
Fundamentals of Air Pollution Meteorology Prof.JIANG Dahe
Fundamentals of Air Pollution Meteorology Prof. JIANG Dahe

1.1 Composition of air and vertical stratification Minor components of clean air Atmospheric stratification Pressure(mb) 0 200 400600800 10001200 Gas % 100000 ppm Thermosphere H20 0~7 90000 C02 80000 0.032 CH4 70000 1.5 Mesosphere co 60000 0.1 Stratopause 50000 03 0.02 40000 NH3 0.01 Stratosphere 30000 NO2 0.001 20000 S02 0.0002 Tropopause 10000 H2S 0.0002 Troposphere 0 100 -80 60 -40 -20 0 20 Temperature(C)
Gas % ppm H2O 0~7 CO2 0.032 CH4 1.5 CO 0.1 O3 0.02 NH3 0.01 NO2 0.001 SO2 0.0002 H2S 0.0002 Minor components of clean air Atmospheric stratification 1.1 Composition of air and vertical stratification

The troposphere is further divided: According to the effect of the earth surface: -planetary boundary layer(PBL,1~2000m)and free atmosphere Within PBL,according to vertical wind profile: Geostrophic wind -Ekman layer Lower atmosphere(0~150m) Constant shear layer
The troposphere is further divided: • According to the effect of the earth surface: – planetary boundary layer (PBL,1~2000m) and – free atmosphere • Within PBL, according to vertical wind profile: – Geostrophic wind – Ekman layer – Lower atmosphere (0~150m) – Constant shear layer

1.2 Principle meteorological factors Temperature Fahrenheit(F),Celsius(C),Kelvin Celsius =(Fahrenheit-32)x5/9 Kelvin Celsius 273.16 Humidity Absolute humidity a(mass/volume) Relative humidity actual water vapor P/saturation vapor P at T Dew point temperature Specific humidity
1.2 Principle meteorological factors • Temperature Fahrenheit (F), Celsius(C), Kelvin Celsius = (Fahrenheit – 32) ×5/9 Kelvin = Celsius + 273.16 • Humidity Absolute humidity a (mass/volume) Relative humidity = actual water vapor P / saturation vapor P at T Dew point temperature Specific humidity …

-Absolute humidity is the water mass per unit volume, (mg/m3). Water vapor pressure(hPa),is a partial pressure, which equals to the pressure of the air parcel where the dry air were not there but the water vapor. Saturated water vapor pressure,(hPa),is the water vapor pressure at saturation of the same temperature. Relative humidity refers to the ratio of water vapor pressure to saturated water vapor pressure,(% Dew point temperature(K)is the temperature when the air parcel is cooled to condensation under constant pressure
– Absolute humidity is the water mass per unit volume, (mg/m3). – Water vapor pressure (hPa), is a partial pressure, which equals to the pressure of the air parcel where the dry air were not there but the water vapor. Saturated water vapor pressure, (hPa), is the water vapor pressure at saturation of the same temperature. – Relative humidity refers to the ratio of water vapor pressure to saturated water vapor pressure, (%) – Dew point temperature (K) is the temperature when the air parcel is cooled to condensation under constant pressure

Pressure -1Pa=1N/m2,1mbar(mb)=100Pa(hPa), 1atm=1013.2mb=0.75mmHg 1hPa=1mb,surface(1000),850,700,600, 500,400hPa ·Wind -Wind speed,wind direction,wind rose Other: Cloudiness (total,and low level), precipitation,visibility
• Pressure – 1Pa=1N/m2, 1mbar(mb) = 100Pa(hPa), – 1atm=1013.2mb=0.75mmHg – 1hPa=1mb, surface (1000), 850, 700, 600, 500, 400hPa • Wind – Wind speed, wind direction, wind rose • Other: – Cloudiness (total, and low level), precipitation, visibility

=3π/2-中 ENE Wind angle and the wind velocity vector
N E S ENE W ø α α = 3π / 2 −φ Wind angle and the wind velocity vector
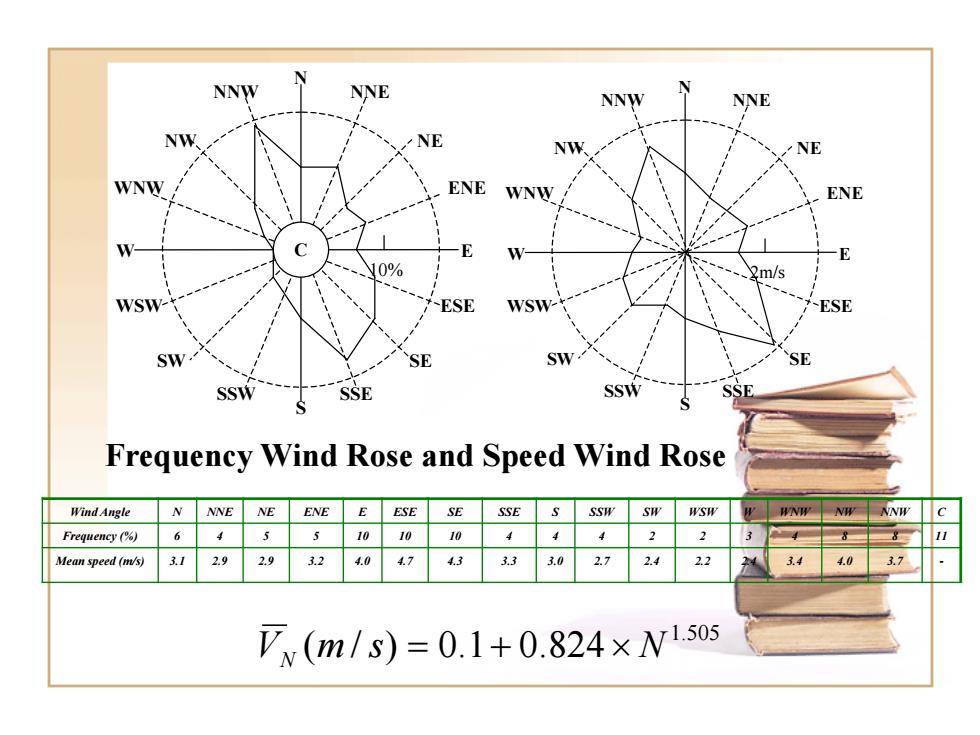
N NNW NNe NNW NNE NW NW NE WNW ENE WNW ENE y0% 2m/s WSW ESE WSW ESE SW. SE SW. SE SSW SSE SSW Frequency Wind Rose and Speed Wind Rose Wind Angle NNNE NE ENE E ESE SE SSE S SSW SW WSW W WNW NW NNW C Frequency (% 6 455101010444 2 Mean speed (m/s) 31 292.9324047433.33.02.72.4 2.2 3.44.0 3.7 Vx(m/s)=0.1+0.824×N1.50s
1.505 VN (m /s) = 0.1+ 0.824× N N S W E NE ENE NNE ESE SE SSE NNW NW WNW WSW SW SSW C 10% N S W E NE ENE NNE ESE SE SSE NNW NW WNW WSW SW SSW 2m/s Frequency Wind Rose and Speed Wind Rose Wind Angle N NNE NE ENE E ESE SE SSE S SSW SW WSW W WNW NW NNW C Frequency (%) 6 4 5 5 10 10 10 4 4 4 2 2 3 4 8 8 11 Mean speed (m/s) 3.1 2.9 2.9 3.2 4.0 4.7 4.3 3.3 3.0 2.7 2.4 2.2 2.4 3.4 4.0 3.7 -
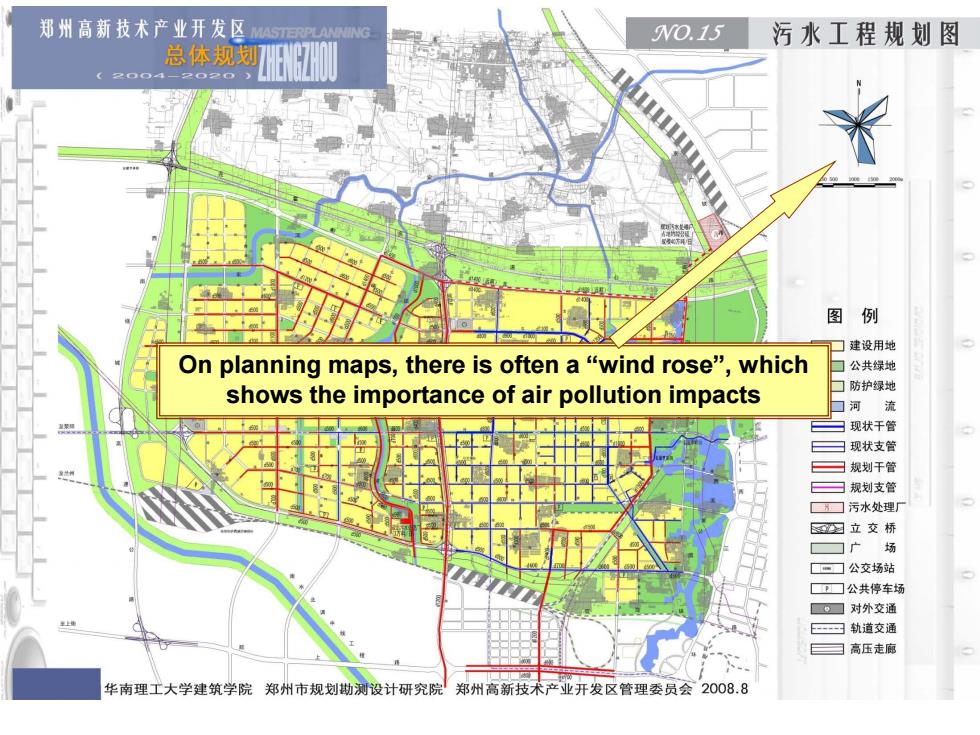
郑州高新技术产业开发区 W0.15 污水工程规划图 总体规划阳肌 图例 口建设用地 On planning maps,there is often a"wind rose",which 口公共绿地 shows the importance of air pollution impacts ☐防护绿地 口河流 日现状干管 现状支管 彐规划干管 曰规划支管 口污水处理厂 四立交桥 ☐广场 ■一☐公交场站 ☐公共停车场 。☐对外交通 回轨道交通 高压走廊 华南理工大学建筑学院郑州市规划勘测设计研究院郑州高新技术产业开发区管理委员会2008.8
On planning maps, there is often a “wind rose”, which shows the importance of air pollution impacts

1.3 Thermal Properties Why important? Air is an compressible gas; -Sun radiation is the input energy; -Changes in weather/climate involve heat processes; ·Energy budget Greenhouse effect Atmospheric instability
1.3 Thermal Properties • Why important? – Air is an compressible gas; – Sun radiation is the input energy; – Changes in weather/climate involve heat processes; • Energy budget • Greenhouse effect • Atmospheric instability