
《国际经济学I川(国际金融)》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 课程代码:18060743 课程名称:国际经济学IⅡ(国际金融) 英文名称:International EconomicsⅡ(Intemational Finance) 课程类别:专业课 学 时:48 学 分分:3 适用对象:国际商务专业本科生 考核方式:考试 先修课程:宏观经济学、微观经济学 二、课程简介 国际经济学是高等院校经济类专业的核心基础课程。国际经济学研究稀缺资 源在世界范围内的最优配置。其宏观部分的内容主要有:汇率决定理论,国际收 支调节理论以及开放经济条件下的宏观政策调节等。 International economics is the core and basic course of economics maior in Institutions of high education.Intemational Economics is the economics that researches the collocation optimization of scarce resources in the whole world.It mainly includes the macrocosmic part which mostly ilustrates the exchange rate determination theory,international balance of payments adjustment theory and Macroeconomic policy coordination under open conditions 三、课程性质与教学目的 国际经济学是高等院校经济学专业的基础与核心专业课程。国际经济学的研 究对象是国家间的经济活动和由此产生的国际经济关系。研究国际范围内的资源 优化配置和国际经济关系对资源配置的影响。本课程主要研究的是国际经济活动 的宏观问题。学生需要掌握以下主要内容:汇率决定理论、国际收支调节理论和 开放条件下的宏观经济政策协调,并能够运用相关理论对现实中的经济问题进行 分析,同时应了解我国的汇率制度安排,理解我国在对外经济中所采取的相关 政策的合理性、必要性和重要性,以及这些政策和制度对我国经济社会发展所 发挥的积极促进作用。 International economics is the core and basic course of economics major in Institutionsofhigher leaming.The research object of intemational conomics is the economic activities between countries and the international economic relations resulting from them.It studies the optimal allocation of resources within the
《国际经济学 II(国际金融)》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 课程代码:18060743 课程名称:国际经济学 II(国际金融) 英文名称:International Economics II(International Finance) 课程类别:专业课 学 时:48 学 分:3 适用对象: 国际商务专业本科生 考核方式:考试 先修课程:宏观经济学、微观经济学 二、课程简介 国际经济学是高等院校经济类专业的核心基础课程。国际经济学研究稀缺资 源在世界范围内的最优配置。其宏观部分的内容主要有:汇率决定理论,国际收 支调节理论以及开放经济条件下的宏观政策调节等。 International economics is the core and basic course of economics major in Institutions of high education. International Economics is the economics that researches the collocation optimization of scarce resources in the whole world. It mainly includes the macrocosmic part which mostly illustrates the exchange rate determination theory, international balance of payments adjustment theory and Macroeconomic policy coordination under open conditions. 三、课程性质与教学目的 国际经济学是高等院校经济学专业的基础与核心专业课程。国际经济学的研 究对象是国家间的经济活动和由此产生的国际经济关系。研究国际范围内的资源 优化配置和国际经济关系对资源配置的影响。本课程主要研究的是国际经济活动 的宏观问题。学生需要掌握以下主要内容:汇率决定理论、国际收支调节理论和 开放条件下的宏观经济政策协调,并能够运用相关理论对现实中的经济问题进行 分析,同时应了解我国的汇率制度安排,理解我国在对外经济中所采取的相关 政策的合理性、必要性和重要性,以及这些政策和制度对我国经济社会发展所 发挥的积极促进作用。 International economics is the core and basic course of economics major in Institutions of higher learning. The research object of international economics is the economic activities between countries and the international economic relations resulting from them. It studies the optimal allocation of resources within the

intemational scope and the influence of intemational economic relations on the allocation of resources.This course focuses on the macro issues of international economic activities.Students are required to master the following main contents exchange rate determination theory,international balance of payments adjustment theory and Macroeconomic policy coordination underopen conditions.Students should be able to use relevant theories to analyze the economic problems in reality Students should understand China's exchange rate system arrangement,and the necessity and importance of relevant policies adopted by China in its foreign economy,and the positive role of these policies and systems in promoting China's economic and social development. 四、教学内容及要求 Chapter 13 National Income Accounting and the Balance of Payments (1Teaching targets and requirements:In this chapter the purpose of teaching is to enable students to understand:the international balance of payments and the balance of intemational payments,the balance of payments structure and doubleen table;the balance and imbalance of interational payments,which are the basis for the following study of intemational payments adjustment theory. (2)Teaching Contents 1.Introduction 2.The National Income Accounts 3.National Income Accounting for an Open Economy 4.The Balance of Payment Accounts Knowledge point:the meaning of National Income Accounting and the Balance of Payments:The balance of payments structure and double entry table (3)Thinking and Practice 1.The balance of payments structure and double entry table 2.How to deal with the balance and imbalance of intemational payments? (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching:Discussion 思政内容:介绍我国改革开放以后的贸易发展,特别是2000年以后经常项 目对世界其他主要经济体保持顺差的情况,这是我国改革开放所取得的经济成 就在国际贸易方面的体现。 Chapter 14 Exchange Rates and the Foreign Exchange Market:An Asset Approach (1Teaching targets and requirements:This chapter is the focus of interational economics,the purpose of teaching is to enable students to understand and grasp:
international scope and the influence of international economic relations on the allocation of resources. This course focuses on the macro issues of international economic activities. Students are required to master the following main contents: exchange rate determination theory, international balance of payments adjustment theory and Macroeconomic policy coordination under open conditions. Students should be able to use relevant theories to analyze the economic problems in reality. Students should understand China's exchange rate system arrangement, and the necessity and importance of relevant policies adopted by China in its foreign economy, and the positive role of these policies and systems in promoting China's economic and social development. 四、教学内容及要求 Chapter 13 National Income Accounting and the Balance of Payments (1)Teaching targets and requirements:In this chapter the purpose of teaching is to enable students to understand: the international balance of payments and the balance of international payments; the balance of payments structure and double entry table; the balance and imbalance of international payments, which are the basis for the following study of international payments adjustment theory. (2)Teaching Contents 1. Introduction 2. The National Income Accounts 3. National Income Accounting for an Open Economy 4. The Balance of Payment Accounts Knowledge point:the meaning of National Income Accounting and the Balance of Payments;The balance of payments structure and double entry table (3)Thinking and Practice 1. The balance of payments structure and double entry table 2. How to deal with the balance and imbalance of international payments? (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching;Discussion 思政内容:介绍我国改革开放以后的贸易发展,特别是 2000 年以后经常项 目对世界其他主要经济体保持顺差的情况,这是我国改革开放所取得的经济成 就在国际贸易方面的体现。 Chapter 14 Exchange Rates and the Foreign Exchange Market: An Asset Approach (1)Teaching targets and requirements:This chapter is the focus of international economics, the purpose of teaching is to enable students to understand and grasp:

foreign exchange,foreign exchange markets and foreign exchange transactions:the concept of exchange rate and its classification. (2)Teaching Contents 1.Introduction 2.Exchange Rates and International Transaction 3.The Foreign Exchange Market 4.The Demand for Foreign Currency Assets 5.Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market 6.Interest Rates,Expectations,and Equilibrium Knowledge point:Exchange Rates and International Transactions;The Foreign Exchange Market;Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market (3)Thinking and Practice Grasp the concepts of Exchange Rates and International Transactions, Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market,and the relationship between Interest Rates,Expectations,and Equilibrium. (4)Teaching Method Multimed ia Teaching:Discussion Chapter 15 Money,Interest Rates,and Exchange Rates (1)Teaching targets and requirements:This chapter combines the foreign-exchange market with the money market to determine the exchange rate in the short run.It analyzes the long-term effects of monetary changes on output prices and expected future exchange rates. (2)Teaching Contents 1.Money Defined:A Brief Review 2.The Demand for Money by Individuals 3.Aggregate Money Demand 4.The Equilibrium Interest Rate The Interaction of Money Supply and Demand 5.The Money Supply and the Exchange Rate in the Short Run 6.Money,the Price Level,and the Exchange Rate in the Long Run 7.Inflation and Exchange Rate Dynamics Knowledge point:Aggregate Money Demand:The Money Supply:The Equilibrium Interest Rate;Inflation and Exchange Rate Dynamics. (3)Thinking and Practice How to explain the determination of The Equilibrium Interest Rate in the short run and in the long run? (4)Teaching Method
foreign exchange, foreign exchange markets and foreign exchange transactions; the concept of exchange rate and its classification. (2)Teaching Contents 1. Introduction 2. Exchange Rates and International Transactions 3. The Foreign Exchange Market 4. The Demand for Foreign Currency Assets 5. Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market 6. Interest Rates, Expectations, and Equilibrium Knowledge point:Exchange Rates and International Transactions; The Foreign Exchange Market; Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market. (3)Thinking and Practice Grasp the concepts of Exchange Rates and International Transactions, Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market, and the relationship between Interest Rates, Expectations, and Equilibrium. (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching;Discussion Chapter 15 Money, Interest Rates, and Exchange Rates (1)Teaching targets and requirements:This chapter combines the foreign-exchange market with the money market to determine the exchange rate in the short run. It analyzes the long-term effects of monetary changes on output prices and expected future exchange rates. (2)Teaching Contents 1. Money Defined: A Brief Review 2. The Demand for Money by Individuals 3. Aggregate Money Demand 4. The Equilibrium Interest Rate: The Interaction of Money Supply and Demand 5. The Money Supply and the Exchange Rate in the Short Run 6. Money, the Price Level, and the Exchange Rate in the Long Run 7. Inflation and Exchange Rate Dynamics Knowledge point: Aggregate Money Demand; The Money Supply; The Equilibrium Interest Rate; Inflation and Exchange Rate Dynamics. (3)Thinking and Practice How to explain the determination of The Equilibrium Interest Rate in the short run and in the long run? (4)Teaching Method

Multimedia Teaching Chapter 16 Price Levels and the Exchange Rate in the Long Run (1)Teaching targets and requirements:This chapter is the focus of international economics.the purpose of teaching is toenable students to understand and grasp: several main exchange rate determination theories:factors that affect exchange rate changes in the long run and short term. (2)Teaching Contents 1.The Law of One Price 2.Purchasing Power Parity 3.A Long-Run Exchange Rate Model Based on PPP 4.Empirical Evidence on PPP and the Law of One Price 5.Explaining the Problems with PPP Knowledge point:The Law ofOne Price;Purchasing Power Parity (3)Thinking and Practice How to determine the exchange rate on the base of LOP or PPP. (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching:Case Analysis Chapter 17 Output and the Exchange Rate in the Short Run (1)Teaching targets and requirements:Macroeconomic changes that affect exchange rates,interest rates.and price levels may also affect output.This chapter introduces a new theory of how the output market adjusts to demand changes when product prices are themselves slow to adjust. (2)Teaching Contents 1.Determinants of Aggregate Demand in an Open Economy 2.The Equation of Aggregate Demand 3.How Output Is Determined in the Short Run 4.Output Market Equilibrium in the Sort Run:The DD Schedule 5.Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run:The A4 Schedule 6.Short-Run Equilibrium for an Open Economy Putting the DD and A44 Schedules Together 7.Temporary Changes in Monetary and Fiscal Policy 8.Inflation Bias and Other Problems of Policy Formulation 9.Permanent Shifts in Monetary and Fiscal Policy 10.Macroeconomic Policies and the Current Account 11.Gradual Trade Flow Adjustment and Current Account Dynamics Knowledge point:The DD Schedule;the 44 Schedule;Short-Run
Multimedia Teaching Chapter 16 Price Levels and the Exchange Rate in the Long Run (1)Teaching targets and requirements:This chapter is the focus of international economics, the purpose of teaching is to enable students to understand and grasp: several main exchange rate determination theories; factors that affect exchange rate changes in the long run and short term. (2)Teaching Contents 1. The Law of One Price 2. Purchasing Power Parity 3. A Long-Run Exchange Rate Model Based on PPP 4. Empirical Evidence on PPP and the Law of One Price 5. Explaining the Problems with PPP Knowledge point:The Law of One Price; Purchasing Power Parity (3)Thinking and Practice How to determine the exchange rate on the base of LOP or PPP. (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching;Case Analysis Chapter 17 Output and the Exchange Rate in the Short Run (1)Teaching targets and requirements:Macroeconomic changes that affect exchange rates, interest rates, and price levels may also affect output. This chapter introduces a new theory of how the output market adjusts to demand changes when product prices are themselves slow to adjust. (2)Teaching Contents 1. Determinants of Aggregate Demand in an Open Economy 2. The Equation of Aggregate Demand 3. How Output Is Determined in the Short Run 4. Output Market Equilibrium in the Sort Run: The DD Schedule 5. Asset Market Equilibrium in the Short Run: The AA Schedule 6. Short-Run Equilibrium for an Open Economy: Putting the DD and AA Schedules Together 7. Temporary Changes in Monetary and Fiscal Policy 8. Inflation Bias and Other Problems of Policy Formulation 9. Permanent Shifts in Monetary and Fiscal Policy 10. Macroeconomic Policies and the Current Account 11. Gradual Trade Flow Adjustment and Current Account Dynamics Knowledge point:The DD Schedule; the AA Schedule; Short-Run

Equilibrium for an Open Economy (3)Thinking and Practice Students should master the effects of macroeconomic policy tools on outpu and the current account and the use of macroeconomic policy tools to maintain full employment (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching:Discussion Chapter 18 Fixed Exchange Rates and Foreign Exchange Intervention (1)Teaching targets and requirements:In reality.the assumption of complete exchange rate flexibility is rarely accurate.A number of developing countries have retained some form of goverment exchange rate fixing.So in this chapter we have to learn something about Fixed Exchange Rates and Foreign Exchange Intervention (2)Teaching Contents 1.Why Study Fixed Exchange Rates? 2.Central Bank Intervention and the Money Supply 3.How the Central Bank Fixes the Exchange Rates 4.Stabilization Policies with a Fixed Exchange Rate 5.Balance of Payments Crises and Capital Flight 6.Managed Floating and Sterilized Intervention 7.Reserve Currencies in the World Monetary System 8.The Gold Standard Knowledge point:Fixed Exchange Rates;Central Bank Intervention; Balance of Payments Crises;Managed Floating:Reserve Currencies,The Gold Standard (3)Thinking and Practice 1.Why the assumption of complete exchange rate flexibility is rarely accurate in reality? 2.How central banks intervene in the foreign exchange market? (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching:Discussion:Case Analysis 思政内容:介绍我国现行汇率制度,解释制度制定的背景,说明我国的制度 安排符合经济发展需要,有力地维护了人民币的稳定,守护了我国经济发展所 取得的成果。 Chapter 19 The International Monetary System,1870-1973 (1)Teaching targets and requirements:The interdependence of open national economies has made it more difficult for governments to achieve full employment and
Equilibrium for an Open Economy. (3)Thinking and Practice Students should master the effects of macroeconomic policy tools on output and the current account and the use of macroeconomic policy tools to maintain full employment. (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching;Discussion Chapter 18 Fixed Exchange Rates and Foreign Exchange Intervention (1)Teaching targets and requirements:In reality, the assumption of complete exchange rate flexibility is rarely accurate. A number of developing countries have retained some form of government exchange rate fixing. So in this chapter we have to learn something about Fixed Exchange Rates and Foreign Exchange Intervention. (2)Teaching Contents 1. Why Study Fixed Exchange Rates? 2. Central Bank Intervention and the Money Supply 3. How the Central Bank Fixes the Exchange Rates 4. Stabilization Policies with a Fixed Exchange Rate 5. Balance of Payments Crises and Capital Flight 6. Managed Floating and Sterilized Intervention 7. Reserve Currencies in the World Monetary System 8. The Gold Standard Knowledge point:Fixed Exchange Rates; Central Bank Intervention; Balance of Payments Crises; Managed Floating; Reserve Currencies; The Gold Standard. (3)Thinking and Practice 1. Why the assumption of complete exchange rate flexibility is rarely accurate in reality? 2. How central banks intervene in the foreign exchange market? (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching;Discussion;Case Analysis 思政内容:介绍我国现行汇率制度,解释制度制定的背景,说明我国的制度 安排符合经济发展需要,有力地维护了人民币的稳定,守护了我国经济发展所 取得的成果。 Chapter 19 The International Monetary System, 1870-1973 (1)Teaching targets and requirements:The interdependence of open national economies has made it more difficult for governments to achieve full employment and

price stability.This chapter examines the evolution of the interational monetary system and how it influenced macroeconomic policy. (2)Teaching Contents 1.Macroeconomic Policy Goals in an Open Economy 2.Intemational Macroeconomic Policy Under the Gold Standard.1870-1914 3.The Interwar Years,1918-1939 4.The Bretton Woods System and the International Monetary Fund 5.Internal and External Balance Under the Bretton Woods System 6.Analyzing Policy Options Under the Bretton Woods System 7.The Extemal Balance Problem of the United States 8.Worldwide Inflation and the Transition to Floating Rates Knowledge point:Macroeconomic Policy Goals in an Open Economy: Policy under the Gold Standard:The Bretton Woods System and the Intemationa Monetary Fund:Worldwide Inflation and the Transition to Floating Rates. (3)Thinking and Practice 1.Know the evolution of the international monetary system 2.How it influenced macroeconomic policy (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching:Discussion:Case Analysis 思政内容:讨论我国自建国以后的汇率制度安排及其演变,说明我国的汇率 制度安排是各时期根据自身经济发展的水平和国际环境背景做出的安排。 Chapter 20 Macroeconomic Policy and Coordination under Floating Exchange Rates (1)Teaching targets and requirements:The floating exchange rate system,in place since 1973,was not well planned before its inception by the mid-1980s, economists and policymakers had become more skeptical about the benefits of an interational monetary system based on floating rates.This chapter compares the macroeconomic policy problems of different exchange rate regimes. (2)Teaching Contents 1.The Case for Floating Exchange Rates 2.The Case Against Floating Exchange Rates 3.Macroeconomic Interdependence Under a Floating Rate 4.What Has Been Leamed Since 1973? 5.Are Fixed Exchange Rates Even and Option for Most Countries? 6.Directions for Reform (3)Thinking and Practice
price stability. This chapter examines the evolution of the international monetary system and how it influenced macroeconomic policy. (2)Teaching Contents 1. Macroeconomic Policy Goals in an Open Economy 2. International Macroeconomic Policy Under the Gold Standard, 1870-1914 3. The Interwar Years, 1918-1939 4. The Bretton Woods System and the International Monetary Fund 5. Internal and External Balance Under the Bretton Woods System 6. Analyzing Policy Options Under the Bretton Woods System 7. The External Balance Problem of the United States 8. Worldwide Inflation and the Transition to Floating Rates Knowledge point: Macroeconomic Policy Goals in an Open Economy; Policy under the Gold Standard; The Bretton Woods System and the International Monetary Fund; Worldwide Inflation and the Transition to Floating Rates. (3)Thinking and Practice 1. Know the evolution of the international monetary system. 2. How it influenced macroeconomic policy. (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching;Discussion;Case Analysis 思政内容:讨论我国自建国以后的汇率制度安排及其演变,说明我国的汇率 制度安排是各时期根据自身经济发展的水平和国际环境背景做出的安排。 Chapter 20 Macroeconomic Policy and Coordination under Floating Exchange Rates (1)Teaching targets and requirements:The floating exchange rate system, in place since 1973, was not well planned before its inception by the mid-1980s, economists and policymakers had become more skeptical about the benefits of an international monetary system based on floating rates. This chapter compares the macroeconomic policy problems of different exchange rate regimes. (2)Teaching Contents 1. The Case for Floating Exchange Rates 2. The Case Against Floating Exchange Rates 3. Macroeconomic Interdependence Under a Floating Rate 4. What Has Been Learned Since 1973? 5. Are Fixed Exchange Rates Even and Option for Most Countries? 6. Directions for Reform (3)Thinking and Practice
1.Why the performance of floating rates has been so disappointing? 2.What direction should reform of the current system take? (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching:Discussion:Case analysis 思政内容:将亚洲金融危机作为案例展开讨论,强调采用符合本国发展情况 的汇率制度的重要性,说明国际游资唯利是图恶意进攻造成重大损失,各国经 济倒退发展受挫。介绍我国在危机中的表现,维护了中国人民辛勤劳动所取得 的经济成果。 五、各教学环节学时分配 教学环节 9 讨 小 教学时数 论 实验 其他散 学环节 课 课程内容 第13章 1 6 第14章 6 6 第15章 6 6 第16章 6 6 第17章 5 1 6 第18章 4 2 第19章 第20章 3 4 复习与答疑 合计 41 48 六、课程考核 (一)考核方式 闭卷考试 (二)成绩构成 平时成绩占比:30% 期末考试占比:70% (三)成绩考核标准
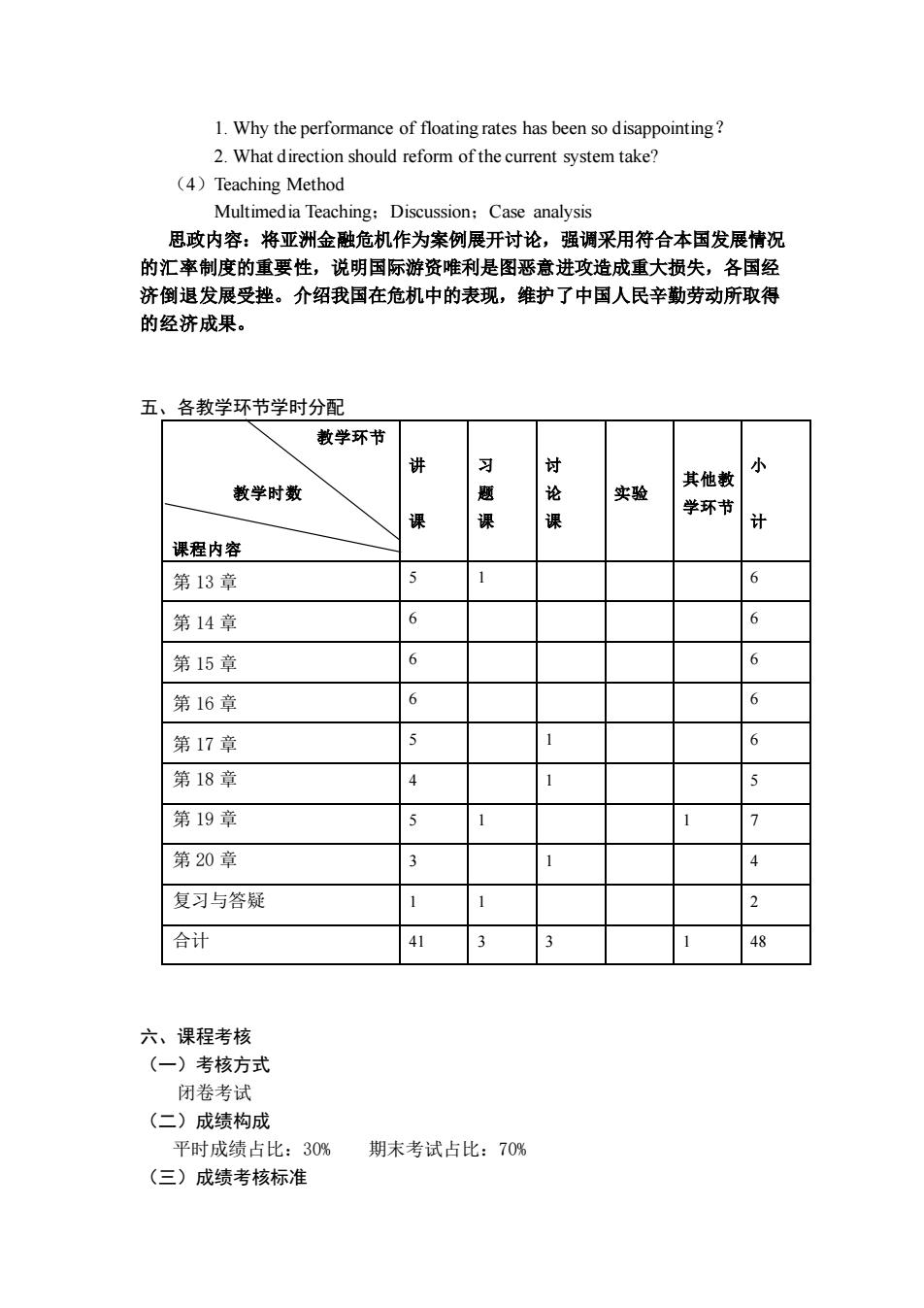
1. Why the performance of floating rates has been so disappointing? 2. What direction should reform of the current system take? (4)Teaching Method Multimedia Teaching;Discussion;Case analysis 思政内容:将亚洲金融危机作为案例展开讨论,强调采用符合本国发展情况 的汇率制度的重要性,说明国际游资唯利是图恶意进攻造成重大损失,各国经 济倒退发展受挫。介绍我国在危机中的表现,维护了中国人民辛勤劳动所取得 的经济成果。 五、各教学环节学时分配 教学环节 教学时数 课程内容 讲 课 习 题 课 讨 论 课 实验 其他教 学环节 小 计 第 13 章 5 1 6 第 14 章 6 6 第 15 章 6 6 第 16 章 6 6 第 17 章 5 1 6 第 18 章 4 1 5 第 19 章 5 1 1 7 第 20 章 3 1 4 复习与答疑 1 1 2 合计 41 3 3 1 48 六、课程考核 (一)考核方式 闭卷考试 (二)成绩构成 平时成绩占比:30% 期末考试占比:70% (三)成绩考核标准

出勤率、课堂表现、课堂报告、期末考试成绩 七、推荐教材和教学参考资源 推荐教材:Paul R.Krugman,Maurice Obstfeld,.Mare J.Melitz.International Economics::Theory and Policy,Ninth Edition.清华大学出版社2016. 教学参考资料: L.Dominick Salvatore.International Economics..清华大学出版社,2004 2.罗塞,罗伯茨刘琳娜、栾晔译.抉择一关于自由贸易与贸易保护主义的寓 言,中国人民大学出版社、北京大学出版社,2001年。 3、海闻.国际贸易、理论、政策、应用,上海人民出版社,1999年。 4、易纲.国际金融,上海人民出版社,1999年版。 5.哈里·兰德雷斯,大卫·C·柯南道尔.周文译.经济思想史.人民邮电出 版社,2014. 6、袁志刚,宋京.国际经济学高等教育出版社,2000年。 7.薛敬孝,佟家栋,李坤望.国际经济学高等教育出版社,2000年。 8.佟家栋高乐咏国际经济学南开大学出版社,2000年。 9.袁志刚,宋京国际经济学上海社会科学院出版社、高等教育出版社,2000 八、其它说明 1.本课堂会适当运用影音视频资料进行播放,提高学生学习兴趣,增强教学 效果。 2.本课程大纲按48学时编制,可根据教学进度适当调整理论讲授和课堂讨 论的时间分配。 大纲修订人:梁碧波/王一卉 修订日期:2020/11/20 大纲审定人:经济学院 审定日期:
出勤率、课堂表现、课堂报告、期末考试成绩 七、推荐教材和教学参考资源 推荐教材:Paul R. Krugman,Maurice Obstfeld, Marc J. Melitz. International Economics: Theory and Policy, Ninth Edition.清华大学出版社 2016. 教学参考资料: 1. Dominick Salvatore. International Economics.清华大学出版社,2004. 2. 罗塞•罗伯茨.刘琳娜、栾晔译.抉择——关于自由贸易与贸易保护主义的寓 言,中国人民大学出版社、北京大学出版社,2001 年。 3、海闻.国际贸易、理论、政策、应用,上海人民出版社,1999 年。 4、易纲.国际金融,上海人民出版社,1999 年版。 5. 哈里·兰德雷斯,大卫·C·柯南道尔.周文译.经济思想史.人民邮电出 版社,2014. 6、袁志刚,宋京.国际经济学.高等教育出版社,2000 年。 7.薛敬孝,佟家栋,李坤望.国际经济学.高等教育出版社,2000 年。 8.佟家栋,高乐咏.国际经济学.南开大学出版社,2000 年。 9.袁志刚,宋京.国际经济学.上海社会科学院出版社、高等教育出版社,2000 年。 八、其它说明 1.本课堂会适当运用影音视频资料进行播放,提高学生学习兴趣,增强教学 效果。 2.本课程大纲按 48 学时编制,可根据教学进度适当调整理论讲授和课堂讨 论的时间分配。 大纲修订人:梁碧波/王一卉 修订日期:2020/11/20 大纲审定人:经济学院 审定日期: