
《国际贸易》课程教学大纲(英文) 一、课程基本信息 课程代码:18060223 课程名称:国际贸易 英文名称:International Trade 课程类别:学科基础课 时,48学时 分:3学分 适用对象:国际经济与贸易专业本科生/国际商务专业本科生 若核方式:考试 先修课程:微观经济学、宏观经济学 二、课程简介 中文简介:本课程主要介绍国际经济学中的微观部分,是我国高等院校经济 管理类本科专业的必修课程之一,注重介绍国际贸易理论的基本思想与开放条件 下微观经济分析的初步方法。主要内容包括:国际贸易的基本理论及其发展动态, 国际贸易政策及其效应分析,要素流动的产生原因及其对各国生产、消费以及社 会福利的影响等:不同条件下的贸易模式:国际贸易政策与产业政策分析:国际 经济发展中的主要现实问题等,旨在帮助学生理解开放的经济世界并掌握开放条 件下进行微视经济分新的基本方法。 Course Description:This course introduces to undergraduate students the microeconomic section of International Economics,including the theory of international trade and trade policy,factors nd it is one of n maio courses the students majoring in Economics and Management must master in ou senior education with emphasis on fundamental theory and analysis tools of international trade.The main topics include:causes of international trade and factor movements.and their effect on production.consumption and social welfare of trading countries;the determinants of trade pattern;the analysis of trade and ies the development of interna tion trade practice aiming to help students to know the real economy world and grasp the basic methods of microeconomics to analyze reality in the open economy condition. 三、课程性质与教学目的 课程性质:国际贸易是我国高等院校经济管理类本科专业的必修课。经济全 球化和我国加入WT0的现实,使经管类学生认识了解和掌握国际贸易的基本到 论、基本知识和基本政策尤显重要。本课程面向国际经济与贸易专业学生,课程 类别为经济学科基础课。 教学目的:(1)系统学习国际贸易理论、区域经济一体化、国际贸易政策 及GATT和WTO等基础知识,掌握分析国际贸易和相关问题的基本方法:(2) 能运用所学的基本原理和方法分析国际经济和国际贸易中的现实问题 (3)跟 踪当前国际经济特别是国际贸易领域的最新动态和发展变化趋势,比如中美贸 易战等,进一步拓展能力,提高综合运用水平
1 《国际贸易》课程教学大纲 (英文) 一、课程基本信息 课程代码:18060223 课程名称:国际贸易 英文名称:International Trade 课程类别:学科基础课 学 时:48 学时 学 分:3 学分 适用对象:国际经济与贸易专业本科生 / 国际商务专业本科生 考核方式:考试 先修课程:微观经济学、宏观经济学 二、课程简介 中文简介:本课程主要介绍国际经济学中的微观部分,是我国高等院校经济 管理类本科专业的必修课程之一,注重介绍国际贸易理论的基本思想与开放条件 下微观经济分析的初步方法。主要内容包括:国际贸易的基本理论及其发展动态, 国际贸易政策及其效应分析,要素流动的产生原因及其对各国生产、消费以及社 会福利的影响等;不同条件下的贸易模式;国际贸易政策与产业政策分析;国际 经济发展中的主要现实问题等,旨在帮助学生理解开放的经济世界并掌握开放条 件下进行微观经济分析的基本方法。 Course Description:This course introduces to undergraduate students the microeconomic section of International Economics, including the theory of international trade and trade policy, factors movements, and it is one of major courses the students majoring in Economics and Management must master in our senior education with emphasis on fundamental theory and analysis tools of international trade. The main topics include:causes of international trade and factor movements, and their effect on production, consumption and social welfare of trading countries; the determinants of trade pattern; the analysis of trade and industry policies; the development of international trade practice, aiming to help students to know the real economy world and grasp the basic methods of microeconomics to analyze reality in the open economy condition. 三、课程性质与教学目的 课程性质:国际贸易是我国高等院校经济管理类本科专业的必修课。经济全 球化和我国加入 WTO 的现实,使经管类学生认识了解和掌握国际贸易的基本理 论、基本知识和基本政策尤显重要。本课程面向国际经济与贸易专业学生,课程 类别为经济学科基础课。 教学目的:(1)系统学习国际贸易理论、区域经济一体化、国际贸易政策 及 GATT 和 WTO 等基础知识,掌握分析国际贸易和相关问题的基本方法;(2) 能运用所学的基本原理和方法分析国际经济和国际贸易中的现实问题;(3)跟 踪当前国际经济特别是国际贸易领域的最新动态和发展变化趋势,比如中美贸 易战等,进一步拓展能力,提高综合运用水平

四、教学内容 Chapter 1:Introduction 1.1 Importance of International Ecconomics 1.2 International trade and the National Standard of Living 1.3 The Subiect Matter of International Economics 1.4 Purpose of nternationalEconomic and Policie 1.Current Problems in the Field of nterational Trade 1.5A Trade Protectionism in Industrial Countries (Curriculum ideology:Discuss the causes of trade disputes between China and United States,so that students should understand the international economic situation and establish a correct world outlook) 1.5B High Structural Unemployment and Slow Growth in Europe and Stagnation in Japan 1.5CJob Insecurity from Restructuring and Downsizing in U.S. 1.5D Restructuring Problems of Transition Economies Chapter 2:The Law of Comparative Advantage 2 1 Introdiction:Brief outline of the Law 2.2The Mercan'sViewn Trade:the History 2.3 Trade Basis on Absolute Advantage:View of Absolute Advantage by Adam Smith,Illustratior of Absolute Advantage 2.4 Trade Based on Comparative Advantage:David Ricardo 2.4A The Law of Comparative Advantage:Tables,Figures and Examples 2.4B The Gains from Trade 2.4C Exception to the Law of Compa ative Advantage 2.4D Comparative Advantage with Money 2.5 Comparative Advantage and Opportunity Costs 2.5A Comparative Advantage and the labour Theory of value 2.5B The Opportunity Cost Theory 2.CThe Production Possibility Frontier under Constant Costs 2.5D Opportunity Costs and Relative Commodity Prices 2.6 The Basis for and the Gains From TradeUnder Costant Costs 2.6A Illustration of the Gains from Trade 2.6B Relative Commodity Prices with Trade Chapter 3:The Standard Theory of International Trade 3.1Introduction 3.2 The Production Possibility Frontier with Increasing Costs 3.2A lllustration of Increasing Coasts 3.2B The Marginal Rate of Transformation 2
2 四、教学内容 Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1 Importance of International Ecconomics 1.2 International trade and the National Standard of Living 1.3 The Subject Matter of International Economics 1.4 Purpose of International Economic and Policies 1.5 Current Problems in the Field of International Trade 1.5A Trade Protectionism in Industrial Countries (Curriculum ideology:Discuss the causes of trade disputes between China and United States,so that students should understand the international economic situation and establish a correct world outlook) 1.5B High Structural Unemployment and Slow Growth in Europe and Stagnation in Japan 1.5C Job Insecurity from Restructuring and Downsizing in U.S. 1.5D Restructuring Problems of Transition Economies Chapter 2: The Law of Comparative Advantage 2.1 Introdiction: Brief Outline of the Law 2.2 The Mercantilism’s View on Trade: Case Study and Illustration, recalling of the History 2.3 Trade Basis on Absolute Advantage: View of Absolute Advantage by Adam Smith, Illustration of Absolute Advantage 2.4 Trade Based on Comparative Advantage: David Ricardo 2.4A The Law of Comparative Advantage: Tables, Figures and Examples 2.4B The Gains from Trade 2.4C Exception to the Law of Comparative Advantage 2.4D Comparative Advantage with Money 2.5 Comparative Advantage and Opportunity Costs 2.5A Comparative Advantage and the Labour Theory of Value 2.5B The Opportunity Cost Theory 2.5C The Production Possibility Frontier under Constant Costs 2.5D Opportunity Costs and Relative Commodity Prices 2.6 The Basis for and the Gains From Trade Under Costant Costs 2.6A Illustration of the Gains from Trade 2.6B Relative Commodity Prices with Trade Chapter 3: The Standard Theory of International Trade 3.1 Introduction 3.2 The Production Possibility Frontier with Increasing Costs 3.2A Illustration of Increasing Coasts 3.2B The Marginal Rate of Transformation

3.2C Reasons for Increasing Costs and Different Production Frontier 3.3 Community Indifference Curve 3.3C Some difficulties with Community Indifference Curve 3.4 Equilibrium InIsolation 3.4A Illustration of Equilibrium In Isolation 3.4B Equilibrium Relative Commodity PricesandC 3.5 The Basis for and the Gains from Trade with Increasing Costs 3.5A Illustration 3.5B Equilibrium-Relative Commodity Prices with Trade 3.5C Incomplete Specilization 3.5D Small-Country Case with Increasing Costs 3.SE The Gains fro m Exch e an from Specialization 3.6 Trade Basedon Difference in Taste 3.6A Illustration of Trade Basedon Difference in Taste 3.6B Case study Chapter 4:Demand and Supply,Offer Curve,and the Terms of Trade 4.1Introduction 4.2 Equilibrium-Relative Commodity Prices with Trade-Partial Equilibrium Analysis 4.3 Offer Curve:Case Stuudy and the Derivation of Offer Curve 4.4 Equilibrium-Relative Commodity Prices with Trade-General Equilibrium Analysis 4.6Tems of Trade 4.6A Difinition and Measurement of the Terms of Trade 4.6B Illustration of Terms of Trade 4.6C Usefulness of the Model and Case Study Chapter 5:Factor Endowment and the Heckscher-Ohlin Theory 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Assumption of the Theory 5.3 Factor Intensity,Factor Abundence,and the Shape of the Production Frontier 5.4 Factor Edowment and the Heckscher-Ohlin Theor 5.4AThe Heckscher-Ohi 5.4B General Equilibrium Framwork of the Heckscher-Ohlin Theory 5.4C Illustration of Heckscher-Ohlin Theory 5.5 Factor-Price Equalization and Income Distribution 5.5B Relativeand Abs e Factor-Price E 5.5C Effects of Trade on the Distribution of Income 5.5D The Specific-Factor Model 5.5E Empirical Relevance
3 3.2C Reasons for Increasing Costs and Different Production Frontier 3.3 Community Indifference Curve 3.3A Illustration of Community Indifference Curve 3.3B The Marginal Rate of Substitution 3.3C Some difficulties with Community Indifference Curve 3.4 Equilibrium In Isolation 3.4A Illustration of Equilibrium In Isolation 3.4B Equilibrium Relative Commodity Prices and Comparative Advantage 3.5 The Basis for and the Gains from Trade with Increasing Costs 3.5A Illustration 3.5B Equilibrium-Relative Commodity Prices with Trade 3.5C Incomplete Specilization 3.5D Small-Country Case with Increasing Costs 3.5E The Gains from Exchange and from Specialization 3.6 Trade Based on Difference in Taste 3.6A Illustration of Trade Based on Difference in Taste 3.6B Case study Chapter 4: Demand and Supply, Offer Curve, and the Terms of Trade 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Equilibrium-Relative Commodity Prices with Trade---Partial Equilibrium Analysis 4.3 Offer Curve: Case Stuudy and the Derivation of Offer Curve 4.4 Equilibrium-Relative Commodity Prices with Trade---General Equilibrium Analysis 4.6 Terms of Trade 4.6A Difinition and Measurement of the Terms of Trade 4.6B Illustration of Terms of Trade 4.6C Usefulness of the Model and Case Study Chapter 5: Factor Endowment and the Heckscher-Ohlin Theory 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Assumption of the Theory 5.3 Factor Intensity, Factor Abundence, and the Shape of the Production Frontier 5.4 Factor Edowment and the Heckscher-Ohlin Theory 5.4A The Heckscher-Ohlin Theorem 5.4B General Equilibrium Framwork of the Heckscher-Ohlin Theory 5.4C Illustration of Heckscher-Ohlin Theory 5.5 Factor-Price Equalization and Income Distribution 5.5A The Factor-Price Equalization Theorem 5.5B Relative and Absolute Factor-Price Equalization 5.5C Effects of Trade on the Distribution of Income 5.5D The Specific-Factor Model 5.5E Empirical Relevance

5.6 Empirical Tests of the Heckscher-Oblin Model 5.6A Empirical Results-The Leontief Paradox 5.6B Explanatio ons of t the Leontief Paradoxand CaseStudy 5.6C Factor Intensity Reversa Chapter 6:Economies of Scale,Imperfect Competition,and Interational Trade 6.1 Introduction 6.2 The Heckscher-Ohlin Model and New Trade Theories 6.3 The Economies of Scale and InterationalTrade 6.4 Imperfect Competition and Inte 6.4B Measuring Intra-Industry Trade 6.4C Formal Model of Intra-Industry Trade 6.4D Another Version of the Intra-Industry Trade 66c sts of Tra ansp tation,Envi ntal s Standard,and International Trade 6.6A Transportation Costsand Non-traded Commodities 6.6B Costs of Transportation and the Location of Industry 6.6C Environmental Standard,Industry Location and International Trade Chapter 7:Economic Growth and International Trade 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Growth of Factors of Production 7.2A Labour Growth and Capital Accumulation Over Time 7.3Techn cal Progress 7.3A Neutral,Labour-Saving and Capital-Saving Technical Progress 7.3B Technical Progress and the Nation's Production frontier 7 4 Growth and trade:The small Country case 7.4A The Effects of Growth on trade Growth,Trade and Welfare 7.4C Technical Progress,Trade,and Welfare 7.5 Growth and Trade:The Large Country Case 7.5A Growth and the Nation's Terms of Trade and Welfare 7 58 Immiserizing Growth 7.5Cllustration of Benificial Growth and Trade 7.6Growth,Change in Tastes,and Tradein Both Nations 7.6A Growth and Trade in Both Nations 7.6B Changein Tastes and Trade in Both Nations
4 5.6 Empirical Tests of the Heckscher-Ohlin Model 5.6A Empirical Results----The Leontief Paradox 5.6B Explanations of the Leontief Paradox and Case Study 5.6C Factor Intensity Reversal Chapter 6: Economies of Scale, Imperfect Competition, and Interational Trade 6.1 Introduction 6.2 The Heckscher-Ohlin Model and New Trade Theories 6.3 The Economies of Scale and Interational Trade 6.4 Imperfect Competition and Interational Trade 6.4A Trade Based on Products Differentiation 6.4B Measuring Intra-Industry Trade 6.4C Formal Model of Intra-Industry Trade 6.4D Another Version of the Intra-Industry Trade 6.5 Trade Based on Dynamic Techological Difference 6.6 Costs of Transportation, Environmental Standard, and International Trade 6.6A Transportation Costs and Non-traded Commodities 6.6B Costs of Transportation and the Location of Industry 6.6C Environmental Standard, Industry Location and International Trade Chapter 7: Economic Growth and International Trade 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Growth of Factors of Production 7.2A Labour Growth and Capital Accumulation Over Time 7.2B The Rybczynski Theorem 7.3 Technical Progress 7.3A Neutral, Labour-Saving and Capital-Saving Technical Progress 7.3B Technical Progress and the Nation’s Production Frontier 7.4 Growth and Trade: The Small Country Case 7.4A The Effects of Growth on Trade 7.4B Illustration of Factor Growth, Trade and Welfare 7.4C Technical Progress, Trade, and Welfare 7.5 Growth and Trade: The Large Country Case 7.5A Growth and the Nation’s Terms of Trade and Welfare 7.5B Immiserizing Growth 7.5C Illustration of Benificial Growth and Trade 7.6 Growth, Change in Tastes,and Trade in Both Nations 7.6A Growth and Trade in Both Nations 7.6B Change in Tastes and Trade in Both Nations

Chapter 8:Trade Restrictions:Tariffs .Analysis of a Tarri 8.3 The Theory of Tarrif Structure 8.3A The Rate of Effective Protection 8.3B Generalization and Evolution of the Theory of Effective Protection 8.General Equilibrium Analysis of Small Country 8.4B Illustration of the Effects of a Tarrif in a Small Country 8.4C The Stolper-Samuelson Theorem 8.5 General Equilibrium Analysis of a Tarrif in a Large Country 8.5A General Equilibrium Effects of a Tarrif in a Large Country of the fffects of a tarrif in a Large t 8.6The Optimum Tarrif 8.6A The Meaning of the Concept of Optimum Tarrif and Retaliatior 8.68 lllustration of the optimum Tarrif and Retaliation (Curriculum ideo ogy:Taking trade-war between Us and other tries as a example,let students understand th es唱n eof our tra further open up) Chapter 9:Nontariff Trade Barriers and the New Protectionism 91Introduction 9.2 Import Quotas 9.2B Comparison of an Import Quota to an Import Tarrift 9.3 Other Nontariff Barriers and the New Protectionism 9.3A Voluntary Export Restraints 9.3B Technical,Administrative and Other Regulations ational cartels 9.3D Dumping 9.3E Export Subsidies 9.4 The Political Economy of Protectionism 9.4A Fallacious and Questionable Aguments for Protection 9.4B The Infant-Industryand Other Qualified Arguments for Protection 9.4CWho Gets Protected? 9.5 StrategicTradeand Industrial Policies 9.5A Strategic Trade Policy 9.5B Strategic Trade and Industrial Policies with Game Theory 9.5CThe U.S.Responseto Fore gnndustrial Targetingand StrategicTrade Policy 9.6History of U.S.Commercial Polic 9.7The Uruguay Round and Outstanding Trade Problems Chapter 10:Economic Integration:Customs Unions and Free Trade 5
5 Chapter 8: Trade Restrictions: Tariffs 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Partial Equilibrium Analysis of a Tarrif 8.3 The Theory of Tarrif Structure 8.3A The Rate of Effective Protection 8.3B Generalization and Evolution of the Theory of Effective Protection 8.4 General Equilibrium Analysis of a Tarrif in a Small Country 8.4A General Equilibrium Effects of a Tarrif in a Small Country 8.4B Illustration of the Effects of a Tarrif in a Small Country 8.4C The Stolper-Samuelson Theorem 8.5 General Equilibrium Analysis of a Tarrif in a Large Country 8.5A General Equilibrium Effects of a Tarrif in a Large Country 8.5B Illustration of the Effects of a Tarrif in a Large Country 8.6 The Optimum Tarrif 8.6A The Meaning of the Concept of Optimum Tarrif and Retaliation 8.6B Illustration of the Optimum Tarrif and Retaliation (Curriculum ideology:Taking trade-war between US and other countries as a example, let students understand the significance of our trade policies to further open up) Chapter 9: Nontariff Trade Barriers and the New Protectionism 9.1 Introduction 9.2 Import Quotas 9.2A Effects of an Import Quotas 9.2B Comparison of an Import Quota to an Import Tarriff 9.3 Other Nontariff Barriers and the New Protectionism 9.3A Voluntary Export Restraints 9.3B Technical, Administrative and Other Regulations 9.3C International Cartels 9.3D Dumping 9.3E Export Subsidies 9.4 The Political Economy of Protectionism 9.4A Fallacious and Questionable Aguments for Protection 9.4B The Infant-Industry and Other Qualified Arguments for Protection 9.4 C Who Gets Protected? 9.5 Strategic Trade and Industrial Policies 9.5A Strategic Trade Policy 9.5B Strategic Trade and Industrial Policies with Game Theory 9.5C The U.S. Response to Foreign Industrial Targeting and Strategic Trade Policy 9.6 History of U.S. Commercial Policy 9.7 The Uruguay Round and Outstanding Trade Problems Chapter 10: Economic Integration: Customs Unions and Free Trade

Areas 10.2 Trade-Creating Customs Unions 10.3 Trade-Diverting Customs Unions 10.4 The Theory of the Second Best and Other Static Welfare Effects of Customs Unions 10.4A The Theory of the Second Best 10.B Conditi ns More Likely to Lead toncreased Welfare 10.4COther Static Welfare Effects of Customs Unions 10.5 Dynamic Benefits from Customs Unions (Curriculum ideology:Introduce the formation of the RECP let students understand the significance of our trade policies to further open up and seeking the optimal allocation of lobalres 10.6 E A History o empts at Economic Integration Chapter 11:International Trade and Economic Development 11 2 The mportance of Trade to Developmen 11.2A Trade Theory and Economic Development 11.2B Trade as an Engine of Growth 11.2C The Controbution of Trade to Development 11.2D International Trade and Endog 11.3 The Te s of Trade and Ec 11.3A The Various Terms of Trade 11.3B Alleged Reasons for Deterioration in the Commodity Terms of Trade 11.3C Historical Movement in the Commodity and Income Terms of Trade 11.4 Export Instability and Economic Development 11.4A Causeand Effects of Export Instability 11.4B Measurement of Export nstabilityand t Effectson Developmen 11.4C International Commodity Agreements 11.5 Import Subtitution versus Export Orientation 11.5A Developmet Through Import Subtitution versus Exports 11.5B The Expe rience with Import Subtitution 11.5CRecen n and Growth in Developing Countries 116 Current Problems Facing Developing Countries 11.6A Poverty in Developing Countries 11.6B The Foreign Debt Problems of Developing Countries 11.6C Trade Problems of Developing Countries Chapter 12:International Resources Movements and Multinational Corportions
6 Areas 10.1 Introduction 10.2 Trade-Creating Customs Unions 10.3 Trade-Diverting Customs Unions 10.4 The Theory of the Second Best and Other Static Welfare Effects of Customs Unions 10.4A The Theory of the Second Best 10.4B Conditions More Likely to Lead to Increased Welfare 10.4C Other Static Welfare Effects of Customs Unions 10.5 Dynamic Benefitsfrom Customs Unions (Curriculum ideology:Introduce the formation of the RECP, let students understand the significance of our trade policies to further open up and seeking the optimal allocation of global resources) 10.6 History of Attempts at Economic Integration Chapter 11: International Trade and Economic Development 11.1 Introduction 11.2 The Importance of Trade to Development 11.2A Trade Theory and Economic Development 11.2B Trade as an Engine of Growth 11.2C The Controbution of Trade to Development 11.2D International Trade and Endogenous Growth Theory 11.3 The Terms of Trade and Economic Development 11.3A The Various Terms of Trade 11.3B Alleged Reasons for Deterioration in the Commodity Terms of Trade 11.3C Historical Movement in the Commodity and Income Terms of Trade 11.4 Export Instability and Economic Development 11.4A Cause and Effects of Export Instability 11.4B Measurement of Export Instability and Its Effects on Development 11.4C International Commodity Agreements 11.5 Import Subtitution versus Export Orientation 11.5A Developmet Through Import Subtitution versus Exports 11.5B The Experience with Import Subtitution 11.5C Recent Trade Liberalization and Growth in Developing Countries 11.6 Current Problems Facing Developing Countries 11.6A Poverty in Developing Countries 11.6B The Foreign Debt Problems of Developing Countries 11.6C Trade Problems of Developing Countries Chapter 12: International Resources Movements and Multinational Corportions
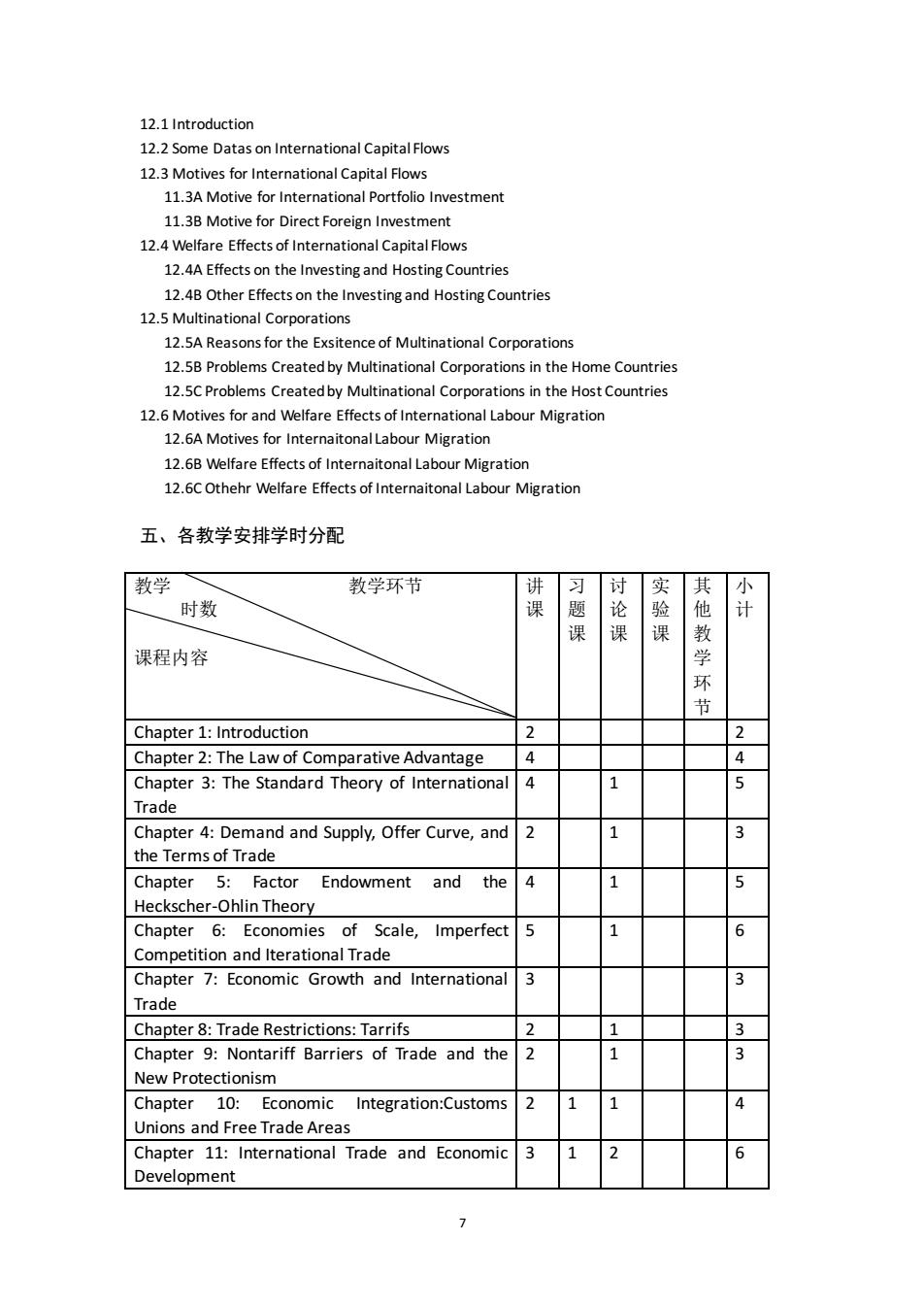
12.1Introduction 12.2 Some Datas on International Capital Flows tive for International Portfolio Investment 11.3B Motive for Direct Foreign Investment 12.4 Welfare Effects of International CapitalFlows 12.4A Effects on the Investing and Hosting Countries 12.4B Other Effectson the Investing and Hosting Countries 12.5M tinational Corporations 12.5A Reasons for the Exsitence of Multinational Corporations 12.5B Problems Created by Multinational Corporations in the Home Countries 12.5C Problems Createdby Multinational Corporations in the Host Countries 12.6 Motives for and Welfare Effects of International Labour Migration 12.6A Motives for Inte naitonalLabour Migration 12.B Welfare Effects of Internaitonal Labour Migration 12.6C Othehr Welfare Effects of Internaitonal Labour Migration 五、各教学安排学时分配 教学 教学环节 习讨 时数 计 课课课 课程内容 学 环 Chapter 1:Introduction 2 Chapter 2:The Law of Comparative Advantage 4 4 Chapter 3:The Standard T neory of International Trad Chapter 4:Demand and Supply,Offer Curve,and 2 3 the Terms of Trade Chapter 5:Factor Endowment and the 5 Heckscher-Ohlin Theory Chapter 6:Economies of Scale,Imperfect 5 1 6 Competition and iterational Trade Chapter 7:Economic Growth and International 3 3 Trade Chapter 8:Trade Restrictions:Tarrifs 2 3 Chapter 9:Nontariff Barriers of trade and the I 2 1 3 New Protectionism Chapter 10:Fconomic Integration:Customs 4 Unions and Free Trade Area Chapter 11:International Trade and Economic Development
7 12.1 Introduction 12.2 Some Datas on International Capital Flows 12.3 Motives for International Capital Flows 11.3A Motive for International Portfolio Investment 11.3B Motive for Direct Foreign Investment 12.4 Welfare Effects of International Capital Flows 12.4A Effects on the Investing and Hosting Countries 12.4B Other Effects on the Investing and Hosting Countries 12.5 Multinational Corporations 12.5A Reasons for the Exsitence of Multinational Corporations 12.5B Problems Created by Multinational Corporations in the Home Countries 12.5C Problems Created by Multinational Corporations in the Host Countries 12.6 Motives for and Welfare Effects of International Labour Migration 12.6A Motives for Internaitonal Labour Migration 12.6B Welfare Effects of Internaitonal Labour Migration 12.6C Othehr Welfare Effects of Internaitonal Labour Migration 五、各教学安排学时分配 教学 教学环节 时数 课程内容 讲 课 习 题 课 讨 论 课 实 验 课 其 他 教 学 环 节 小 计 Chapter 1: Introduction 2 2 Chapter 2: The Law of Comparative Advantage 4 4 Chapter 3: The Standard Theory of International Trade 4 1 5 Chapter 4: Demand and Supply, Offer Curve, and the Terms of Trade 2 1 3 Chapter 5: Factor Endowment and the Heckscher-Ohlin Theory 4 1 5 Chapter 6: Economies of Scale, Imperfect Competition and Iterational Trade 5 1 6 Chapter 7: Economic Growth and International Trade 3 3 Chapter 8: Trade Restrictions: Tarrifs 2 1 3 Chapter 9: Nontariff Barriers of Trade and the New Protectionism 2 1 3 Chapter 10: Economic Integration:Customs Unions and Free Trade Areas 2 1 1 4 Chapter 11: International Trade and Economic Development 3 1 2 6

Mid-term Test,Overall Reviewing,examination or 4 4 Depending 合 计 3729 48 六、指定教材和教学参考教材 指定教材:(美)Dominick Salvatore著:《国际经济学》(英文版),北京: 清华大学出版社,2015年版 教学参考教材: 1.Paul Krugman,Maurice Obstfeld,International Economics:Theory and Policy (9th Edition):Addison Wesley Longman,2013 2.Paul Krugman and Maurice Obstfeld,International Economics:Theory and Policy,5th Edition,Addison-Wesley,2000 (the ChineseVersion,China Remin University Press,2002 3.中共中央宜传部,习近平新时代中国特色社会主义思想三十讲,学习出 版社,2018年5月 4.习近平,习近平谈治国理政(全三套),外文出版社,2017年11月: 5.海闻、P林德特、王新奎:《国际贸易》,格致出版社,2012年: 6.薛荣久主编:《国际贸易(第6版)》,对外经济贸易大学出版社,2016 年版 .胡涵钧主编:《新编国际贸易(第2版)》,上海:复旦大学出版社, 2010年版: 推荐阅读期刊: 《国际贸易》、《国际贸易问题》、《世界经济》、《国际经贸探索》、《国际 经济评论》 《国际经济合作》 《国际贸易论坛》等 大纲修订人:陈燕、刘娟 修订日期:2020/12/6 大纲审定人: 审定日期:
8 Mid-term Test, Overall Reviewing, examination or Depending 4 4 合 计 37 2 9 48 六、指定教材和教学参考教材 指定教材:(美)Dominick Salvatore 著:《国际经济学》(英文版),北京: 清华大学出版社,2015 年版 教学参考教材: 1. Paul Krugman, Maurice Obstfeld,International Economics:Theory and Policy (9th Edition); Addison Wesley Longman,2013 2. Paul Krugman and Maurice Obstfeld, International Economics: Theory and Policy, 5th Edition, Addison-Wesley, 2000 (the ChineseVersion, China Remin University Press, 2002; 3. 中共中央宣传部,习近平新时代中国特色社会主义思想三十讲,学习出 版社,2018 年 5 月 4. 习近平,习近平谈治国理政(全三套),外文出版社,2017 年 11 月; 5. 海闻、P.林德特、王新奎:《国际贸易》,格致出版社,2012 年; 6. 薛荣久主编:《国际贸易(第 6 版)》,对外经济贸易大学出版社,2016 年版; 7. 胡涵钧主编:《新编国际贸易(第 2 版)》,上海:复旦大学出版社, 2010 年版; 推荐阅读期刊: 《国际贸易》、《国际贸易问题》、《世界经济》、《国际经贸探索》、《国际 经济评论》、《国际经济合作》、《国际贸易论坛》等 大纲修订人:陈燕、刘娟 修订日期:2020/12/6 大纲审定人: 审定日期: