
同济经管 TONGJI SEM MANAGEMENT OF TECHNOLOGICAL INNOVATION Professor CHEN Song(陈松),Ph.D. School of Economics Management, Tongji University chens@tongji.edu.cn Professor WANG Qing,Ph.D Warwick Business School, University of Warwick Qing.Wang@wbs.ac.uk April 2013 EOUIS
1 MANAGEMENT OF TECHNOLOGICAL INNOVATION Professor CHEN Song (陈 松),Ph.D. School of Economics & Management, Tongji University chens@tongji.edu.cn Professor WANG Qing,Ph.D. Warwick Business School, University of Warwick Qing.Wang@wbs.ac.uk April 2013

同济经管 TONGJI SEM Chapter 1 490 Introduction EOUIS
Chapter 1 Introduction

同济经管 TONGJI SEM Importance of Technological Innovation Technological innovation now the single most important driver of competitive success in many industries -Many firms earn over one-third of sales on products developed within last five years -Product innovations help firms protect margins by offering new,differentiated features. -Process innovations help make manufacturing more efficient. EFMC EQUIS 6
6 Importance of Technological Innovation Technological innovation now the single most important driver of competitive success in many industries – Many firms earn over one-third of sales on products developed within last five years – Product innovations help firms protect margins by offering new, differentiated features. – Process innovations help make manufacturing more efficient

同济经管 TONGJI SEM Importance of Technological Innovation -Advances in information technology have enabled faster innovation CAD/CAM systems enable rapid design and shorter production runs -Importance of innovation and advances in information technology have lead to: Shorter product lifecycles(more rapid product obsolescence) More rapid new product introductions Greater market segmentation EQUIS
7 Importance of Technological Innovation –Advances in information technology have enabled faster innovation • CAD/CAM systems enable rapid design and shorter production runs –Importance of innovation and advances in information technology have lead to: • Shorter product lifecycles (more rapid product obsolescence) • More rapid new product introductions • Greater market segmentation

同济经管 TONGJI SEM Impact on Society -Innovation enables a wider range of goods and services to be delivered to people worldwide -More efficient food production,improved medical technologies,better transportation,etc. -Increases Gross Domestic Product by making labor and capital more effective and efficient -However,may result in negative externalities. E.g.,pollution,erosion,antibiotic-resistant bacteria EQUIS 8
8 Impact on Society Innovation enables a wider range of goods and services to be delivered to people worldwide – More efficient food production, improved medical technologies, better transportation,etc. – Increases Gross Domestic Product by making labor and capital more effective and efficient – However, may result in negative externalities, • E.g., pollution, erosion, antibiotic-resistant bacteria

同济经管 Impact on Society TONGJI SEM The majority of R&D funds spent in OECD countries come from industry,and percentage has been increasing. A90> FIGURE 1.2 Percentage of R&D Funds 70.0 from Industry 60.0 Government, 50.0 and Other 40.0 Sources,for OECD 30.0 countries. 20.0 1982-2000 10.0 0.0 Source:Science g的ocs的s9 Board. Government Industry- Other 9 EOUIS
9 Impact on Society The majority of R&D funds spent in OECD countries come from industry, and percentage has been increasing
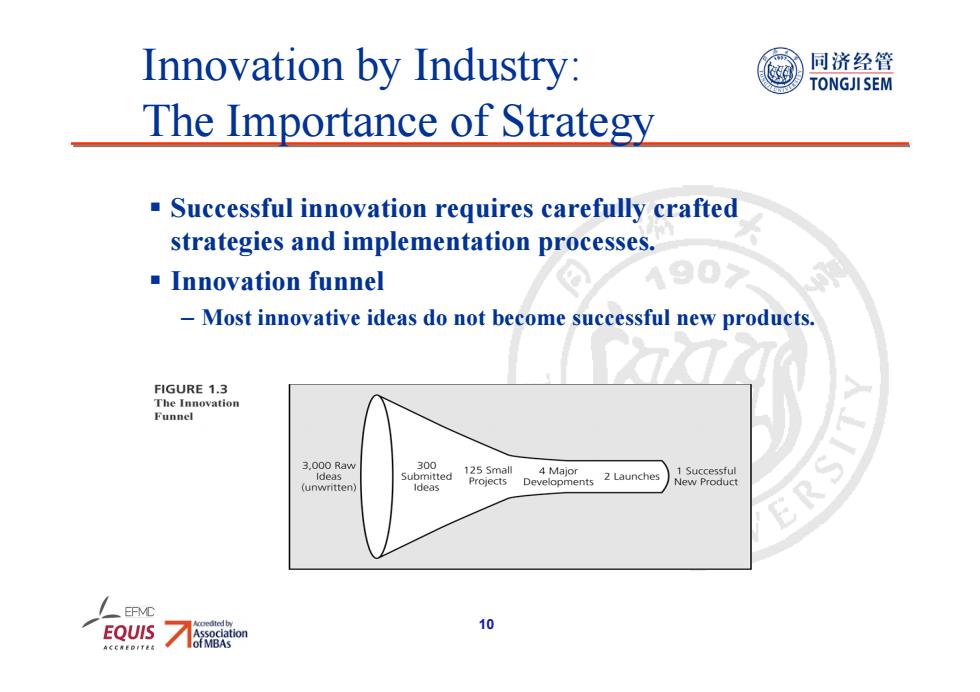
Innovation by Industry: 同济经管 TONGJI SEM The Importance of Strategy Successful innovation requires carefully crafted strategies and implementation processes. Innovation funnel Most innovative ideas do not become successful new products. FIGURE 1.3 The Innovation Funnel 3,000Raw 300 Developments 2 Launches 4 Major 1 Successful New Product ERS EOUIS 10
10 Innovation by Industry: The Importance of Strategy Successful innovation requires carefully crafted strategies and implementation processes. Innovation funnel – Most innovative ideas do not become successful new products

同济经管 Research Brief TONGJI SEM How long does new product development take? -Study by Abbie Griffin of 116 firms found: Length of development cycle varies with innovativeness of project Incremental improvements took 8.6 months from concept to market introduction Next generation improvements took 22 months. New-to-the-firm product lines took 36 months New-to-the-world products took 53 months. Half of the companies had reduced their cycle time by an average of 33%over last five years. EQUIS 11
11 How long does new product development take? –Study by Abbie Griffin of 116 firms found: • Length of development cycle varies with innovativeness of project • Incremental improvements took 8.6 months from concept to market introduction • Next generation improvements took 22 months. • New-to-the-firm product lines took 36 months • New-to-the-world products took 53 months. • Half of the companies had reduced their cycle time by an average of 33% over last five years. Research Brief

同济经管 Discussion Questions TONGJI SEM 1.Why is innovation so important for firms to compete in many industries? A90 2.What are some of the advantages of technological innovation?Disadvantages? 3.Why do you think so many innovation projects fail to generate an economic return? EFMC EQUIS 12
12 Discussion Questions 1. Why is innovation so important for firms to compete in many industries? 2. What are some of the advantages of technological innovation? Disadvantages? 3. Why do you think so many innovation projects fail to generate an economic return?

Industry Dynamics of Technological 同济经管 TONGJI SEM Innovation The sources from which innovation arises,including the role of individuals,organizations,government institutions,and networks, A8 Types of innovations,and common industry patterns of technological evolution and diffusion, The factors that determine whether industries experience pressure to select a dominant design,and what drives which technologies dominate others, Effects of timing of entry,and how firms can identify (and manage)their entry options. EFMC EQUIS 13
13 Industry Dynamics of Technological Innovation The sources from which innovation arises, including the role of individuals, organizations, government institutions, and networks, Types of innovations, and common industry patterns of technological evolution and diffusion, The factors that determine whether industries experience pressure to select a dominant design, and what drives which technologies dominate others, Effects of timing of entry, and how firms can identify (and manage) their entry options