
同济经管 TONGJI SEM CHAPTER 6 DEFINING THE ORGANIZATION'S STRATEGIC DIRECTION ----Assessing the firm's position and defining its strategic direction EOUIS
CHAPTER 6 DEFINING THE ORGANIZATION’S STRATEGIC DIRECTION ----Assessing the firm’s position and defining its strategic direction

同济经管 Overview TONGJI SEM A coherent technological innovation strategy leverages the firm's existing competitive position and provides direction for future development of the firm. Formulating this strategy requires: -Appraising the firm's environment, -Appraising the firm's strengths,weaknesses,competitive advantages,and core competencies. -Articulating an ambitious strategic intent. /EFMC EQUIS 2
2 Overview A coherent technological innovation strategy leverages the firm’s existing competitive position and provides direction for future development of the firm. Formulating this strategy requires: – Appraising the firm’s environment, – Appraising the firm’s strengths, weaknesses, competitive advantages, and core competencies, – Articulating an ambitious strategic intent

同济经管 Assessing the Firm's Current Position TONGJI SEM External Analysis Two common methods are Porter's Five-Force Model and Stakeholder Analysis. Porter's Five-Force Model A90 1.Degree of existing rivalry.Determined by number of firms, relative size,degree of differentiation between firms,demand conditions,exit barriers. 2.Threat of potential entrants.Determined by attractiveness of industry,height of entry barriers(e.g.,start-up costs,brand loyalty,regulation,etc.) 3. Bargaining power of suppliers.Determined by number of suppliers and their degree of differentiation,the portion of a firm's inputs obtained from a particular supplier,the portion of a supplier's sales sold to a particular firm,switching costs,and potential for vertical integration. EOUIS 3
3 Assessing the Firm’s Current Position External Analysis – Two common methods are Porter’s Five-Force Model and Stakeholder Analysis. – Porter’s Five-Force Model 1. Degree of existing rivalry. Determined by number of firms, relative size, degree of differentiation between firms, demand conditions, exit barriers. 2. Threat of potential entrants. Determined by attractiveness of industry, height of entry barriers (e.g., start-up costs, brand loyalty, regulation, etc.) 3. Bargaining power of suppliers. Determined by number of suppliers and their degree of differentiation, the portion of a firm’s inputs obtained from a particular supplier, the portion of a supplier’s sales sold to a particular firm, switching costs, and potential for vertical integration

同济经管 Assessing the Firm's Current Position TONGJI SEM 4. Bargaining power of buyers.Determined by number of buyers, the firm's degree of differentiation,the portion of a firm's inputs sold to a particular buyer,the portion of a buyer's purchases bought from a particular firm,switching costs,and potential for vertical integration. 5. Threat of substitutes.Determined by number of potential substitutes,their closeness in function and relative price. Recently Porter has acknowledged the role of complements.Must consider: a)whether complements are differentially available for the products of various rivals(impacting the attractiveness of their goods),and b)how important complements are in the industry, who captures the value offered by the complements. EQUIS 4
4 Assessing the Firm’s Current Position 4. Bargaining power of buyers. Determined by number of buyers, the firm’s degree of differentiation, the portion of a firm’s inputs sold to a particular buyer, the portion of a buyer’s purchases bought from a particular firm, switching costs, and potential for vertical integration. 5. Threat of substitutes. Determined by number of potential substitutes, their closeness in function and relative price. Recently Porter has acknowledged the role of complements. Must consider: a) whether complements are differentially available for the products of various rivals (impacting the attractiveness of their goods), and b) how important complements are in the industry, c) who captures the value offered by the complements

同济经管 Assessing the Firm's Current Position TONGJI SEM -Five-Force Model FIGURE 6.1 Porter's Five- Force Model hreat of Potent Source:Adapted with Entrants the permission of The Free Press,a Division of Simon Schuster Adult Publishing Group,from Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Bargaining Power egree of Existi Bargaining Analyzing Industries of Suppliers Rrvalry Power of Buyers etitors by Michael E.Port Threat of Substitutes 5 EOUIS
5 Assessing the Firm’s Current Position Five-Force Model

同济经管 Assessing the Firm's Current Position TONGJI SEM Stakeholder Analysis 1.Who are the stakeholders. FIGURE 6.2 Stakeholder stomer Analysis ploye 2.What does each stakeholder want. Local 3.What resources Stockholders do they contribute to the vernm organization. 4.What claims are they likely to make on the organization. EFMC EQUIS 6
6 Assessing the Firm’s Current Position Stakeholder Analysis 1. Who are the stakeholders. 2. What does each stakeholder want. 3. What resources do they contribute to the organization. 4. What claims are they likely to make on the organization

同济经管 Assessing the Firm's Current Position TONGJI SEM ■ Internal Analysis 1.Identify the firm's strengths and weaknesses.Helpful to consider each element of value chain. FIGURE 6.3 Porter's Value Chain Source:Adapted with the permission of The Free Press,a Division of Simon Schuster Adult Publishing Group.from Comperirive Advantage:Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance by Michael E.Proter.Copyright 1985,1998 by Michael E.Porter. Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Management Technology Development Procurement Inbound Operations Outbound Marketing Service Logistics Logistics
7 Assessing the Firm’s Current Position Internal Analysis 1. Identify the firm’s strengths and weaknesses. Helpful to consider each element of value chain

同济经管 Assessing the Firm's Current Position TONGJI SEM 2.Assess which strengths have potential to be sustainable competitive advantage ·Rare Competitive ·Valuable Advantage Sustainable Competitive ·Durable Advantage ·Inimitable -Resources are difficult(or impossible)to imitate when they are: Tacit -Path dependent Socially complex EFMC -Causally ambiguous EQUIS 16熙oa 8
8 2. Assess which strengths have potential to be sustainable competitive advantage • Rare • Valuable • Durable • Inimitable –Resources are difficult (or impossible) to imitate when they are: – Tacit – Path dependent – Socially complex – Causally ambiguous Assessing the Firm’s Current Position Competitive Advantage Sustainable Competitive Advantage

同济经管 Identifying Core Competencies TONGJI SEM -Core Competencies:A set of integrated and harmonized abilities that distinguish the firm in the marketplace. Competencies typically combine multiple kinds of abilities. Several core competencies may underlie a business unit. Several business units may draw from same competency. Core competencies should: Be a significant source of competitive differentiation -Cover a range of businesses Be hard for competitors to imitate dted by EOUIS
9 Identifying Core Competencies Core Competencies: A set of integrated and harmonized abilities that distinguish the firm in the marketplace. • Competencies typically combine multiple kinds of abilities. • Several core competencies may underlie a business unit. • Several business units may draw from same competency. • Core competencies should: – Be a significant source of competitive differentiation – Cover a range of businesses – Be hard for competitors to imitate
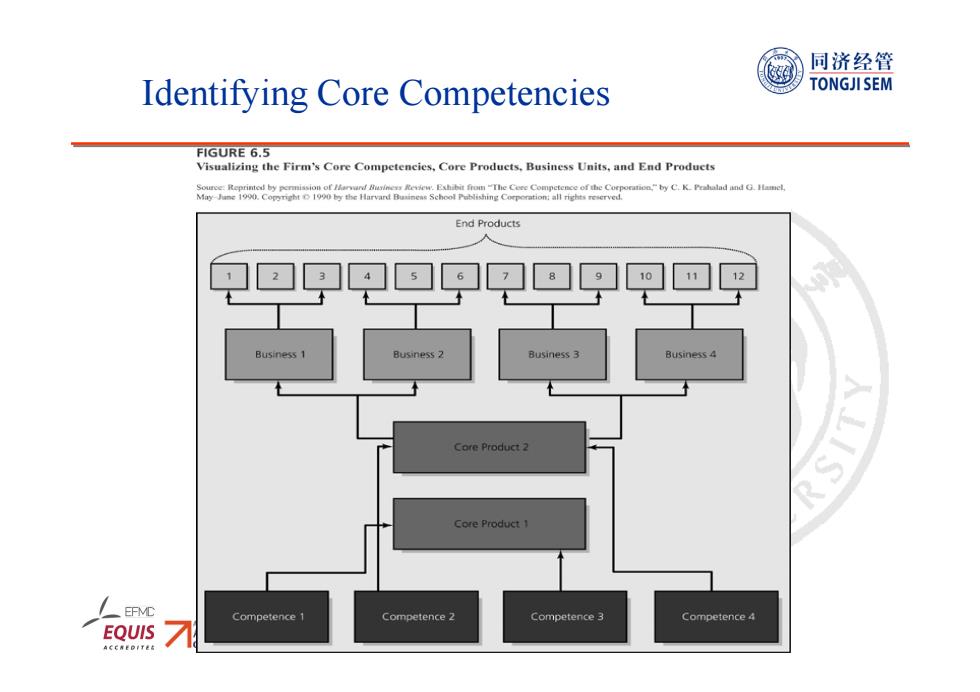
同济经管 Identifying Core Competencies TONGJI SEM FIGURE 6.5 Visualizing the Firm's Core Competencies,Core Produets.Business Units,and End Products End Products 245☑6?☑8☑☐2 Core Product 2 Core Product 1 /EFMC Competence Competence 2 Competence 3 Competence 4 EQUIS
10 Identifying Core Competencies