
UNEP Environmental Science- Solid waste management(4) composting Niu Dongjie niudongjie@tongji.edu.cn
Environmental Science— Solid waste management(4) composting Niu Dongjie niudongjie@tongji.edu.cn
Content oIntroduction o Principle of composting o Composting technology Water UNEP
Content Introduction Principle of composting Composting technology
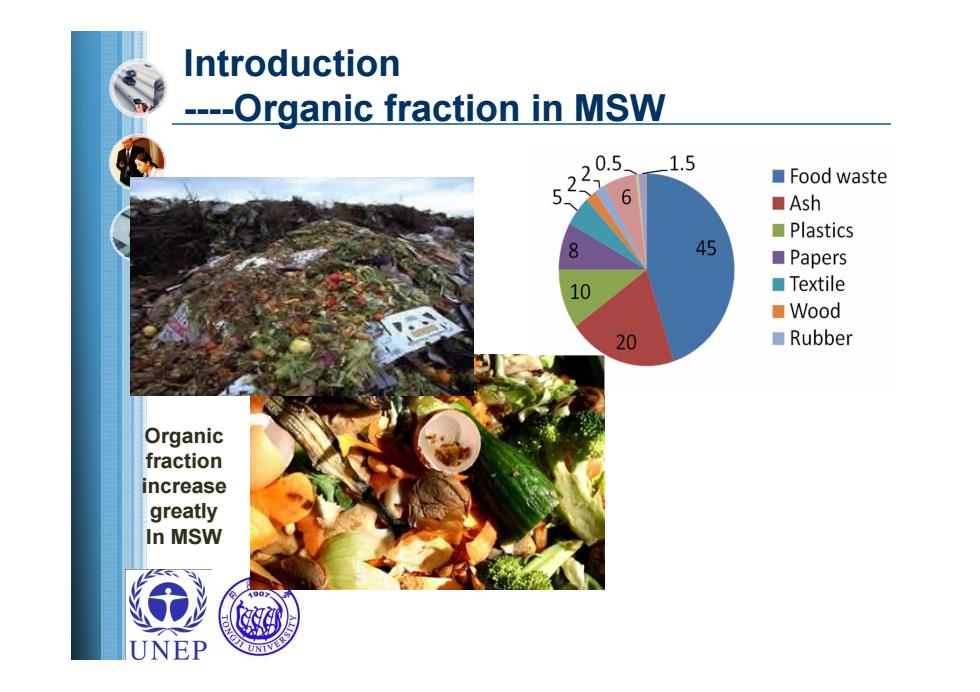
Introduction ----Organic fraction in MSW 0.5 1.5 ■Food waste 51 Ash ■Plastics 8 45 ■Papers 10 ■Textile ■Wood 20 ■Rubber Organic fraction increase greatly In MSW UNEP
Introduction ----Organic fraction in MSW Organic fraction increase greatly In MSW

Why Compost? o Percentage of organic material increase o Agricultural wastes potential for nutrient pollution o Yard wastes-banned from landfills in some developed countries o Compost benefits to soil -11.4 kg N, 5.9kg P(as P2Os),and 3.2kg K (as K2O) per ton of compost o Environmental sustainability UNEP
Why Compost? Percentage of organic material increase Agricultural wastes potential for nutrient pollution Yard wastes – banned from landfills in some developed countries Compost benefits to soil – 11.4 kg N, 5.9kg P (as P 2 O 5), and 3.2kg K (as K 2O) per ton of compost Environmental sustainability

What is composting? UNEP
What is composting?
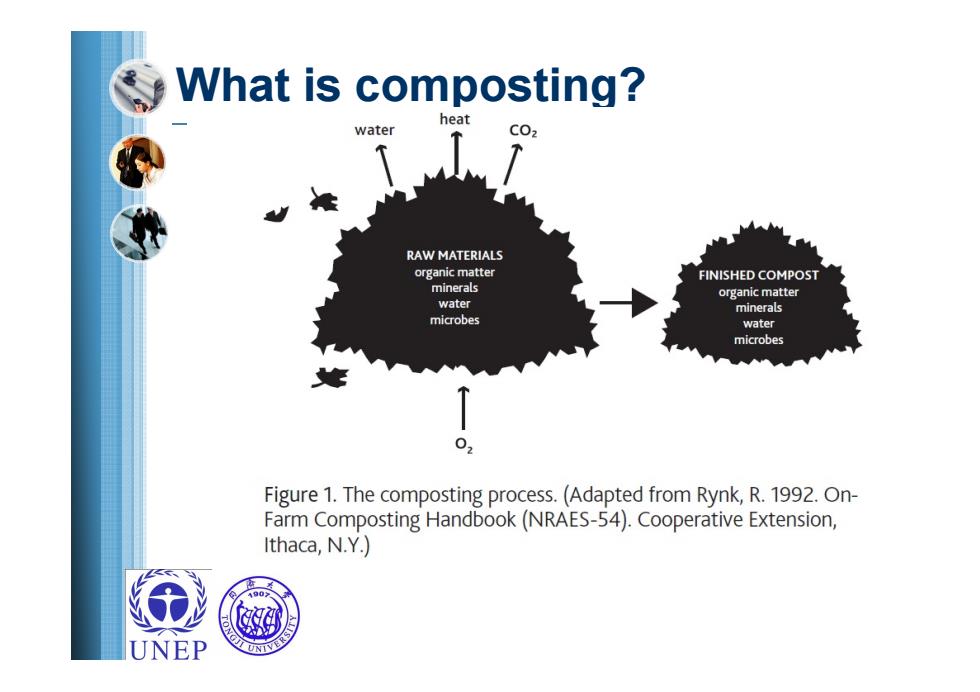
What is composting? heat water C02 RAW MATERIALS organic matter FINISHED COMPOST minerals organic matter water minerals microbes water microbes 0 Figure 1.The composting process.(Adapted from Rynk,R.1992.On- Farm Composting Handbook(NRAES-54).Cooperative Extension, Ithaca,N.Y.) UNEP
What is composting?

Introduction o Composting is an aerobic process,that gives rise to partially decomposed organic fraction of the MSW. o Composting is often promoted as a "natural"process of solid waste treatment because compost piles can be readily constructed in the backyard,and the product is a useful soil conditioner. o It saves communities'money that would be used in burning of MSW and land 趣g UNEP
Introduction Composting is an aerobic process, that gives rise to partially decomposed organic fraction of the MSW. Composting is often promoted as a “natural” process of solid waste treatment because compost piles can be readily constructed in the backyard, and the product is a useful soil conditioner. It saves communities’ money that would be used in burning of MSW and land filling

PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSTING UNEP
PRINCIPLES OF COMPOSTING

Principles of Composting o Organic Materials Landfilled wastes (food,wood, textiles,sludges,etc.) Agricultural wastes (plant or animal) Industrial manufacturing byproducts Yard trimmings Seafood processing wastes In short,anything that can be biodegraded UNEP
Principles of Composting Organic Materials • Landfilled wastes (food, wood, textiles, sludges, etc.) • Agricultural wastes (plant or animal) • Industrial manufacturing byproducts •Yard trimmings • Seafood processing wastes • In short, anything that can be biodegraded
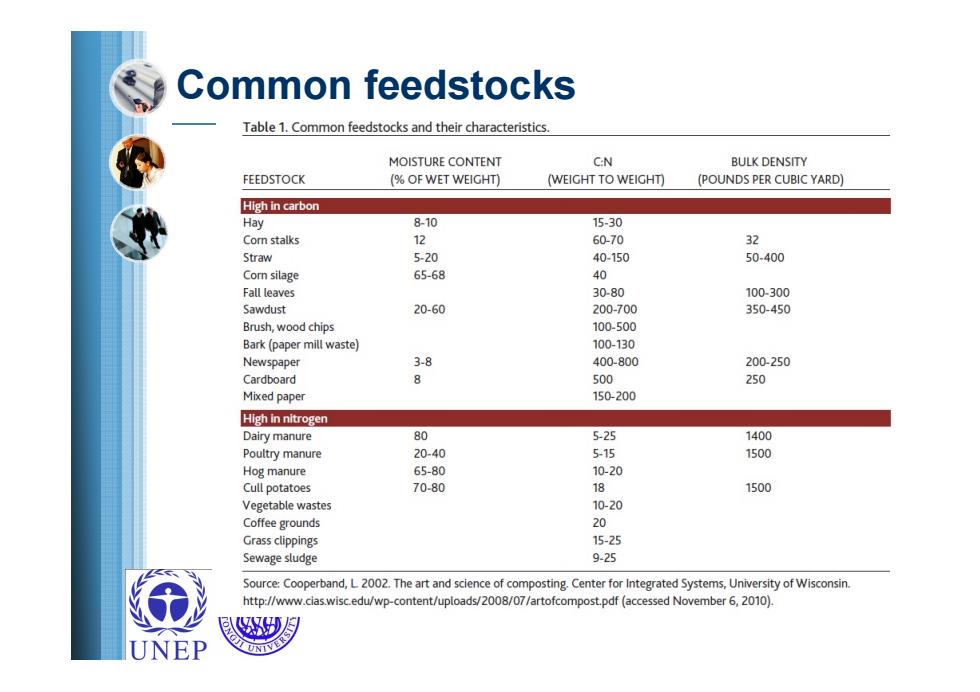
Common feedstocks Table 1.Common feedstocks and their characteristics. MOISTURE CONTENT CN BULK DENSITY FEEDSTOCK (OF WET WEIGHT) (WEIGHT TO WEIGHT) (POUNDS PER CUBIC YARD) High in carbon Hay 8-10 15-30 Corn stalks 12 60-70 Straw 520 40-150 50-400 Com silage 65-68 40 Fall leaves 30-80 100-300 Sawdust 20-60 200-700 350-450 Brush,wood chips 100-500 Bark(paper mill waste) 100-130 Newspaper 3-8 400-800 200-250 Cardboard 8 500 250 Mixed paper 150-200 High in nitrogen Dairy manure 80 5-25 1400 Poultry manure 20-40 515 1500 Hog manure 65-80 10-20 Cull potatoes 70-80 18 1500 Vegetable wastes 10-20 Coffee grounds 20 Grass clippings 15-25 Sewage sludge 9-25 Source:Cooperband,L 2002.The art and science of composting.Center for Integrated Systems,University of Wisconsin. http://www.cias.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2008/07/artofcompost.pdf(accessed November 6,2010). UNEP
Common feedstocks