
-Agenda -Discuss the case of food and beverage forecasting -Discuss the case of forecasting of wind power capacity in China -Discuss the details of simple linear regression -Multiple Regression
Agenda Discuss the case of food and beverage forecasting Discuss the case of forecasting of wind power capacity in China Discuss the details of simple linear regression Multiple Regression

寻 Session 11 Simple Linear Regression
Session 11 Simple Linear Regression

Learning Objectives In this chapter, you learn: To use regression analysis to predict the value of a dependent variable based on an independent variable The meaning of the regression coefficients bo and b . To evaluate the assumptions of regression analysis and know what to do if the assumptions are violated . To make inferences about the slope and correlation coefficient . To estimate mean values and predict individual values
Learning Objectives
Correlation vs.Regression A scatter plot (or scatter diagram)can be used to show the relationship between two numerical variables Correlation analysis is used to measure strength of the association (linear relationship) between two variables Correlation is only concerned with strength of the relationship No causal effect is implied with correlation Correlation was first presented in Chapter 3
Correlation vs. Regression A scatter plot (or scatter diagram) can be used to show the relationship between two numerical variables Correlation analysis is used to measure strength of the association (linear relationship) between two variables Correlation is only concerned with strength of the relationship No causal effect is implied with correlation Correlation was first presented in Chapter 3

Regression Analysis Regression analysis is used to: Predict the value of a dependent variable based on the value of at least one independent variable Explain the impact of changes in an independent variable on the dependent variable Dependent variable:the variable you wish to explain Independent variable:the variable used to explain the dependent variable
Regression Analysis Regression analysis is used to: Predict the value of a dependent variable based on the value of at least one independent variable Explain the impact of changes in an independent variable on the dependent variable Dependent variable: the variable you wish to explain Independent variable: the variable used to explain the dependent variable
Simple Linear Regression Model Only one independent variable,X Relationship between X and Y is described by a linear function Changes in Y are related to changes in X
Simple Linear Regression Model Only one independent variable, X Relationship between X and Y is described by a linear function Changes in Y are related to changes in X

Types of Relationships Linear relationships Curvilinear relationships
Types of Relationships Y X Y X Y Y X X Linear relationships Curvilinear relationships
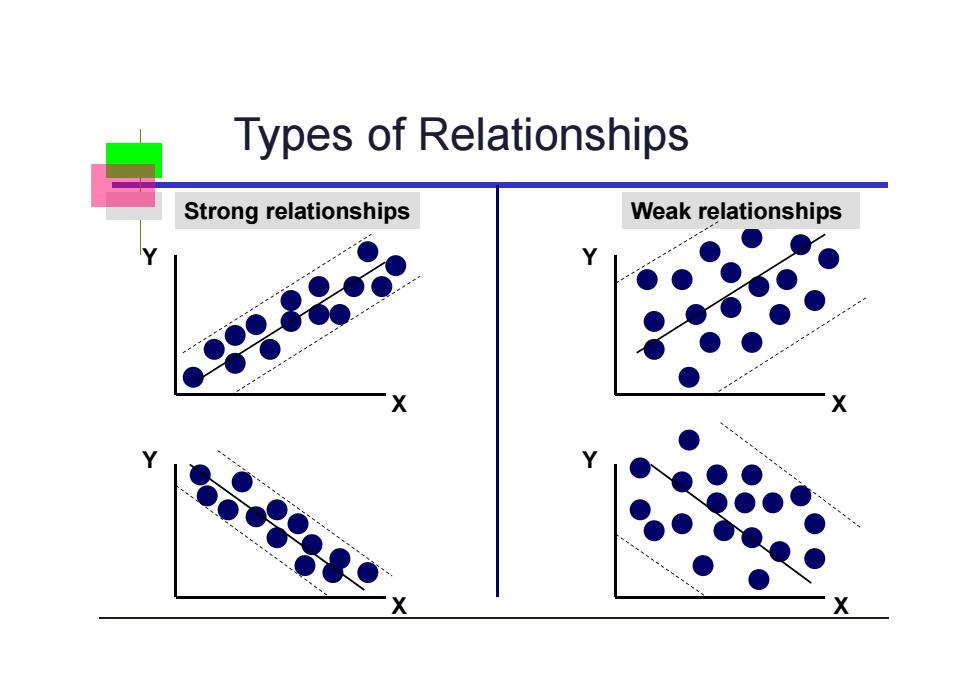
Types of Relationships Strong relationships Weak relationships
Types of Relationships Y X Y X Y Y X X Strong relationships Weak relationships

Types of Relationships No relationship 8988 X
Types of Relationships Y X Y X No relationship
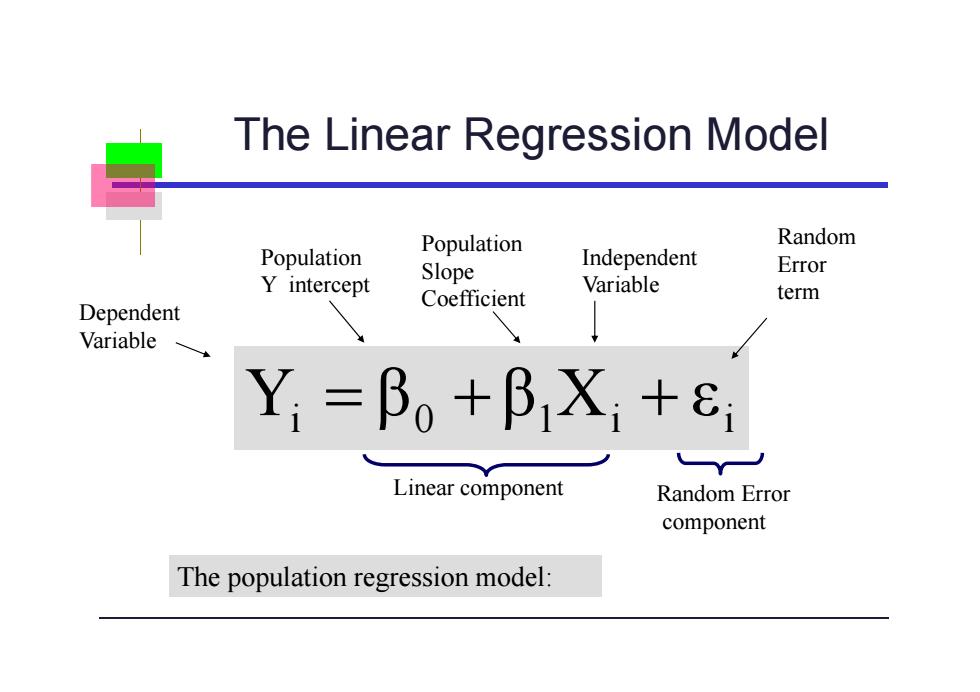
The Linear Regression Model Population Random Population Slope Independent Error Y intercept Variable Coefficient term Dependent Variable Yi=Bo+BXi+ Linear component Random Error component The population regression model:
The Linear Regression Model i 0 1 i i Y β β X ε Linear component The population regression model: Population Y intercept Population Slope Coefficient Random Error term Dependent Variable Independent Variable Random Error component