are implemented as standard facilities in modern commercial GIS packages such as ArcGIS. . Chapter 5, which focuses on

statistical methods.and Chapters 7 and 8 which address Network and Location Analysis.and Geocomputation,are much less commonly supported in GIS packages,but may provide loose-or instances we provide detailed examples and commentary on software tools that are readily available. 3.Course goals and objectives spatial analysis n which to examine events,patterns,and processes that operate on or near the surface of our planet.This course presents students with the fundamental concepts and advanced techniques of spatial analysis.GIS and statistical techniques are discussed for managing.analyzing and modeling spatial data.Students will gain practical experience in publicly presenting spatial analysis topics This course also intends to prepare students for applying spatial analysis techniques to handle geospatial data in various fields and provide students opportunities to gain practical experience of undertaking GIS projects. 4.Course materials [1]Michael Smith,Michael Goodchild,Paul Longley.Geospatial Analysis:A Comprehensive Guide to Principles,Techniques and Software Tools (3rd edition)2012 Splint 21黎夏,刘凯。GIS与空间分析-原理与方法。科学出版社,2011 [3]王劲峰,廖一兰,刘鑫 空间数据分析教程.科学出版社,2010 5.Course topical outline The following topics will be covered in the semester 1Introduction 1.1Geospatial analysis and application areas 1.2 Basic concepts Curriculum ideological and political point: How to analyze the New Era Ecological Civilization dynamics with Geospatial analysis? Objective: To depict dynamics of the New Era with geospatial analysis methods. 2 Datapresentation Curriculum ideological and political point: How to assess COVID-19 cases dynamics with nightingale rose diagram of our country? 2
2 statistical methods, and Chapters 7 and 8 which address Network and Location Analysis, and Geocomputation, are much less commonly supported in GIS packages, but may provide loose- or close-coupling with such systems, depending upon the application area. In all instances we provide detailed examples and commentary on software tools that are readily available. 3. Course goals and objectives Geospatial analysis provides a distinct perspective on the world, a unique lens through which to examine events, patterns, and processes that operate on or near the surface of our planet. This course presents students with the fundamental concepts and advanced techniques of spatial analysis. GIS and statistical techniques are discussed for managing, analyzing and modeling spatial data. Students will gain practical experience in publicly presenting spatial analysis topics. This course also intends to prepare students for applying spatial analysis techniques to handle geospatial data in various fields and provide students opportunities to gain practical experience of undertaking GIS projects. 4. Course materials [1] Michael Smith, Michael Goodchild, Paul Longley. Geospatial Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Principles, Techniques and Software Tools (3rd edition). 2012, Splint. [2] 黎夏,刘凯。GIS 与空间分析--原理与方法。科学出版社,2011. [3] 王劲峰,廖一兰,刘鑫. 空间数据分析教程.科学出版社,2010. 5. Course topical outline The following topics will be covered in the semester. 1 Introduction 1.1Geospatial analysis and application areas 1.2 Basic concepts Curriculum ideological and political point: How to analyze the New Era Ecological Civilization dynamics with Geospatial analysis? Objective: To depict dynamics of the New Era with geospatial analysis methods. 2 Data presentation 2.1 Attributes data presentation 2.2 Geospatial data presentation Curriculum ideological and political point: How to assess COVID-19 cases dynamics with nightingale rose diagram of our country?

Objective: To understand the people-centered approach of our country. 3Numerical Descriptive Techniques 3.1 Measures of Central Location 3.2 Measures of Variability 3.3 Measures of Relative Standing How to assess economic development dynamics with of our country? Objective: To understand development is of paramount importance in our country 4 Continuous Probability Distributions 4.I uniform probability distribution 4.2 normal distribution 4.3 exponential distribution 44 Studentt Distribution 4.5 Chi-Squared Distribution 4.6 FDistribution 5 Sampling Distributions 5.1 Sampling Distribution of the Mean 5.2 Using the Sampling Distribution for Inference 5.3 Sampling Distribution ofa Proportior 5.4 Sampling Distribution:Difference of two means Curriculum ideological and political point: How to assess economic development difference of north and south of our country? Objective To understand common prosperity from the difference of north and south in our country. 6Introduction to Estimation 6.1Point Est 6.2 Interval Estimator 6.3Qualities of Estimators 6.4 Unbiased Estimators 7Introduction to Hypothesis Testing 7.1 Nonstatistical Hypothesis Testing 7.2 Standardized Test Statistic 7.3Developing an Understanding of Statistical Concepts
3 Objective: To understand the people-centered approach of our country. 3 Numerical Descriptive Techniques 3.1 Measures of Central Location 3.2 Measures of Variability 3.3 Measures of Relative Standing 3.4 Measures of Linear Relationship Curriculum ideological and political point: How to assess economic development dynamics with of our country? Objective: To understand development is of paramount importance in our country. 4 Continuous Probability Distributions 4.1 uniform probability distribution 4.2 normal distribution 4.3 exponential distribution 4.4 Student t Distribution 4.5 Chi-Squared Distribution 4.6 F Distribution 5 Sampling Distributions 5.1 Sampling Distribution of the Mean 5.2 Using the Sampling Distribution for Inference 5.3 Sampling Distribution of a Proportion 5.4 Sampling Distribution: Difference of two means Curriculum ideological and political point: How to assess economic development difference of north and south of our country? Objective: To understand common prosperity from the difference of north and south in our country. 6 Introduction to Estimation 6.1 Point Estimator 6.2 Interval Estimator 6.3Qualities of Estimators 6.4 Unbiased Estimators 7 Introduction to Hypothesis Testing 7.1 Nonstatistical Hypothesis Testing 7.2 Standardized Test Statistic 7.3Developing an Understanding of Statistical Concepts

Curriculum ideological and political point: How to test economic development difference of north and south of our country? Objective To understand common prosperity from the difference of north and south in our country. 8 Inference About A Population 8.1 Inference With Variance Unknown 8.2 Estimating Totals of Finite Populations 8.3 Inference About Population Variance 8.4 Inference:Population Proportion 9Inference About Comparing Two Populations 9.1 Difference between Two Means 9.2 Inference about the ratio of two variances 9.3 One-Way Analysis of Variance 94 Chi-Squared Tests Curriculum ideological and political point: How to inference economic development difference of north and south of our country? Objective: To understand common prosperity from the difference of north and south in our country. 10 correlation and regression 10.1 correlation analysis 10.2 linear regression analysis 10.3 nonlinear regression analysis 10.4 ridge reg and politic point: How to find economic development factors with geospatial analysis? Objective: To help students know the development process of our country. 11 spatial regression 11.1 spatial lag regression 11.2 spatial error regression 11.3 spatial filtering regression Curriculum ideological and political point: Does economic development associated with location or city? Objective To help students know the development process and neighbors effects of our country. 4
4 Curriculum ideological and political point: How to test economic development difference of north and south of our country? Objective: To understand common prosperity from the difference of north and south in our country. 8 Inference About A Population 8.1 Inference With Variance Unknown 8.2 Estimating Totals of Finite Populations 8.3 Inference About Population Variance 8.4 Inference: Population Proportion 9 Inference About Comparing Two Populations 9.1 Difference between Two Means 9.2 Inference about the ratio of two variances 9.3 One-Way Analysis of Variance 9.4 Chi-Squared Tests Curriculum ideological and political point: How to inference economic development difference of north and south of our country? Objective: To understand common prosperity from the difference of north and south in our country. 10 correlation and regression 10.1 correlation analysis 10.2 linear regression analysis 10.3 nonlinear regression analysis 10.4 ridge regression Curriculum ideological and political point: How to find economic development factors with geospatial analysis? Objective: To help students know the development process of our country. 11 spatial regression 11.1 spatial lag regression 11.2 spatial error regression 11.3 spatial filtering regression Curriculum ideological and political point: Does economic development associated with location or city? Objective: To help students know the development process and neighbors effects of our country
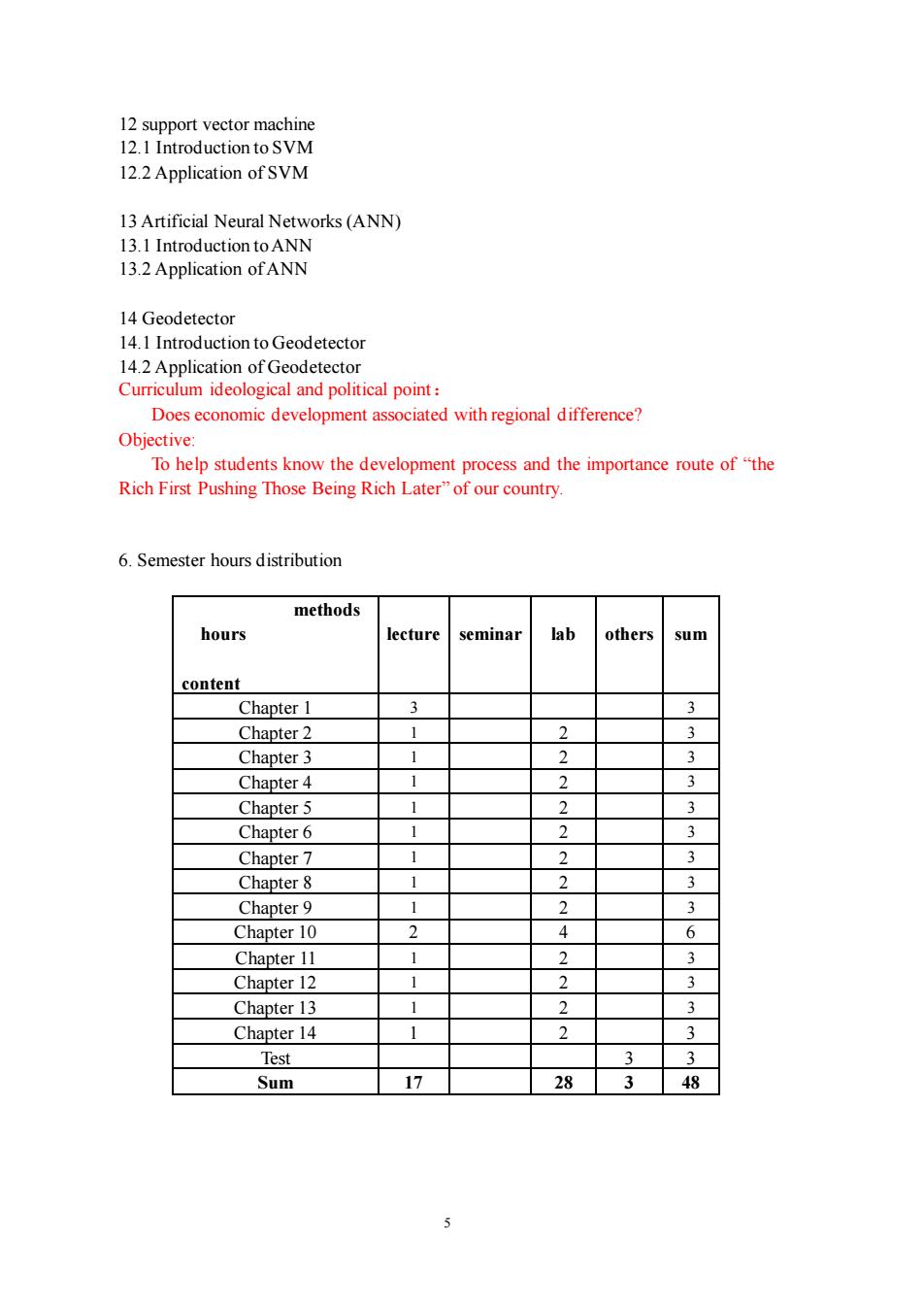
12 support vector machine 12.1 Introduction to SVM 12.2 Application ofSVM 13 Artificial Neural Networks(ANN) 13.1 Introduction to ANN 13.2 Application ofANN 14.1 Introduction to Geodetector 14.2 Application of Geodetector Curriculum ideological and political point: Does economic development associated with regional difference? Objective: To help students know the development process and the importance route of"the Rich First Pushing Those Being Rich Later"of our country. 6.Semester hours distribution methods hours lectureseminar lab others sum content Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter8 Chapter 9 Chapter 10 4 6 Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Chapter 13 Chapter 14 1 2 3 Test Sum 3
5 12 support vector machine 12.1 Introduction to SVM 12.2 Application of SVM 13 Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) 13.1 Introduction to ANN 13.2 Application of ANN 14 Geodetector 14.1 Introduction to Geodetector 14.2 Application of Geodetector Curriculum ideological and political point: Does economic development associated with regional difference? Objective: To help students know the development process and the importance route of “the Rich First Pushing Those Being Rich Later” of our country. 6. Semester hours distribution methods hours content lecture seminar lab others sum Chapter 1 3 3 Chapter 2 1 2 3 Chapter 3 1 2 3 Chapter 4 1 2 3 Chapter 5 1 2 3 Chapter 6 1 2 3 Chapter 7 1 2 3 Chapter 8 1 2 3 Chapter 9 1 2 3 Chapter 10 2 4 6 Chapter 11 1 2 3 Chapter 12 1 2 3 Chapter 13 1 2 3 Chapter 14 1 2 3 Test 3 3 Sum 17 28 3 48

7.Others At all times students should to be cordial,courteous and respectful of faculty members and fellow students. .Cellphones,laptops and videotaping.and other electronic devices are not allowed in lecture or lab. Syllabus written by:Qingsheng Yang Time:Dec.22.2021 Syllabus reviewed by: Time: 6
6 7. Others • At all times students should to be cordial, courteous and respectful of faculty members and fellow students. • Cellphones, laptops and videotaping, and other electronic devices are not allowed in lecture or lab. Syllabus written by:Qingsheng Yang Time:Dec. 22, 2021 Syllabus reviewed by: Time: