
Environmental Science Part 2:Water Resources and Treatment Topic 1:Water resources Prof.LI Fengting UNEP TONGJI Institute of Environment for Sustainable Development College of Environmental Science and Engineering Tongji University
Environmental Science Part 2: Water Resources and Treatment Topic 1: Water resources Prof. LI Fengting UNEP TONGJI Institute of Environment for Sustainable Development College of Environmental Science and Engineering Tongji University
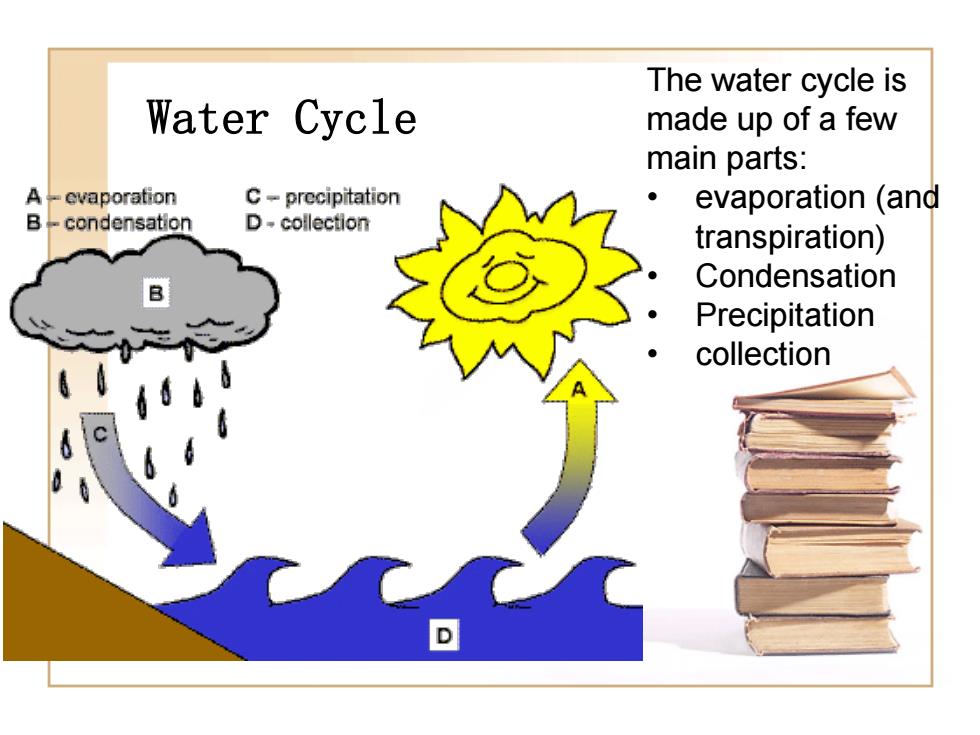
The water cycle is Water Cycle made up of a few main parts: A-evaporation C-precipitation evaporation (and B-condensation D-collection transpiration) Condensation Precipitation collection D
Water Cycle The water cycle is made up of a few main parts: • evaporation (and transpiration) • Condensation • Precipitation • collection
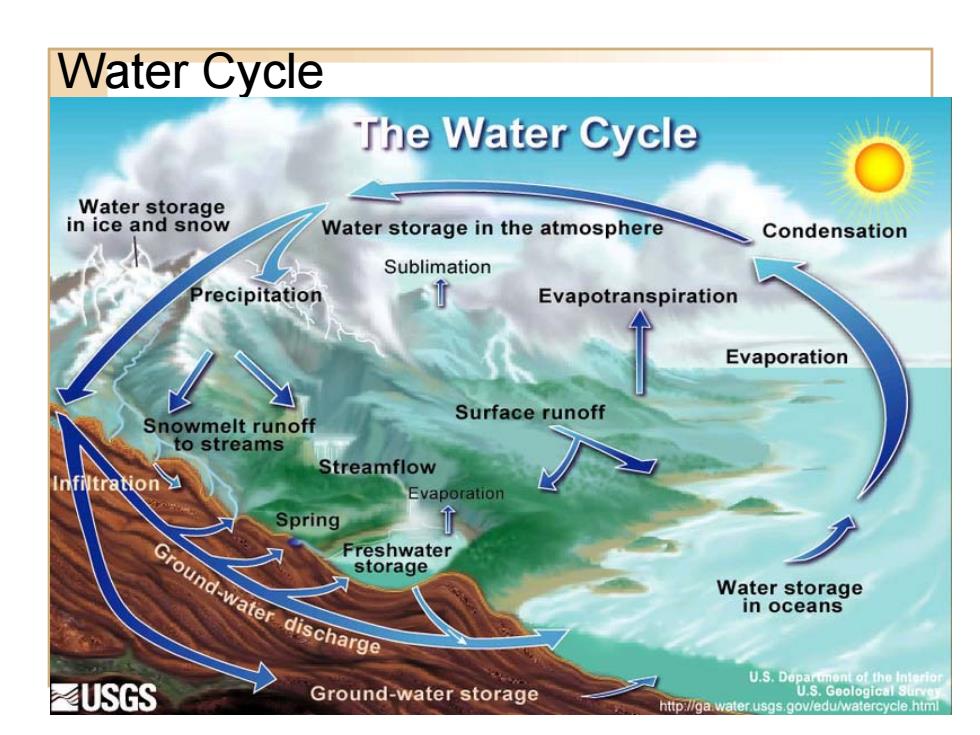
Water Cycle The Water Cycle Water storage in ice and snow Water storage in the atmosphere Condensation Sublimation Precipitation Evapotranspiration Evaporation Surface runoff Snowmelt runoff to streams Streamflow Evaporation Spring Ground-water discharge Freshwater storage Water storage in oceans U.S.Dopartmont of the Interio ≤USGS Ground-water storage U.S.Goological Suirve nttp://ga water.usgs.gov/edu/watercycle.html
Water Cycle
Hydrologic Cycle Hydrologic cycle circulation and transformation of water through atmosphere, hydrosphere,lithosphere,and biosphere Importance climate and weather modeling understanding global change ◆sea level changes global temperature change managing water resources-quantity and quality
Hydrologic Cycle

Water resources Water resources are sources of water that are useful or potentially useful. Uses of water include agricultural,industrial,household, recreational and environmental activities. Virtually all of these human uses require fresh water. 97%of the water on the Earth is salt water. ● However,only three percent is fresh water; slightly over two thirds of this is frozen in glaciers and polar ice caps. The remaining unfrozen freshwater is found mainly as groundwater,with only a small fraction present above ground or in the air
Water resources • Water resources are sources of water that are useful or potentially useful. • Uses of water include agricultural, industrial, household, recreational and environmental activities. • Virtually all of these human uses require fresh water. • 97% of the water on the Earth is salt water. • However, only three percent is fresh water; • slightly over two thirds of this is frozen in glaciers and polar ice caps. • The remaining unfrozen freshwater is found mainly as groundwater, with only a small fraction present above ground or in the air
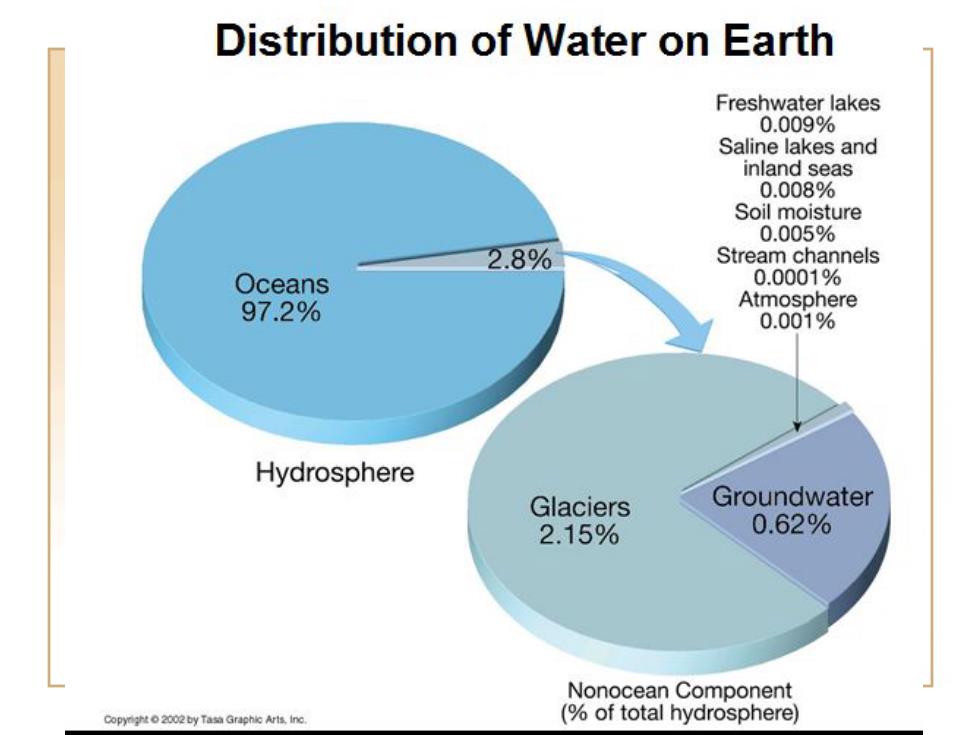
Distribution of Water on Earth Freshwater lakes 0.009% Saline lakes and inland seas 0.008% Soil moisture 0.005% 2.8% Stream channels Oceans 0.0001% 97.2% Atmosphere 0.001% Hydrosphere Glaciers Groundwater 2.15% 0.62% Nonocean Component opy002yTasraphc Arts inc. (of total hydrosphere)

The world's water resources 70 per cent is used for agricultural purposes; 20 per cent is used by industry (including power generation);and 10 per cent is used for direct human consumption
The world’s water resources • 70 per cent is used for agricultural purposes; • 20 per cent is used by industry (including power generation); and • 10 per cent is used for direct human consumption
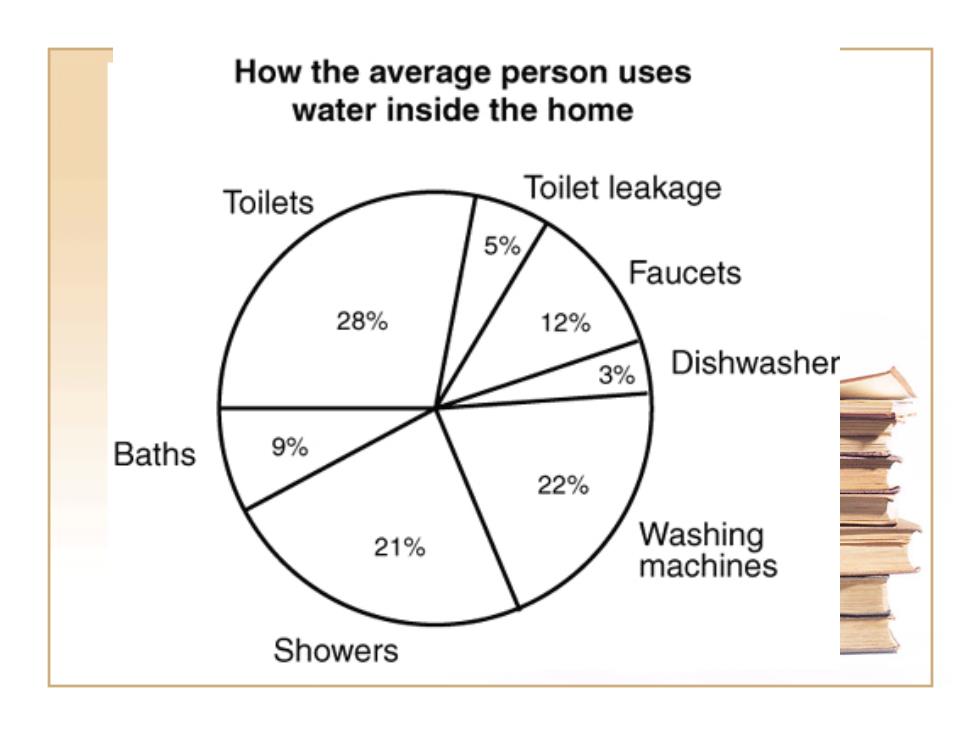
How the average person uses water inside the home Toilets Toilet leakage 5% Faucets 28% 12% 3% Dishwasher Baths 9% 22% 21% Washing machines Showers

Water footprint
Water footprint

CONCEPT Water Footprint the total volume of freshwater that is used to produce the goods and services consumed by the individual or community or produced by the business
CONCEPT Water Footprint the total volume of freshwater that is used to produce the goods and services consumed by the individual or community or produced by the business