
《西方社会工作理论与实践》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 课程代码:125053 课程名称:西方社会工作理论与实践(英语)》 英文名称:Social Work Theory and Practice 课程类别:专业课 学时:48 分: 适用对象:Social work bachelor students 考核方式:考试 教学语言:English 先修课程:Introduction to Social Work 二、课程简介 社会工作是价值和理论指导下的助人实践。社会工作专业发源并主要发展于西方社会 其发展成果在时代变迁和全球化的浪潮中不断沉淀和锤炼,为社会工作专业学生提供了丰 富而可靠的理论和实践基础。 司时,理解社会工作理论和实践的相互 关联是专业学 习的重 要内容。作为一门专业核心课程,西方社会工作理论和实践指在使社会工作专业本科学生 熟悉主要的社会工作实务知识和技能,以及相关的理论原理。这门课程也将开启学生通过 英文资料学习专业知识的大门。 Social and theo As ped ts to y the nt to understa eret and in the orie ted bet een theory an Social Wor grad ored 000 practice xpeced to prepare the studentsfor proactive eaming retical rati 三、课程性质与教学目的 课程性质:specialized course for social work bachelor students 教学目的:The course objectives are4 folded:(l)to demonstrate the relationships between practice and theory in view of empirical research providing "evidence":(2)to introduce the main domains of social work practice and relevant techniques:(3)to illustrate the theoretical frameworks and p erspectives commonly applied in social work practice:and(4)to facilitate students with terminologies in social work for future professional exchange and study with English. 四、教学内容及要求 Lecture I Introduction to theory and practice for social work (一)教学目的和要求objectives and requirements: 教学目的:Overview on course contents and requirements 1
1 《西方社会工作理论与实践》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 课程代码: 125053 课程名称: 西方社会工作理论与实践(英语) 英文名称: Social Work Theory and Practice 课程类别: 专业课 学 时: 48 学 分: 3 适用对象: Social work bachelor students 考核方式: 考试 教学语言: English 先修课程: Introduction to Social Work 二、课程简介 社会工作是价值和理论指导下的助人实践。社会工作专业发源并主要发展于西方社会。 其发展成果在时代变迁和全球化的浪潮中不断沉淀和锤炼,为社会工作专业学生提供了丰 富而可靠的理论和实践基础。同时,理解社会工作理论和实践的相互关联是专业学习的重 要内容。作为一门专业核心课程,西方社会工作理论和实践旨在使社会工作专业本科学生 熟悉主要的社会工作实务知识和技能,以及相关的理论原理。这门课程也将开启学生通过 英文资料学习专业知识的大门。 Social work aims to provide helping practice illuminated by values and theories. As a profession, social work originated from and developed mainly in the West. It is vital for social work students to be equipped by the theories and practical skills accumulated and verified in the past. It is also important to understand the relationships between theory and practice. Social Work Theory and Practice is a core course to familiarize undergraduates majored in social work with a rich body of practice knowledge and techniques and the underpinning theoretical rationale. Meanwhile, the course is expected to prepare the students for proactive learning about professional knowledge in English. 三、课程性质与教学目的 课程性质:specialized course for social work bachelor students 教学目的:The course objectives are 4 folded: (1) to demonstrate the relationships between practice and theory in view of empirical research providing “evidence”; (2) to introduce the main domains of social work practice and relevant techniques; (3) to illustrate the theoretical frameworks and perspectives commonly applied in social work practice; and (4) to facilitate students with terminologies in social work for future professional exchange and study with English. 四、教学内容及要求 Lecture 1 Introduction to theory and practice for social work (一)教学目的和要求 objectives and requirements: 教学目的:Overview on course contents and requirements

教学要求:Students should understand the rationale of this course,.the relationships between theory and practice in social work and the course requirements. (二)教学内容 1.Course overview ·What is social work? Social work is simply about helping but Complex,Comprehensive,Creative,and Challenging mplex due to diverse human needs Bio-psycho-.-spirital--socio生心灵t社 o Compreh e knowle ge and skills Creative n esigning tair-made service o Challenging for multi-tasking and ever-changing Why to learn this course? o Social work originated and developed in the West. o Adoptable for indigenous social work o Introductory but highlighting theory application o Preparation for higher degree and work chance o English enhancement ·Course objectives o to demonstrate the relationships between practice and theory in view of :循证的实践 ntroduce the main domains of soctal work practice and relevant niques oto illustrate the theoretical frameworks and perspectives commonly applied in social work practice,and理论框架和视角 o to facilitate students with terminologies in social work for future professional exchange and study in English. ·Course outline o Introduction o Major social work practice and techniques o Established theoretical fra orks and (mid-term erspectives for social work practice English literature readin n(end -of-term presentation) 20 ition,purpose,basis and foc ocial work is a.profession that is committed to improving the quality of life for vulnerable people by helping them...with the challenges they face and/or helping to change the social and economic conditions that create or exacerbate individual and social problems."(Sheafor Horejsi, 2015,p.xvii). oSocial work purpose:To Improve social functioning (people)and social conditions(environment) o Social work basis: 社会工作价值观和伦理(values and ethics) 多样性(di ersity) 理解社会和经济公正(social and economic justice):
2 教学要求:Students should understand the rationale of this course, the relationships between theory and practice in social work and the course requirements. (二)教学内容 1. Course overview What is social work? Social work is simply about helping but Complex, Comprehensive, Creative, and Challenging. o Complex due to diverse human needs Bio-psycho-spiritual-socio 生心灵社 o Comprehensive knowledge and skills o Creative in designing tailor-made service o Challenging for multi-tasking and ever-changing Why to learn this course? o Social work originated and developed in the West. o Adoptable for indigenous social work o Introductory but highlighting theory application o Preparation for higher degree and work chance o English enhancement Course objectives o to demonstrate the relationships between practice and theory in view of empirical “evidence”; 循证的实践 o to introduce the main domains of social work practice and relevant techniques; o to illustrate the theoretical frameworks and perspectives commonly applied in social work practice; and 理论框架和视角 o to facilitate students with terminologies in social work for future professional exchange and study in English. Course outline o Introduction o Major social work practice and techniques o Established theoretical frameworks and perspectives for social work practice o English literature reading (mid-term quiz) o Service plan design (end-of-term presentation) o Course assessment 2. Defining the key concepts Social work: the definition, purpose, basis and focus o Definition: “Social work is a …profession that is committed to improving the quality of life for vulnerable people by helping them… with the challenges they face and/or helping to change the social and economic conditions that create or exacerbate individual and social problems.” (Sheafor & Horejsi, 2015, p. xvii). o Social work purpose: To Improve social functioning (people) and social conditions (environment) o Social work basis: 社会工作价值观和伦理 (values and ethics) 多样性(diversity) 理解社会和经济公正(social and economic justice):

人类行为和社会环境(human behavior and social environment) 社会福利政策与服务(social welfare and service) 社会工作实务(practice:knowledge,.values,.and skills) a研究research(for need evaluation and impact assessment,.定量quantitative 和定质qualitative research) oSocial work focus: Wholeness of person To l social To i social nment) ocalgaro Social just Help people help themselves Practice I worker. ...implies insights,and never content to do what they have always done"(Sheafor Horejsi,2015,p.xvii). .Theory:Theory is "a supposition or a system of ideas intended to explain something,especially one based on general principles independent of the thing to be explained."(Oxford Dictionaries). o Theories for social work(社会工作支持理论)to understand people and social phenomena and to guide actice with validated frameworks 。Theories of i work社会作的理论):,.domain and character of social work within a society. 3.Social work theory and practice Interrelationships among Theory,Research,and Practice .Evidence-based practice Evidence-based practice np"mnyoourc (三)思考与实践
3 人类行为和社会环境 (human behavior and social environment) 社会福利政策与服务(social welfare and service) 社会工作实务 (practice:knowledge, values, and skills) 研究 research (for need evaluation and impact assessment, 定量 quantitative 和定质 qualitative research) o Social work focus: Person-in-environment Wholeness of person Help people help themselves Practice: “Practice infers action and performance by the social worker. …implies that social workers always are learning from what they do, always open to new insights, and never content to do what they have always done” (Sheafor & Horejsi, 2015, p. xvii). Theory: Theory is “a supposition or a system of ideas intended to explain something, especially one based on general principles independent of the thing to be explained.” (Oxford Dictionaries). o Theories for social work (社会工作支持理论): to understand people and social phenomena and to guide practice with validated frameworks. o Theories of social work(社会工作的理论): to explain the purpose, domain and character of social work within a society. 3. Social work theory and practice Interrelationships among Theory, Research, and Practice Evidence-based practice (三)思考与实践

Reflection on 1.What iss 2 What cial work? theory Why d work practice need theory? (四)教学方法与手段 教学方法:lecturing,group discussion,literature reading 教学手段:multimedia presentation,network-assisted teaching Lecture 2 Social workers'roles and principles (一)教学目的和要求objectives and requirements: 教学目的:elaborate on social workersroles and principles 教学要求:Students should understand the key roles and principles of social workers. (二)教学内容 1.The direct roles of social worker and relevant functions. Cou ment and diagnosis:e.g.using GHQ-12 Social treatr di or behaviors to prot re:stabilize the situation and relieve suffering for severe disability and terminal illness.e.g.hospice care .Teacher o Teaching the clients in interview or workshop o Social and daily living skills(problem solving,self-management,adjustment, communication skills.role skills) o Behavior change(role modeling,value classification,behavior modification) o Primary prevention(self-protection,family planning,parenting skills) o Informed decision (information.advice or insight.possible consequences and alternatives) ·Broker Broker Client Resources ·Advocate oEssential resources and services for clients oImprove a social condition
4 Reflection on 1. What is social work? 2. What is theory? 3. Why does social work practice need theory? (四)教学方法与手段 教学方法:lecturing, group discussion, literature reading 教学手段:multimedia presentation, network-assisted teaching Lecture 2 Social workers’ roles and principles (一)教学目的和要求 objectives and requirements: 教学目的:elaborate on social workers’ roles and principles 教学要求:Students should understand the key roles and principles of social workers. (二)教学内容 1. The direct roles of social worker and relevant functions. Counselor/clinician o Psychosocial assessment and diagnosis: e.g. using GHQ-12 o Social treatment /interventions: change perceptions, attitudes or behaviors to improve social functioning, modify social relationships and solve problems o Social care: stabilize the situation and relieve suffering for severe disability and terminal illness. e.g. hospice care Teacher o Teaching the clients in interview or workshop o Social and daily living skills (problem solving, self-management, adjustment, communication skills, role skills) o Behavior change (role modeling, value classification, behavior modification) o Primary prevention (self-protection, family planning, parenting skills) o Informed decision (information, advice or insight, possible consequences and alternatives) Broker Advocate oEssential resources and services for clients oImprove a social condition

oPrevent a social problem oClients to be their own advocates ·Case manager dentificatior Planning Follow-up Support Coordination 2.The indirect roles of social worker and relevant functions. .Work load manager:Work planning,Time management,Quality review, Information processing per:Orientation and training,Personnel management. nagement,Intemal and external coordination,Policy and agent:Social problem or policy analysis,Mobilization of community concern,S ocial resource Researcher/evaluator:Evaluate existing knowledge /theory.Practice evaluation. Research for Professional:Self-assessment,Personal/professional development,Contribution to the profession and knowledge 3.The principles for social worker Practice social work (social function and conditions) Use consciously of self(passion,commitment,personality,capacity,skill,value, belief,behavior,etc.) Maintain professional objectivity (controlled emotional involvement) Embrace human diversity (sensitivity and no stereotypes) .Adopt people-first thinking(personhood before symptoms) Challenge social injustices .Enhance professional competence(know more and keep updated) ork tice m(m m ethical method,beh -ha pract dence from web resources olle etc.) relev value and ethic (right vs.wr ong) Address all relevant client systems (whole person.SWOT.environment) Serve the most vulnerable
5 oPrevent a social problem oClients to be their own advocates Case manager 2. The indirect roles of social worker and relevant functions. Work load manager: Work planning, Time management, Quality review, Information processing, Supervisor/staff developer: Orientation and training, Personnel management, Supervision, Consultation Administrator: Management, Internal and external coordination, Policy and program development Social change agent: Social problem or policy analysis, Mobilization of community concern, Social resource development Researcher/evaluator: Evaluate existing knowledge / theory, Practice evaluation, Research for development Professional: Self-assessment, Personal/ professional development, Contribution to the profession and knowledge 3. The principles for social worker Practice social work (social function and conditions) Use consciously of self (passion, commitment, personality, capacity, skill, value, belief, behavior, etc.) Maintain professional objectivity (controlled emotional involvement) Embrace human diversity (sensitivity and no stereotypes) Adopt people-first thinking (personhood before symptoms) Challenge social injustices Enhance professional competence (know more and keep updated) 4. The principles for social work practice Do no harm (minimize mistakes in ethical, method, behavior, etc.) Engage in evidence-based practice (evidence from literature, web resources, professional conferences, colleagues, etc.) Be guided by relevant value and ethics (right vs. wrong) Address all relevant client systems (whole person, SWOT, environment) Serve the most vulnerable

·lnd e the client:unique needs,capacity.limitation,experience at here and reat clients as the expert oftheir own lives(information source) Lend vision to the client(whether,what and how to change) Build on client strengths (positive thinking,potential not problem) Maximize client participation (do with not to or for the client) Maximize client self-determination (with no harm) Help the client learn self-directed problem-solving skills (for future) Empower the client (with belief,information,resource,skill,etc. Protect client confidentiality (relative,on ethics,law,policy) Adhere to the philosophy of normalization (integration) Keep evaluating the progress of the change process Be accountable to clients,agency,community and profession (三)思考与实践 What are the possible roles and practice principles of a hospital social worker in preventi 教学方法:lecturing,case study,group discussion and presentation,literature reading 教学手段:multimedia presentation,network-assisted teaching Lectures 3-5 Practice Frameworks for Social Work (一)教学目的和要求objectives and requirements:: 教学目的:introduce the contents and application of established social work practice frameworks 教学a要求:Students should understand the key points of these practice frameworks and link them with real social problems. (二)教学内容 通才视角Generalist perspectives Who Client(system):individual or group What Problem/purpose:multiple and interrelated Where- Context/background:diverse When .Circumstances:diverse Phase:beginning(assessment) Change target:client or environment How le,esp.case manager Skill of SW:versatile 6
6 Treat the client with dignity, acceptance, respect Individualize the client: unique needs, capacity, limitation, experience at here and now Treat clients as the expert of their own lives (information source) Lend vision to the client (whether, what and how to change) Build on client strengths (positive thinking, potential not problem) Maximize client participation (do with not to or for the client) Maximize client self-determination (with no harm) Help the client learn self-directed problem-solving skills (for future) Empower the client (with belief, information, resource, skill, etc. ) Protect client confidentiality (relative, on ethics, law, policy) Adhere to the philosophy of normalization (integration) Keep evaluating the progress of the change process Be accountable to clients, agency, community and profession. (三)思考与实践 What are the possible roles and practice principles of a hospital social worker in preventing the tragedy of the jumped mother-to-be in Shannxi? (四)教学方法与手段 教学方法:lecturing, case study, group discussion and presentation, literature reading 教学手段:multimedia presentation, network-assisted teaching Lectures 3-5 Practice Frameworks for Social Work (一)教学目的和要求 objectives and requirements: 教学目的:introduce the contents and application of established social work practice frameworks 教学要求:Students should understand the key points of these practice frameworks and link them with real social problems. (二)教学内容 通才视角 Generalist perspectives

生态系统视角ecosystems perspective Who Client(system):person in environment What Problem/purpose:adaptive capacity of people, environmental obstacles,survival in competition Where .Context/background:supra-,focal,sub-system When ange target:focal system(inter ersonal level) How Role of SW: .Skill of SW:Define and work with the focal system 优势视角strengths perspective Who .Client(system):individual or group What Problem/purpose:identify and build on strength. Where Context/background:no limitation Wher :oan8aete How ange laboration with the client Skill of SW: 民族敏感视角Ethnic--sensitive perspective Who .Client(system):individual or group What 8pee2urpoedsa0vanage.dscmrnaion Where ethnicity,culture,religion Circu mstances:disadvantage,discrimination. When oppression. ·Phase:al How n Role of SW: ultiple ought,behavior,and values Skill of SW:cultural competence,self-awareness
7 生态系统视角 ecosystems perspective 优势视角 strengths perspective 民族敏感视角 Ethnic-sensitive perspective

女性主义视角Feminist perspective Who .Client(system):women What Problem/purpose:oppression and exploitation of Where Context/background:male-dominant society When ·8msammseeahps.marmeoe Phase:all,esp.problem definition and assessment How Role of SW:multiple,teacher,advocate,partner. iof SW:empowerment.political action and 行为理论Behavior theory Who Client(system):individual,couple,family,organization What Where Context/background:residential and mandated setting When Phase:intervention and monitoring Change target observable behavior Media of change:treatment (reinforce/punish) How Role of SW:clinician,teacher... 认知行为Cognitive-behavioral theory Who .Client(system):individual,couple,family,organization What Where :Cigs2gaentwihcogntvecapaecyand When et Change target:one's belief/thought/interpretation How Media of change:intervention Role of SW: clinician,teacher Skill of SW:discussion,teaching,behavioral experiment
8 女性主义视角 Feminist perspective 行为理论 Behavior theory 认知行为 Cognitive-behavioral theory
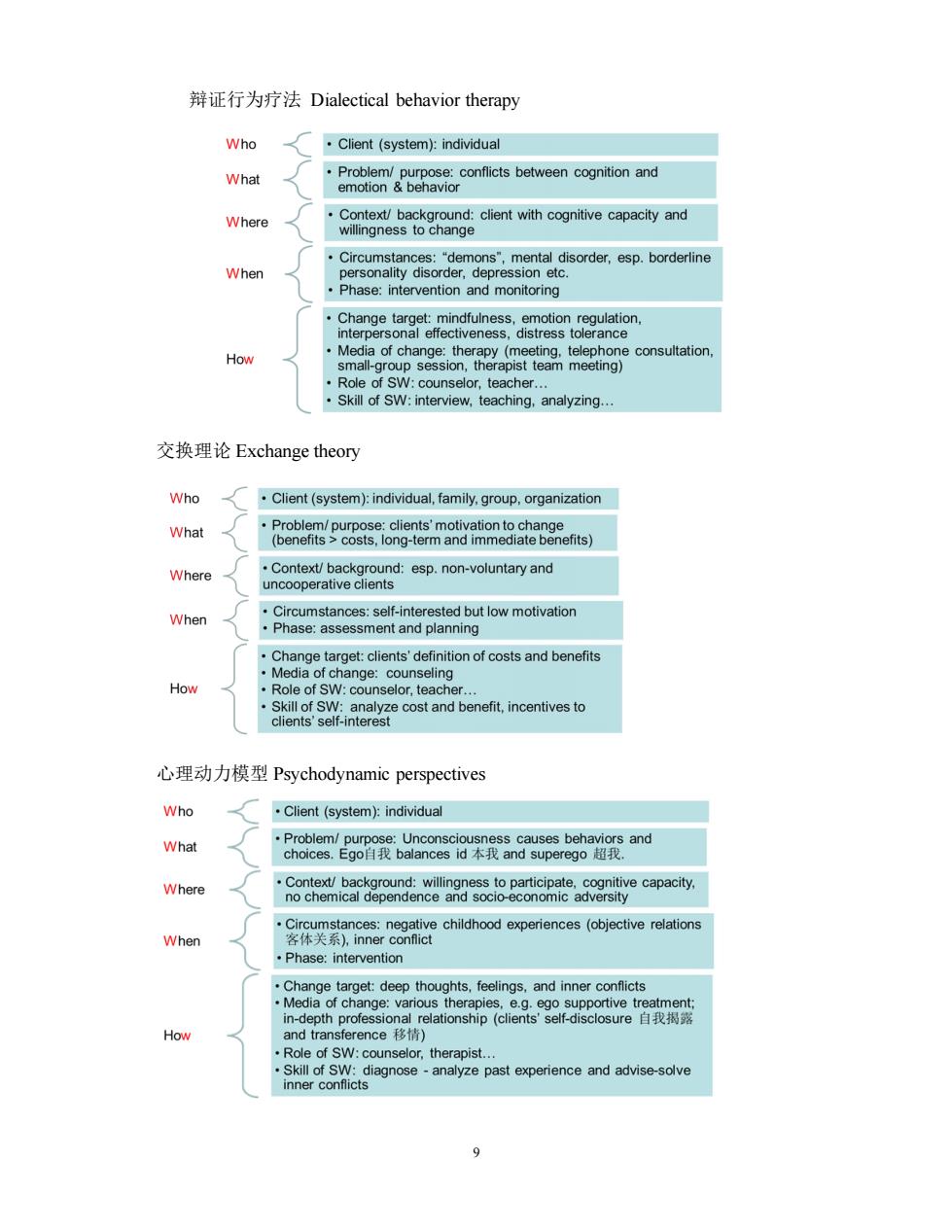
辩证行为疗法Dialectical behavior therapy Who Client (system):individual What conflicts between cognition anc Where client with cognitive capacity and When Phase:intervention and monitoring How e consultation ching.analyzing. 交换理论Exchange theory Who .Client(system):individual,family.group,organization What Where When How Role of SW:counseor,teacher 心理动力模型Psychodynamic perspectives Who Client(system):individual What Where When Phase:intervention .Ch How and transference移情) nmercocgiagnose analyze pas experience and advise-solve
9 辩证行为疗法 Dialectical behavior therapy 交换理论 Exchange theory 心理动力模型 Psychodynamic perspectives

危机千预Crisis intervention Who Client (system):individual What Where Cpeybackgrountwingnessiopatcpaacogntve When 96ee8eng6mcgrngeant8c8s,byomaka How tional first aid kill of W:advice,guidance (quick and frequent),seek suppor 创伤干f预Trauma-related interventions Who Client(system):individua What Where Context/background:willingness to participate.cognitive capacity caused s:trauma ( When Phase:intervention Change target:disturbing 性应 How o/therapist with special training Skill of SW:counseling 心理教育Psychoeducation model Who Client(system):individual and family What Where. :Cpgeybacgoundtwngnestoparicpale,cogntve circu When .Change target:anxiety.worry.misunderstanding.coping How Role of SW: 8ac8rucationsesions Skill of SW:information preparation and teaching
10 危机干预 Crisis intervention 创伤干预 Trauma-related interventions 心理教育 Psychoeducation model