
《人机工程学》课程教学大纲 Curriculum syl labus of ergonomics 课程编号:012014 Course No.:012014 课程名称(中/英文):人机工程学/Ergonomics Course name(Chinese/English):ergonomics/Ergonomics 课程类型:专业课 Course type:professional course 总学时:48 讲课学时:32 实验学时:16 Total class hours:48 lecture hours:32 experimental hours:16 学分:3 Credit:3 适用对象:工业设计专业本科生 Applicable object:undergraduate of industrial design major 先修课程:工业设计概论 Pre course:introduction to industrial design 后续课程:产品设计 Follow up course:product design 开课单位:机械与动力工程学院 Opening unit:College of mechanical and power engineering 一、课程性质和教学目标 1.Course nature and teaching objectives 人机工程学是工业设计专业的专业课程,主要研究人在某种工作环境中的解剖学、生理学和心理学 等方面的各种因素:研究人和机器及环境的相互作用:研究在工作中、家庭生活中和休闲时怎样统一 考虑工作效率、人的健康、安全和舒适等问题的学科。通过本课程的学习,让学生了解人机工程学的 基本理论和研究方法,能够在设计中应用基本理论、方法和技术资料解决实际问题。 Ergonomics is a professional course of industrial design major,which mainly studies various factors of anatomy,physiology and psychology in a certain working environment:Study the interaction of human,machine and environment:It studies how to consider work efficiency
《人机工程学》课程教学大纲 Curriculum syllabus of ergonomics 课程编号: 012014 Course No.: 012014 课程名称(中/英文): 人机工程学/ Ergonomics Course name (Chinese / English): ergonomics / Ergonomics 课程类型: 专业课 Course type: professional course 总 学 时:48 讲课学时:32 实验学时:16 Total class hours: 48 lecture hours: 32 experimental hours: 16 学 分:3 Credit: 3 适用对象: 工业设计专业本科生 Applicable object: undergraduate of industrial design major 先修课程:工业设计概论 Pre course: introduction to industrial design 后续课程:产品设计 Follow up course: product design 开课单位:机械与动力工程学院 Opening unit: College of mechanical and power engineering 一、课程性质和教学目标 1、 Course nature and teaching objectives 人机工程学是工业设计专业的专业课程,主要研究人在某种工作环境中的解剖学、生理学和心理学 等方面的各种因素;研究人和机器及环境的相互作用;研究在工作中、家庭生活中和休闲时怎样统一 考虑工作效率、人的健康、安全和舒适等问题的学科。通过本课程的学习,让学生了解人机工程学的 基本理论和研究方法,能够在设计中应用基本理论、方法和技术资料解决实际问题。 Ergonomics is a professional course of industrial design major, which mainly studies various factors of anatomy, physiology and psychology in a certain working environment; Study the interaction of human, machine and environment; It studies how to consider work efficiency

human health.safety and comfort in work.family life and leisure.Through the study of this course,students can understand the basic theories and research methods of ergonomics,and be able to apply the basic theories,methods and technical data in design to solve practical problems. 二、教学基本要求 2.Basic teaching requirements 通过该课程的学习,要求学生掌握和设计有关的人的生理与心理的特点,能够把所学理论应用于 实践,从人机工程学角度实践人性化设计方法。要求学生掌握相关数据的查阅与应用原则方法,结合具 体案例熟练应用。 Through the study of this course,students are required to master the physiological and psychological characteristics of people related to design,apply the theory to practice,and practice the humanized design method from the perspective of ergonomics.Students are required to master the principles and methods of relevant data access and application,and skillfully apply them in combination with specific cases. 三、教学内容及要求 3.Teaching contents and requirements 第一章人机工程学概论 Chapter 1 Introduction to ergonomics 教学目的与要求: Teaching obiectives and reguirements: 通过本章的学习,使学生能够比较全面、系统地了解人机工程学的研究对象、目的、内容和方法。 Through the study of this chapter,students can understand the research object,purpose content and method of ergonomics comprehensively and systematically 本章主要内容: The main contents of this chapter are as follows 1.1人机学的命名和定义 1.INomenclature and definition of ergonomics 1.2人机学发展简史 1.2 A brief history of ergonomics 1.3人机系统与人机工程设计
human health, safety and comfort in work, family life and leisure. Through the study of this course, students can understand the basic theories and research methods of ergonomics, and be able to apply the basic theories, methods and technical data in design to solve practical problems. 二、教学基本要求 2、 Basic teaching requirements 通过该课程的学习,要求学生掌握和设计有关的人的生理与心理的特点,能够把所学理论应用于 实践,从人机工程学角度实践人性化设计方法。要求学生掌握相关数据的查阅与应用原则方法,结合具 体案例熟练应用。 Through the study of this course, students are required to master the physiological and psychological characteristics of people related to design, apply the theory to practice, and practice the humanized design method from the perspective of ergonomics. Students are required to master the principles and methods of relevant data access and application, and skillfully apply them in combination with specific cases. 三、教学内容及要求 3、 Teaching contents and requirements 第一章 人机工程学概论 Chapter 1 Introduction to ergonomics 教学目的与要求: Teaching objectives and requirements: 通过本章的学习,使学生能够比较全面、系统地了解人机工程学的研究对象、目的、内容和方法。 Through the study of this chapter, students can understand the research object, purpose, content and method of ergonomics comprehensively and systematically. 本章主要内容: The main contents of this chapter are as follows 1.1 人机学的命名和定义 1.1Nomenclature and definition of ergonomics 1.2 人机学发展简史 1.2 A brief history of ergonomics 1.3 人机系统与人机工程设计

1.3 Man machine system and man machine engineering design 1.4人机学的研究内容与方法 1.4 Research contents and methods of ergonomics 1.5人机学的学科体系及其应用领域 1.5 Subject system and application field of ergonomics 1.6人机工程学与工业设计的关系 1.6 The relationship between ergonomics and industrial design 1.7常用软件介绍 1.7 introduction of common software 1.8日常生活中的人机学问题 1.8 ergonomics in daily life 第二章人体测量及其应用 Teaching objectives and requirements 通过对人体测量方面知识的讲解,让学生掌握人体测量的方法、测量标准和具体测量项目,能够熟 练地查阅相关标准,将数据科学地应用于具体设计案例中。 By explaining the knowledge of anthropometry,students can master the methods,standards and specific measurement items of anthropometry,skillfully consult the relevant standards. and scientifically apply the data to specific design cases. 本章主要内容: The main contents of this chapter are as follows 2.1人体测量基本知识 2.1 basic knowledge of anthropometry 22人体测量术语及定义 2.2 anthropometric terms and definitions 2.3人体测量数据的统计特性 2.3 statistical characteristics of anthropometric data 2.4常用人体测量数据 2.4 common anthropometric data 2.5人体各部分结构参数的计算 2.5 calculation of structural parameters of various parts of human body 2.6人体尺寸的应用
1.3 Man machine system and man machine engineering design 1.4 人机学的研究内容与方法 1.4 Research contents and methods of ergonomics 1.5 人机学的学科体系及其应用领域 1.5 Subject system and application field of ergonomics 1.6 人机工程学与工业设计的关系 1.6 The relationship between ergonomics and industrial design 1.7 常用软件介绍 1.7 introduction of common software 1.8 日常生活中的人机学问题 1.8 ergonomics in daily life 第二章 人体测量及其应用 Chapter 2 anthropometry and its application 教学目的与要求: Teaching objectives and requirements: 通过对人体测量方面知识的讲解,让学生掌握人体测量的方法、测量标准和具体测量项目,能够熟 练地查阅相关标准,将数据科学地应用于具体设计案例中。 By explaining the knowledge of anthropometry, students can master the methods, standards and specific measurement items of anthropometry, skillfully consult the relevant standards, and scientifically apply the data to specific design cases. 本章主要内容: The main contents of this chapter are as follows 2.1 人体测量基本知识 2.1 basic knowledge of anthropometry 2.2 人体测量术语及定义 2.2 anthropometric terms and definitions 2.3 人体测量数据的统计特性 2.3 statistical characteristics of anthropometric data 2.4 常用人体测量数据 2.4 common anthropometric data 2.5 人体各部分结构参数的计算 2.5 calculation of structural parameters of various parts of human body 2.6 人体尺寸的应用

2.6 application of body size 2.7人体测量与数据应用案例分析 2.7 case analysis of anthropometry and data application 第三章人体感知与运动特征 The third chapter is human perception and motion characteristics 本章主要内容: The main contents of this chapter are as follows 3.1人在系统中的功能 3.1 function of human in the system 3.2感觉和知觉的特征 3.2 characteristics of sensation and perception 3.3视觉机能及其特征 3.3 visual function and its characteristics 3.4听觉机能及其特征 3.4 auditory function and its characteristics 3.5其它感觉机能及其特征 3.5 other sensory functions and their characteristics 3.6运动系统的机能及其特征 3.6 function and characteristics of motor system 3.7人的运动输出 3.7 human motor output 第四查信息品示转置设计 Chapter 4 Design of information display device 4.1信息显示装置概述 4.1 information display device overview 4.2视觉信息显示设计 4.2 visual information display design 43听觉信息传示设计 4.3 design of auditory information transmission 4.4触觉显示设计 4.4 tactile display design 4.5嗅觉显示设计 4.5 olfactory display design
2.6 application of body size 2.7 人体测量与数据应用案例分析 2.7 case analysis of anthropometry and data application 第三章 人体感知与运动特征 The third chapter is human perception and motion characteristics 本章主要内容: The main contents of this chapter are as follows 3.1 人在系统中的功能 3.1 function of human in the system 3.2 感觉和知觉的特征 3.2 characteristics of sensation and perception 3.3 视觉机能及其特征 3.3 visual function and its characteristics 3.4 听觉机能及其特征 3.4 auditory function and its characteristics 3.5 其它感觉机能及其特征 3.5 other sensory functions and their characteristics 3.6 运动系统的机能及其特征 3.6 function and characteristics of motor system 3.7 人的运动输出 3.7 human motor output 第四章 信息显示装置设计 Chapter 4 Design of information display device 4.1 信息显示装置概述 4.1 information display device overview 4.2 视觉信息显示设计 4.2 visual information display design 4.3 听觉信息传示设计 4.3 design of auditory information transmission 4.4 触觉显示设计 4.4 tactile display design 4.5 嗅觉显示设计 4.5 olfactory display design

46多诵道品示设计 4.6 multi channel display design 4.7显示器选用与设计的基本原则 4.7 basic principles of display selection and design 第五章操纵装置设计 Chapter 5 control device design 5.1操纵装置概述 5.1 overview of control device 5.2手动操纵装置设计 5.2 design of manual control device 5.3脚动操纵装置设计 5.3 design of foot control device 5.4操纵与显示相合性 5.4 consistency of operation and display 5.5操纵装置选用与设计的基本原则 5.5 basic principles of control device selection and design 第六章工作台椅与手握工具设计 Chapter 6 design of worktable chair and hand tools 6.1控制台设计 6.1 console design 6.3工作椅设计主要依据 6.3 main design basis of work chair 64工作椅设计 6.4 design of work chair 6.5手握工具设计 6.5 hand tool design 第七章作业岗位与作业空间设计
4.6 多通道显示设计 4.6 multi channel display design 4.7 显示器选用与设计的基本原则 4.7 basic principles of display selection and design 第五章 操纵装置设计 Chapter 5 control device design 5.1 操纵装置概述 5.1 overview of control device 5.2 手动操纵装置设计 5.2 design of manual control device 5.3 脚动操纵装置设计 5.3 design of foot control device 5.4 操纵与显示相合性 5.4 consistency of operation and display 5.5 操纵装置选用与设计的基本原则 5.5 basic principles of control device selection and design 第六章 工作台椅与手握工具设计 Chapter 6 design of worktable chair and hand tools 6.1 控制台设计 6.1 console design 6.2 办公台设计 6.2 office desk design 6.3 工作椅设计主要依据 6.3 main design basis of work chair 6.4 工作椅设计 6.4 design of work chair 6.5 手握工具设计 6.5 hand tool design 第七章 作业岗位与作业空间设计

Chapter 7 design of work post and work space 7.1作业岗位的类型及选择 7.1 job type and selection 7,2手工作业岗位设计 7.2 post design of manual operation 7.3视觉信息作业岗位设计 7.3 post design of visual information operation 7.4作业空间的人体尺寸 7.4 body size of working space 7.5作业面设计 7.5 working face design 7.6作业空间的布置 7.6 layout of working space 7.7作业空间设计的社会心理因素 7.7 social and psychological factors of work space design 第八章作业环境设计 Chapter 8 design of working environment 8.1热环境及其设计 8.I thermal environment and its design 8.2噪声环境及其设计 8.2 noise environment and its design 8.3振动环境及其设计 8.3 vibration environment and its design 8.4光环境及其设计 8.4 light environment and its design Chapter 9o man-machine system 9.1人机系统设计概述 9.1 overview of human machine system design 9,2人机系统总体设计的原则 9.2 overall design principle of man machine system 9.3人机系统总体设计的程序与方法 9.for overall desig of syste 9.5人机系统总体设计的评价 9.5 evaluation of overall design of man machine system 9.6人机系统设计案例分析
Chapter 7 design of work post and work space 7.1 作业岗位的类型及选择 7.1 job type and selection 7.2 手工作业岗位设计 7.2 post design of manual operation 7.3 视觉信息作业岗位设计 7.3 post design of visual information operation 7.4 作业空间的人体尺寸 7.4 body size of working space 7.5 作业面设计 7.5 working face design 7.6 作业空间的布置 7.6 layout of working space 7.7 作业空间设计的社会心理因素 7.7 social and psychological factors of work space design 第八章 作业环境设计 Chapter 8 design of working environment 8.1 热环境及其设计 8.1 thermal environment and its design 8.2 噪声环境及其设计 8.2 noise environment and its design 8.3 振动环境及其设计 8.3 vibration environment and its design 8.4 光环境及其设计 8.4 light environment and its design 第九章 人机系统总体设计 Chapter 9 overall design of man-machine system 9.1 人机系统设计概述 9.1 overview of human machine system design 9.2 人机系统总体设计的原则 9.2 overall design principle of man machine system 9.3 人机系统总体设计的程序与方法 9.3 procedures and methods for overall design of man-machine system 9.4 人机系统总体设计的要点 9.4 key points of overall design of man-machine system 9.5 人机系统总体设计的评价 9.5 evaluation of overall design of man machine system 9.6 人机系统设计案例分析

9.6 case analysis of human machine system design 四、课程建设与改革(含教学思想、教学方法、教学手段) 4.Curriculum construction and Reform (including teaching ideas,teaching methods and teaching means) 1.课程的实践环节为实验和课外课题设计。实验和课外课题设计安排在课程相应章节中。 1.The practice part of the course is experiment and extracurricular project design.The experiment and extracurricular project design are arranged in the corresponding chapters of the course. 2.为达到本课程的教学基本要求,课外习题及课程讨论如下: 2.In order to meet the basic requirements of this course,the extracurricular exercises and cou scu 我们 s follows 相关的产品,并选1一2种产品,讨论产品中的哪些部分属于 人机工程 (D)List the s in our daily life. and choose 1-2 kinds of product which rts of the ucts belong t o the obie omics design and which parts do not belong to ergonomics design? ct of ergor (2)应用人体测量学知识,对日常生活中一种物品进行评析。 (2)Applying the knowledge of anthropometry,this paper evaluates an object in daily life. (3)产品显示与控制设计与分析 (3)Product display and control design and analysis. (4)新产品的人机学创意开发, (4)Human machine creative development of new products. 3.《人机工程学》在工业设计专业课程群中是一门较为孤立的课程,根据本门课程的理论特色, 为避免由于简单介绍繁项的数据造成学生厌倦,教学方法不拘一格。教学中以学生为主体,以实际产 品评析为内容的启发式教学。 3.Ergonomics is a relatively isolated course in the course group of industrial design ma jor.According to the theoretical characteristics of this course,in order to avoid students boredom caused by simple introduction of tedious data,the teaching methods are not stick to one pattern.In the teaching,students are the main body,and the actual product evaluation is the content of heuristic teaching. 五、各教学环节学时分配
9.6 case analysis of human machine system design 四、课程建设与改革(含教学思想、教学方法、教学手段) 4、 Curriculum construction and Reform (including teaching ideas, teaching methods and teaching means) 1.课程的实践环节为实验和课外课题设计。实验和课外课题设计安排在课程相应章节中。 1. The practice part of the course is experiment and extracurricular project design. The experiment and extracurricular project design are arranged in the corresponding chapters of the course. 2.为达到本课程的教学基本要求,课外习题及课程讨论如下: 2. In order to meet the basic requirements of this course, the extracurricular exercises and course discussion are as follows: (1)举出我们日常生活中与人机工程学相关的产品,并选 1~2 种产品,讨论产品中的哪些部分属于 人机工程设计的对象、哪些部分不属于? (1) List the products related to ergonomics in our daily life, and choose 1-2 kinds of products to discuss which parts of the products belong to the object of ergonomics design and which parts do not belong to ergonomics design? (2)应用人体测量学知识,对日常生活中一种物品进行评析。 (2) Applying the knowledge of anthropometry, this paper evaluates an object in daily life. (3)产品显示与控制设计与分析。 (3) Product display and control design and analysis. (4)新产品的人机学创意开发。 (4) Human machine creative development of new products. 3.《人机工程学》在工业设计专业课程群中是一门较为孤立的课程,根据本门课程的理论特色, 为避免由于简单介绍繁琐的数据造成学生厌倦,教学方法不拘一格。教学中以学生为主体,以实际产 品评析为内容的启发式教学。 3. Ergonomics is a relatively isolated course in the course group of industrial design major. According to the theoretical characteristics of this course, in order to avoid students' boredom caused by simple introduction of tedious data, the teaching methods are not stick to one pattern. In the teaching, students are the main body, and the actual product evaluation is the content of heuristic teaching. 五、各教学环节学时分配

5.Class hour allocation of each teaching link 各教学环节学时分配见表 1.The class hour allocation of each teaching link is shown in Table 1 表1各教学环节学时分配 Table 1 class hour allocation of each teaching link 节 讨论课 Chapter 讲课 习题课 实验 其他 合 计 Lectures Uebung class experiment other total 第一章人机工程学概论 Chapter 1 Introduction to 3 ergonomics 第二章人体测量及其应用 1 Chapter 2 anthropometry and its 2 8 application 第三章人体感知与运动特征 The third chapter is human 6 8 perception and motion characteristics 第四章信总显示装置设计The fourth chapter is the desigr of information display 2 6 device 第五章操纵装置设计Chapter 5 control device design 2 4 使个章工作合椅与手工 apter 6 design of worktable chair and hand tools 2 6 第七章作业岗位与作业空间 设计
5、 Class hour allocation of each teaching link 各教学环节学时分配见表 1. The class hour allocation of each teaching link is shown in Table 1 表 1 各教学环节学时分配 Table 1 class hour allocation of each teaching link 章 节 Chapter 讲 课 Lectures 习题课 Uebung 讨论课 Discussion class 实 验 experiment 其 他 other 合 计 total 第一章 人机工程学概论 Chapter 1 Introduction to ergonomics 3 1 4 第二章 人体测量及其应用 Chapter 2 anthropometry and its application 5 1 2 8 第三章 人体感知与运动特征 The third chapter is human perception and motion characteristics 6 8 14 第四章 信息显示装置设计 The fourth chapter is the design of information display device 4 2 6 第五章 操纵装置设计 Chapter 5 control device design 2 2 4 第六章 工作台椅与手握工具 设计 Chapter 6 design of worktable chair and hand tools 4 2 6 第七章 作业岗位与作业空间 设计 2 2
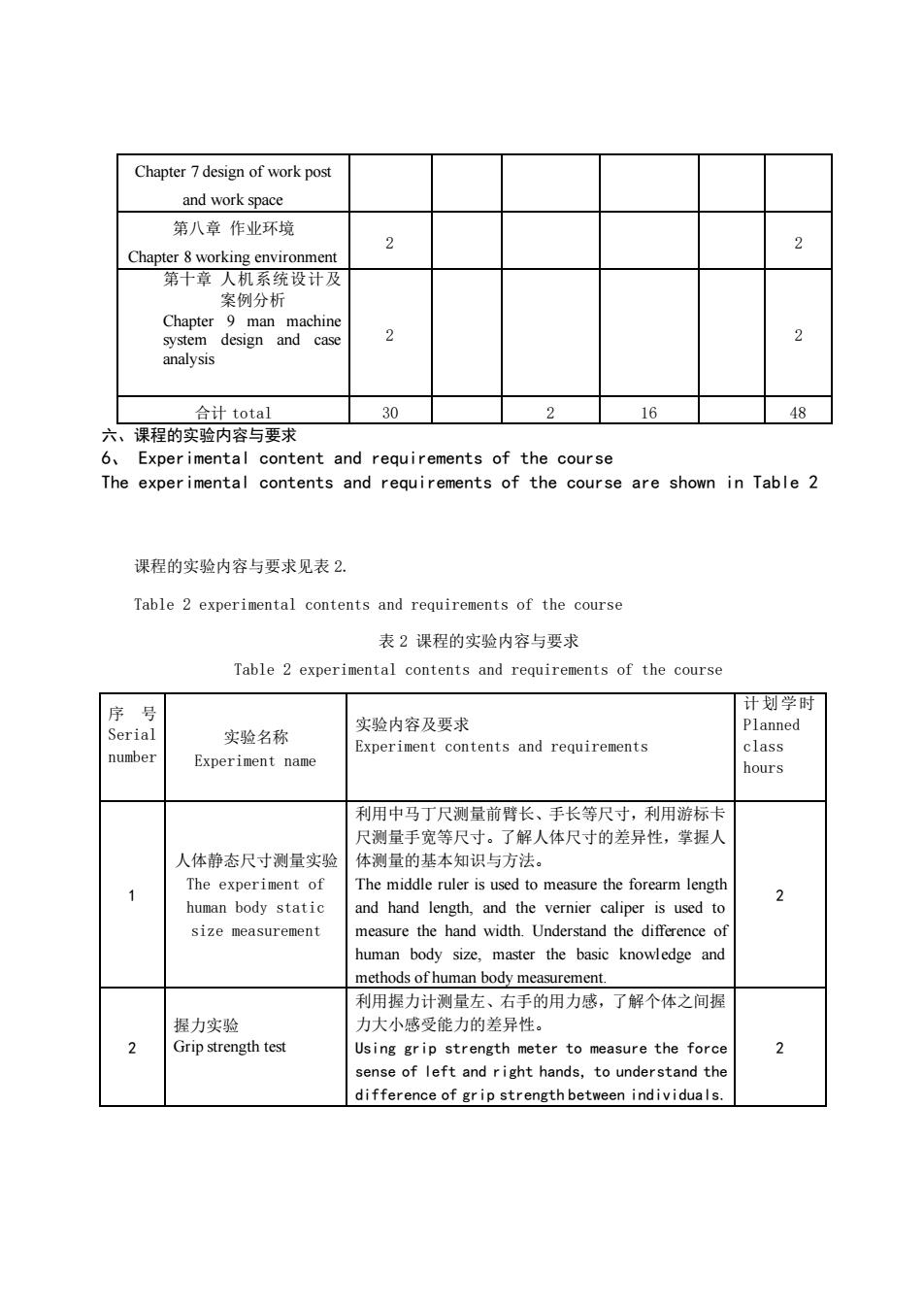
Chapter 7 design of work post and work space 第八章作业环境 Chapter 8 working environment 第十章人机系统设计及 案例分析 合计total 30 2 16 48 六、课程的实验内容与要求 6.Exper imental content and requirements of the course The exper imental contents and requirements of the course are shown in Table 2 课程的实验内容与要求见表2. Table 2 experimental contents and requirements of the course 表2课程的实验内容与要求 Table 2 experimental contents and requirements of the course 序号 Serial 实哈内容及要求 实验名称 Experiment contents and requirements 。1a number Experiment name hours 利用中马丁尺测量前长、手长第尺,利用游标卡 解人体尺寸的差异性,掌握人 人体静态尺寸测量实验 体测量的基本知识与方法 The experiment of The middle ruler is used to measure the forearm lengt 2 human body static and hand length,and the vernier caliper is used to size measurement measure the hand width.Understand the difference of human body size,master the basic knowledge and methods of human body measurement 利用握力计测量左、右手的用力感,了解个体之间捏 握力实验 力大小成受能力的并异性 Grip strength test to measure the force rstand the difference of grip strength between individuals
Chapter 7 design of work post and work space 第八章 作业环境 Chapter 8 working environment 2 2 第十章 人机系统设计及 案例分析 Chapter 9 man machine system design and case analysis 2 2 合计 total 30 2 16 48 六、课程的实验内容与要求 6、 Experimental content and requirements of the course The experimental contents and requirements of the course are shown in Table 2 课程的实验内容与要求见表 2. Table 2 experimental contents and requirements of the course 表 2 课程的实验内容与要求 Table 2 experimental contents and requirements of the course 序 号 Serial number 实验名称 Experiment name 实验内容及要求 Experiment contents and requirements 计划学时 Planned class hours 1 人体静态尺寸测量实验 The experiment of human body static size measurement 利用中马丁尺测量前臂长、手长等尺寸,利用游标卡 尺测量手宽等尺寸。了解人体尺寸的差异性,掌握人 体测量的基本知识与方法。 The middle ruler is used to measure the forearm length and hand length, and the vernier caliper is used to measure the hand width. Understand the difference of human body size, master the basic knowledge and methods of human body measurement. 2 2 握力实验 Grip strength test 利用握力计测量左、右手的用力感,了解个体之间握 力大小感受能力的差异性。 Using grip strength meter to measure the force sense of left and right hands, to understand the difference of grip strength between individuals. 2
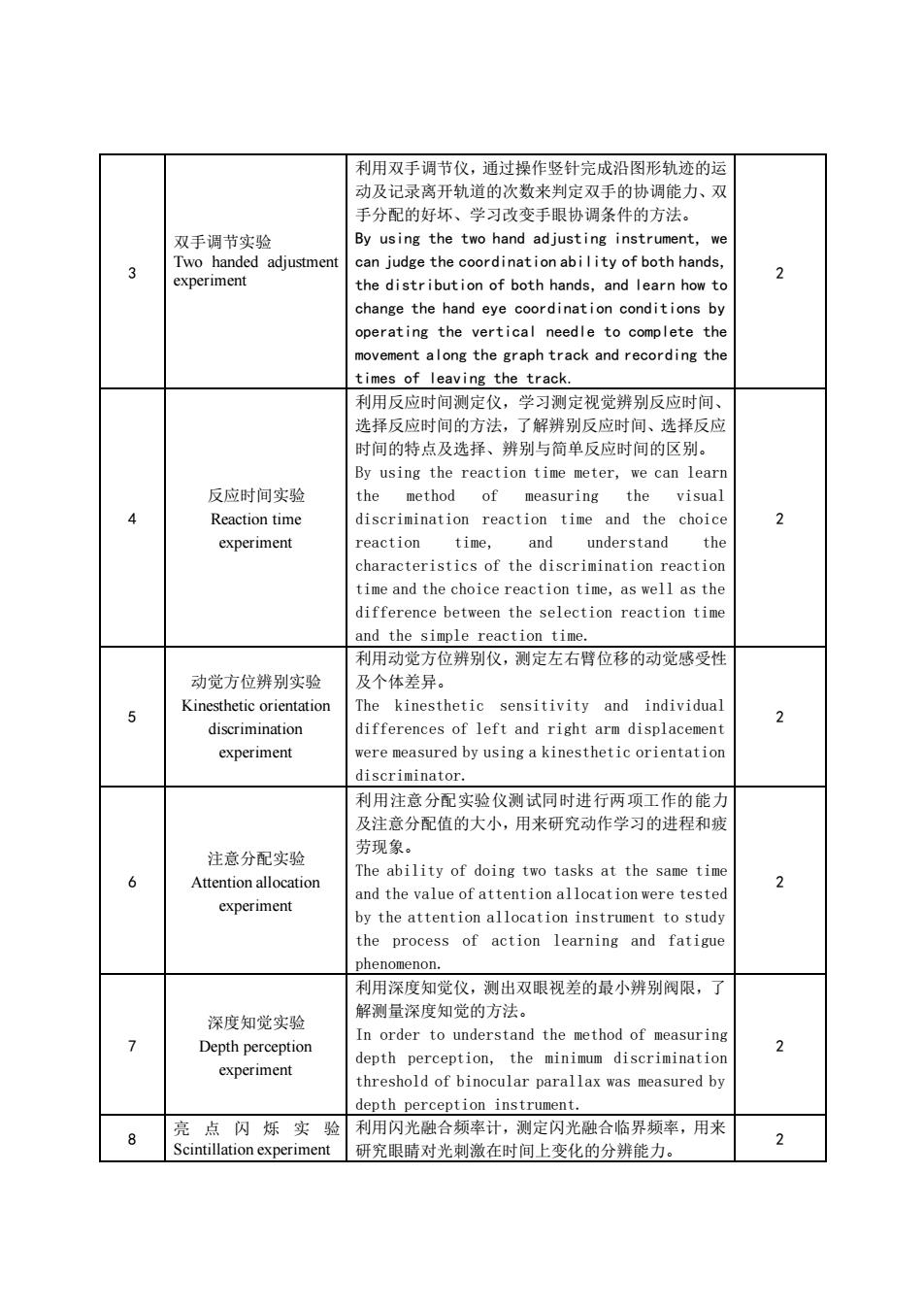
利用双手调节仪,通过操作竖针完成沿图形轨迹的运 动及记录离开轨道的次数来判定双手的协调能力、双 手分配的好坏、学习改变手眼协调条件的方法。 By usine the two hand adiusting inst we adjustmen ability of both hands and learn how to change the hand eye coordination conditions by operating the vertical needle to complete the movement along the graph track and recording the times of leaving the track. 利用反应时间测定仪,学习测定视觉辨别反应时间、 选择反应时间的方法,了解辨别反应时间、选择反应 时间的特点及洗择、辨别与简单反应时间的区别。 D. using the reactionti ter e can lear 反应时间实验 method measuring Reaction time discrimination reaction time and the choic 2 experiment reaction time, and understand the characteristics of the discrimination reaction time and the choice reaction time.as well as the difference between the selection reaction time and the simple reaction time 利用动觉方位辨别仪,测定左右臂位移的动觉成受性 觉方位辨别实验 乃及个体差异」 Kine thcticoricntalion The kinesthetic sensitivity and individua of left and right arm displacement 2 experiment discriminator 利用注意分配实验仪测试同时进行两项工作的能力 及注意分配值的大小,用来研究动作学习的进程和疲 告而龟 注意分配实验 The ability of doing two tasks at the same time 6 Attention allocation 2 experimen tion instrument to stud the process of action learning and fatigue phenomenon. 利用深度知觉仪,测出双眼视差的最小辨别阀限,了 深度知微实验 解测量深度知觉的方法。 In order to understand the method of measuring Depth perception depth perception,the minimum discrimination 2 threshold of binocular parallax was measured by depth instrumen 实 光融合临界频率,用来 8 experin 研究眼睛对光刺激在时间上变化的分辨能力 2
3 双手调节实验 Two handed adjustment experiment 利用双手调节仪,通过操作竖针完成沿图形轨迹的运 动及记录离开轨道的次数来判定双手的协调能力、双 手分配的好坏、学习改变手眼协调条件的方法。 By using the two hand adjusting instrument, we can judge the coordination ability of both hands, the distribution of both hands, and learn how to change the hand eye coordination conditions by operating the vertical needle to complete the movement along the graph track and recording the times of leaving the track. 2 4 反应时间实验 Reaction time experiment 利用反应时间测定仪,学习测定视觉辨别反应时间、 选择反应时间的方法,了解辨别反应时间、选择反应 时间的特点及选择、辨别与简单反应时间的区别。 By using the reaction time meter, we can learn the method of measuring the visual discrimination reaction time and the choice reaction time, and understand the characteristics of the discrimination reaction time and the choice reaction time, as well as the difference between the selection reaction time and the simple reaction time. 2 5 动觉方位辨别实验 Kinesthetic orientation discrimination experiment 利用动觉方位辨别仪,测定左右臂位移的动觉感受性 及个体差异。 The kinesthetic sensitivity and individual differences of left and right arm displacement were measured by using a kinesthetic orientation discriminator. 2 6 注意分配实验 Attention allocation experiment 利用注意分配实验仪测试同时进行两项工作的能力 及注意分配值的大小,用来研究动作学习的进程和疲 劳现象。 The ability of doing two tasks at the same time and the value of attention allocation were tested by the attention allocation instrument to study the process of action learning and fatigue phenomenon. 2 7 深度知觉实验 Depth perception experiment 利用深度知觉仪,测出双眼视差的最小辨别阀限,了 解测量深度知觉的方法。 In order to understand the method of measuring depth perception, the minimum discrimination threshold of binocular parallax was measured by depth perception instrument. 2 8 亮 点 闪 烁 实 验 Scintillation experiment 利用闪光融合频率计,测定闪光融合临界频率,用来 研究眼睛对光刺激在时间上变化的分辨能力。 2