
第二单元 空气环境与健豪

第一部分 空气的物理性状及其卫生学意义

空气的物理性状及其卫生学意义 ■一、大气圈及大气垂直结构 ■二、太阳辐射 ■三、气象因素 ■四、空气离子化 ■五、室内空气物理性状及其对健康的影响

教学目的要求 了解空气物理性状的概念及强度单位,掌握其卫生学意义 掌握室内微小气候的评价指标: 本部分重点: 气温垂直分布及其对污染物扩散的影响,天气与气候对人 体健康的影响,空气物理性状及其卫生学意义; 重要基本概念: 太阳辐射、空气离子化,逆温,微小气候

一、大气圈及大气垂直结构 大圈(atmosphere). 大气圈是指包围在地球周围,距地球表面约 1000多公里厚度的气体构成
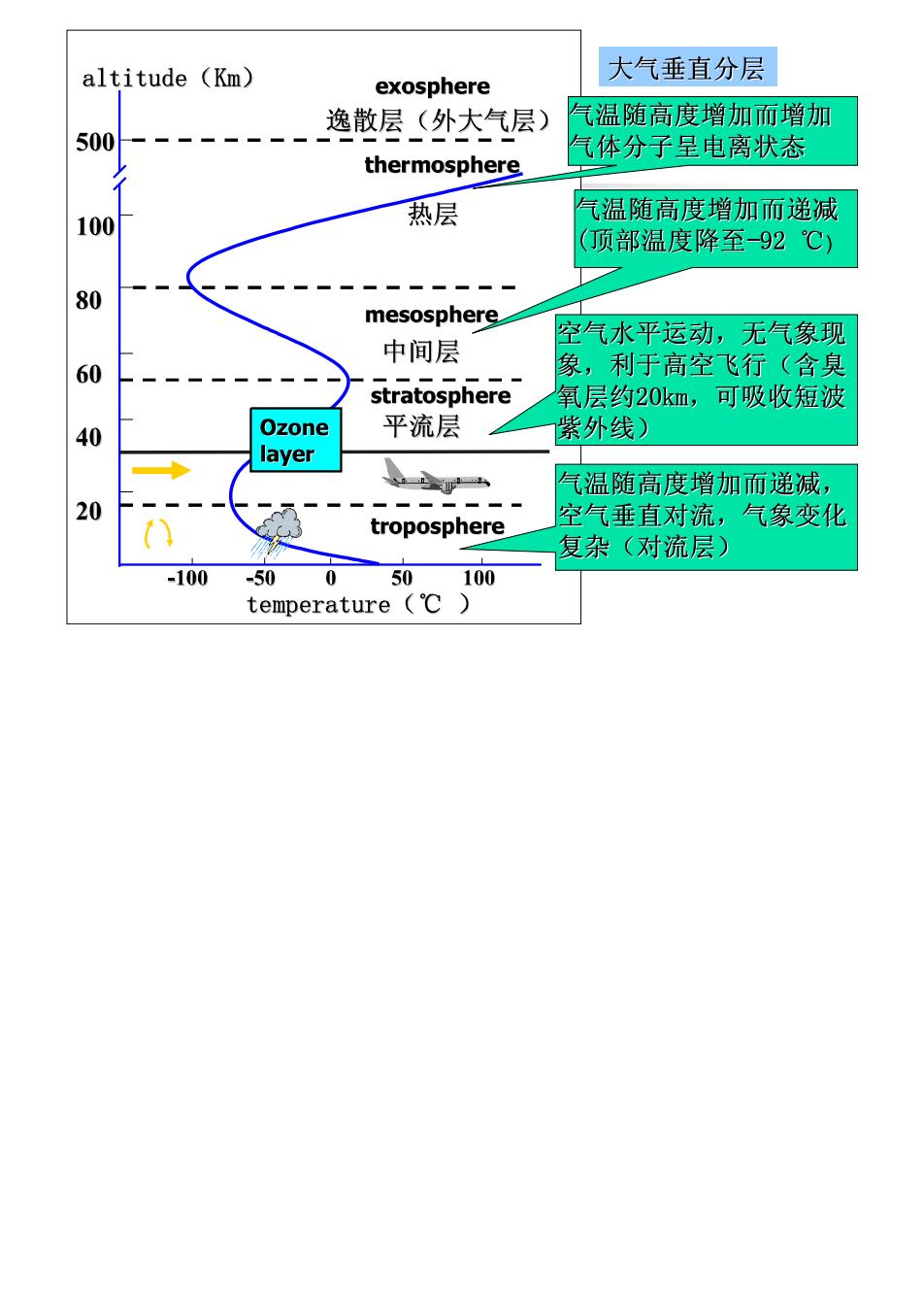
altitude (Km) 大气垂直分层 exosphere 逸散层(外大气层) 气温随高度增加而增加 500 气体分子呈电离状态 thermosphere 气温随高度增加而递减 100 热层 (顶部温度降至-92℃) 80 mesosphere 中间层 空气水平运动,无气象现 60 象,利于高空飞行(含臭 stratosphere 氧层约20km,可吸收短波 40 Ozone 平流层 紫外线) layer 山 气温随高度增加而递减, 20 troposphere 空气垂直对流,气象变化 复杂(对流层) -100 -=50 0 50 100 temperature(℃)

二、太阳辐射(solar radiation) 垂直方向 太阳表面温度6000°K 以电磁波形式传播的太阳能。表示单位:卡/厘米2·分 紫外线:150-400nm Some solar Some of the infrared radiatian radiation is passes through the 可见光:400-760nm reflected by the atmosphere,and some is Earth and the absorbed and re-amitted in all atmosphere. eeat时 红外线:760-3000nm to warm the Earth's surface and lower the atmosphere. Solar radiation ATMOSP passes through the clear atmosphere Most radiation nfrared radi ni emitted f折om the absorbed by th Earth's surface Earth's surface and wams it
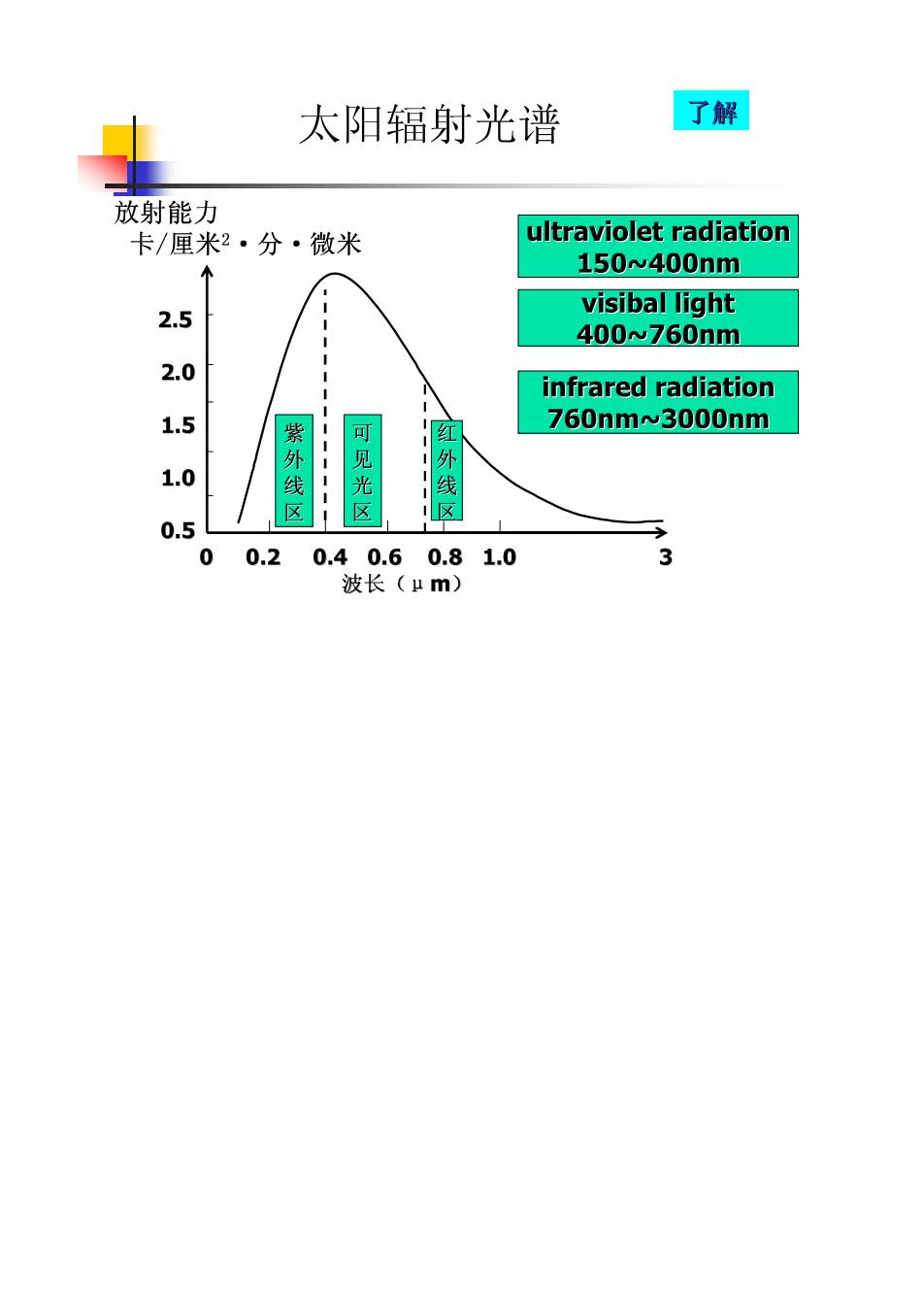
太阳辐射光谱 了解 放射能力 卡/厘米2·分·微米 ultraviolet radiation 150w400nm 2.5 visibal light 400w760nm 2.0 infrared radiation 1.5 760nmw3000nm, 1.0 紫外线 见光 线 区 0.5 0 0.2 0.40.6 0.8 1.0 3 波长(μm)

p67 (ultraviolet radiation UV 紫外线分段(第二届哥本哈根光学会议) UV-A320一400nm:穿透皮肤强,生物效应弱,色素沉着, 保护皮肤深层组织; UV-B275一320nm:部分达地表,抗佝偻病、增强免疫力, 生理促进作用最强; UV-C200-275nm: 臭氧层吸收,辐射最强时少量达地表: 短波紫外线有杀菌作用,也 能损伤细胞。 过强紫外线:日光性皮炎、光电性眼炎、皮肤癌,参与光化学烟 雾和硫酸雾的形成

(二)infrared ray p67 生物学作用的基础是热效应,故又称热射线。 长波红外线(1400nm一3000nm): 穿透能力较弱,主要加温皮肤 表层。 短波红外线(760nm一1400nm): 穿透能力较强,可加温组织沙临床理疗 部。 适量:促进新陈代谢和细胞增生,消炎镇静; 过强:日射病,红外线白内障