
电子件发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC Chapter06 Color mage Processing 张萍 电子科技大学光电科学与工程学院 E-mail:pingzh@uestc.edu.cn
张 萍 电子科技大学 光电科学与工程学院 E-mail: pingzh@uestc.edu.cn

电子转技女草光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 为什么,要研究彩色图像处理? 符合人类视觉特点 >人类可以辨别几千种颜色色调和亮度 只能辨别几十种灰度层次 ■有用的描述子 ,简化目标物的区分 ,目标识别:根据目标的颜色特征
◼ 符合人类视觉特点 ➢ 人类可以辨别几千种颜色色调和亮度 ➢ 只能辨别几十种灰度层次 ◼ 有用的描述子 ➢ 简化目标物的区分 ➢ 目标识别:根据目标的颜色特征 为什么要研究彩色图像处理?

电子科发女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 彩色图像处理的两个主要领域: 全彩色处理 ,图像用全彩色传感器获取,如数码 相机和彩色扫描仪 伪彩色处理 ,对特定的单一亮度或亮度范围赋予 一种颜色
◼ 全彩色处理 ➢ 图像用全彩色传感器获取,如数码 相机和彩色扫描仪 ◼ 伪彩色处理 ➢ 对特定的单一亮度或亮度范围赋予 一种颜色 彩色图像处理的两个主要领域:
电子科妓女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC Outline Color Fundamentals Color Models Pseudocolor Image Processing 楚 Basics of Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformations Smoothing and Sharpening ◆ Image Segmentation Based on Color 应 ◆ Noise in Color Images Color Image Compression
Outline ◆ Color Fundamentals ◆ Color Models ◆ Pseudocolor Image Processing ◆ Basics of Full-Color Image Processing ◆ Color Transformations ◆ Smoothing and Sharpening ◆ Image Segmentation Based on Color ◆ Noise in Color Images ◆ Color Image Compression 基 础 应 用

电子科技女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 6,7 Color Fundamentals FIGURE 6.1 Color spectrum seen by passing white INFRARED light through a prism.(Courtesy of the General Electric Co., WHITE LIGHT Lamp Business Division.) OPTICAL PRISM ULTRAVIOLET In 1666,Sir Isaac Newton,24 year old,discovered white light spectrum. Isaac Newton (1643-1727)
6.1 Color Fundamentals Isaac Newton (1643-1727) In 1666, Sir Isaac Newton, 24 year old, discovered white light spectrum
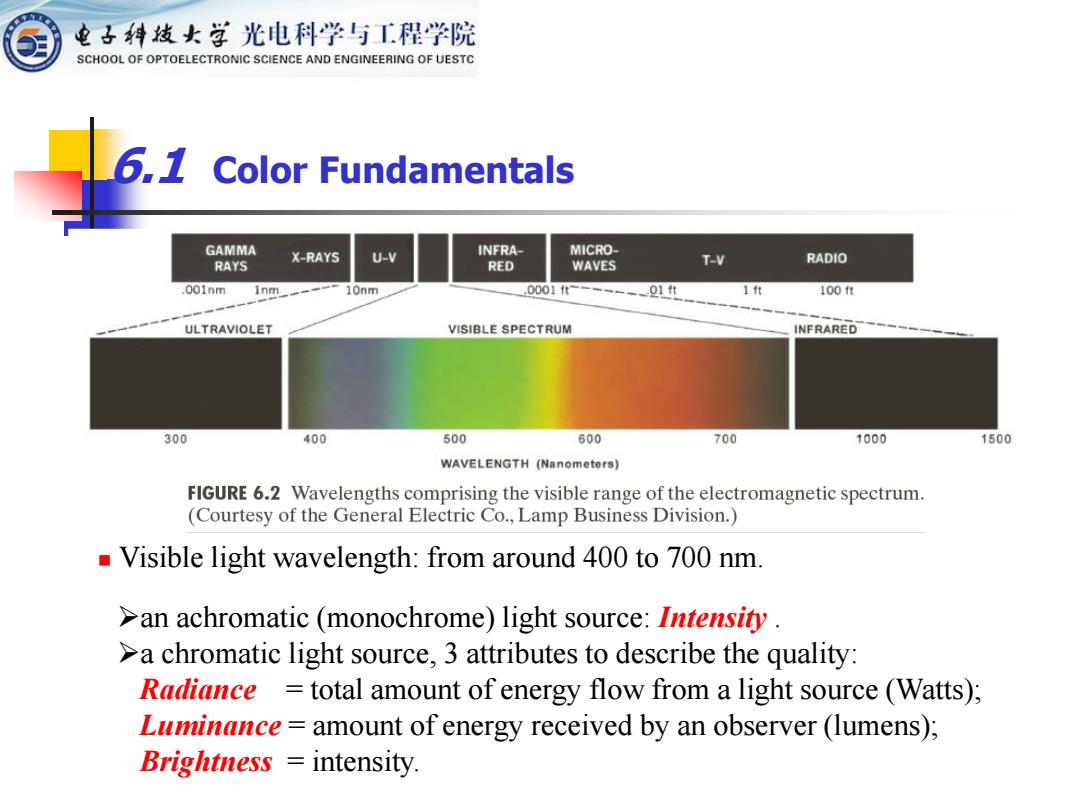
电子科妓女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 6,7 Color Fundamentals GAMMA X-RAYS U-V INFRA- MICRO- RAYS RED WAVES T-V RADIO 001nm 1nm 10nm .0001ft 1 ft 100ft ULTRAVIOLET VISIBLE SPECTRUM INFRARED 300 400 500 600 700 1000 1500 WAVELENGTH (Nanometers) FIGURE 6.2 Wavelengths comprising the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. (Courtesy of the General Electric Co.,Lamp Business Division.) Visible light wavelength:from around 400 to 700 nm. >an achromatic (monochrome)light source:Intensity. >a chromatic light source,3 attributes to describe the quality: Radiance total amount of energy flow from a light source (Watts); Luminance amount of energy received by an observer(lumens); Brightness intensity
6.1 Color Fundamentals ◼ Visible light wavelength: from around 400 to 700 nm. ➢an achromatic (monochrome) light source: Intensity . ➢a chromatic light source, 3 attributes to describe the quality: Radiance = total amount of energy flow from a light source (Watts); Luminance = amount of energy received by an observer (lumens); Brightness = intensity
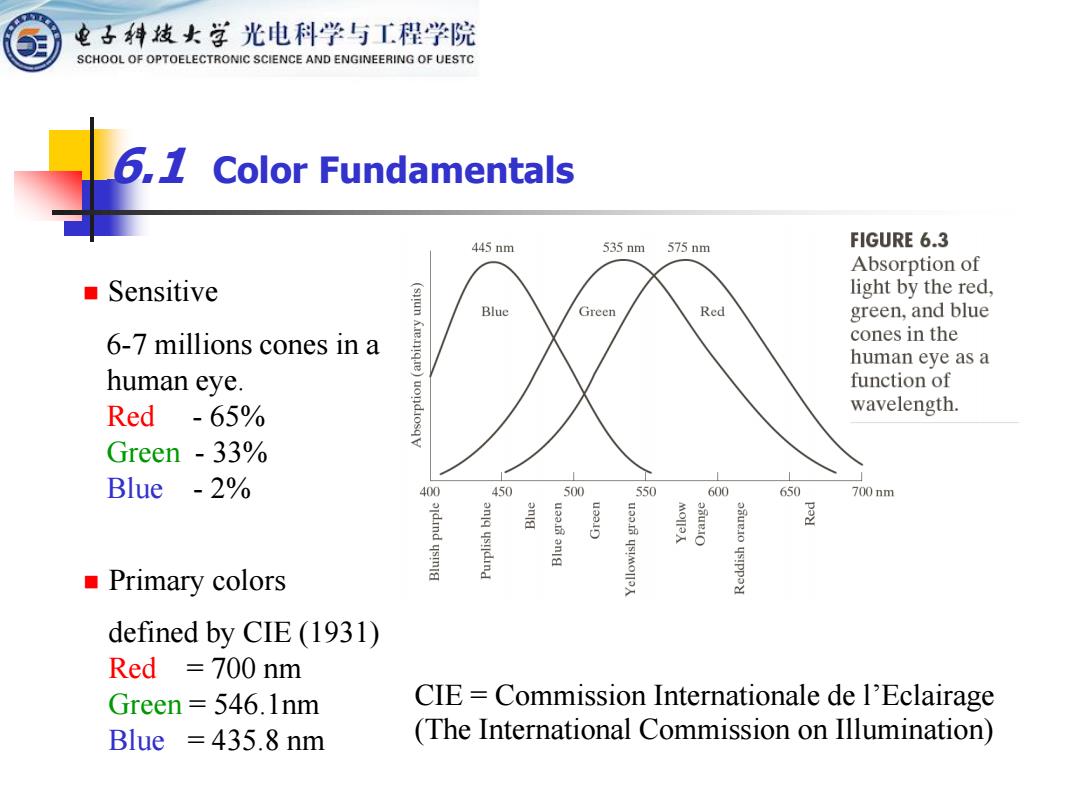
电子科妓女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 6,1 Color Fundamentals 445nm 535nm 575nm FIGURE 6.3 Absorption of Sensitive light by the red, Blue Green Red green,and blue 6-7 millions cones in a cones in the human eye as a human eye. function of Red -65% wavelength. Green -33% Blue -2% 400 450 500 550 600 650 700nm 盖 ysydind ■Primary colors defined by CIE(1931) Red =700 nm Green 546.1nm CIE Commission Internationale de l'Eclairage Blue =435.8 nm (The International Commission on Illumination)
6.1 Color Fundamentals defined by CIE (1931) Red = 700 nm Green = 546.1nm Blue = 435.8 nm CIE = Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage (The International Commission on Illumination) 6-7 millions cones in a human eye. Red - 65% Green - 33% Blue - 2% ◼ Primary colors ◼ Sensitive
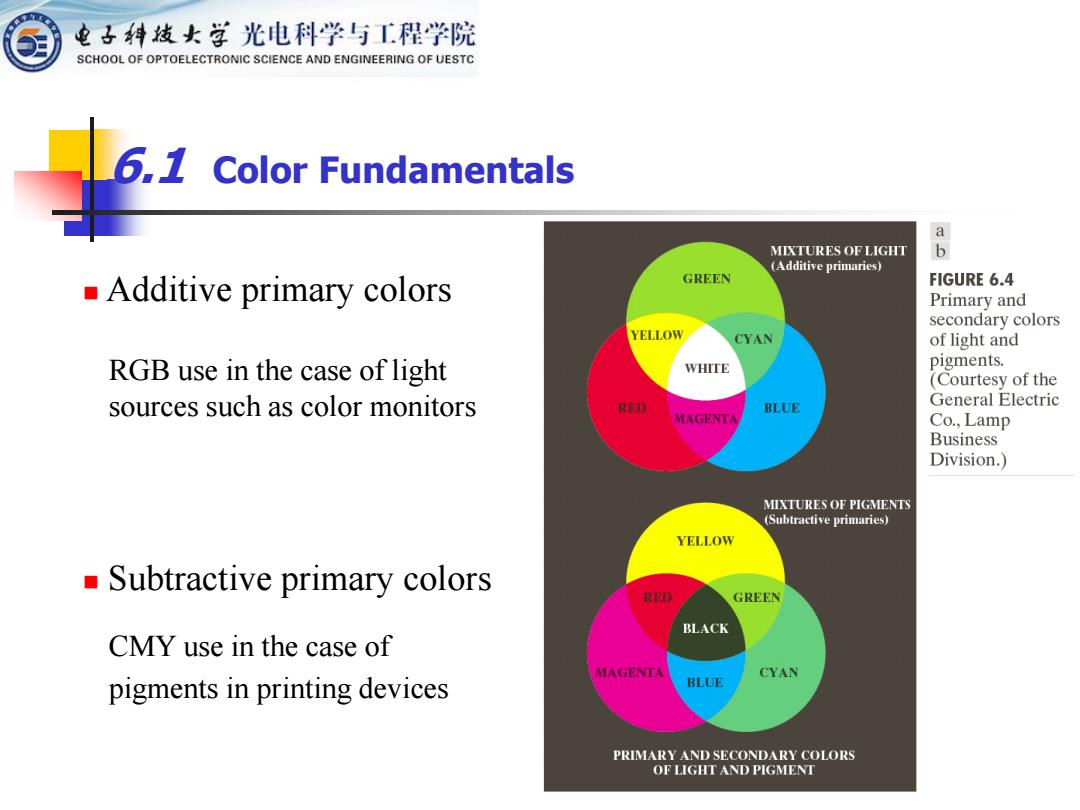
电子科妓女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 6,1 Color Fundamentals MIXTURES OF LIGHT b (Additive primaries) Additive primary colors GREEN FIGURE 6.4 Primary and secondary colors YELLOW CYAN of light and RGB use in the case of light WHITE pigments. (Courtesy of the sources such as color monitors BLUE General Electric MAGENTA Co.,Lamp Business Division.) MIXTURES OF PIGMENTS (Subtractive primaries) YELLOW Subtractive primary colors GREEN BLACK CMY use in the case of MAGENTA CYAN pigments in printing devices BLUE PRIMARY AND SECONDARY COLORS OF LIGHT AND PIGMENT
6.1 Color Fundamentals RGB use in the case of light sources such as color monitors CMY use in the case of pigments in printing devices ◼ Additive primary colors ◼ Subtractive primary colors
电子科妓女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC Color Characterization Brightness:Intensity. ■Hue: Dominant color corresponding to a dominant wavelength of mixture light wave. Saturation: Relative purity or amount of white light mixed with a hue (inversely proportional to amount of white light added) Hue }hrom(色度) Saturation Amount of red (X),green (Y)and blue (Z)to form any particular color is called Tristimulus(三色激劢)
◼ Brightness: Intensity. ◼ Hue: Dominant color corresponding to a dominant wavelength of mixture light wave. ◼ Saturation: Relative purity or amount of white light mixed with a hue (inversely proportional to amount of white light added). Color Characterization Hue Saturation Chromaticity (色度) Amount of red (X), green (Y) and blue (Z) to form any particular color is called Tristimulus(三色激励)
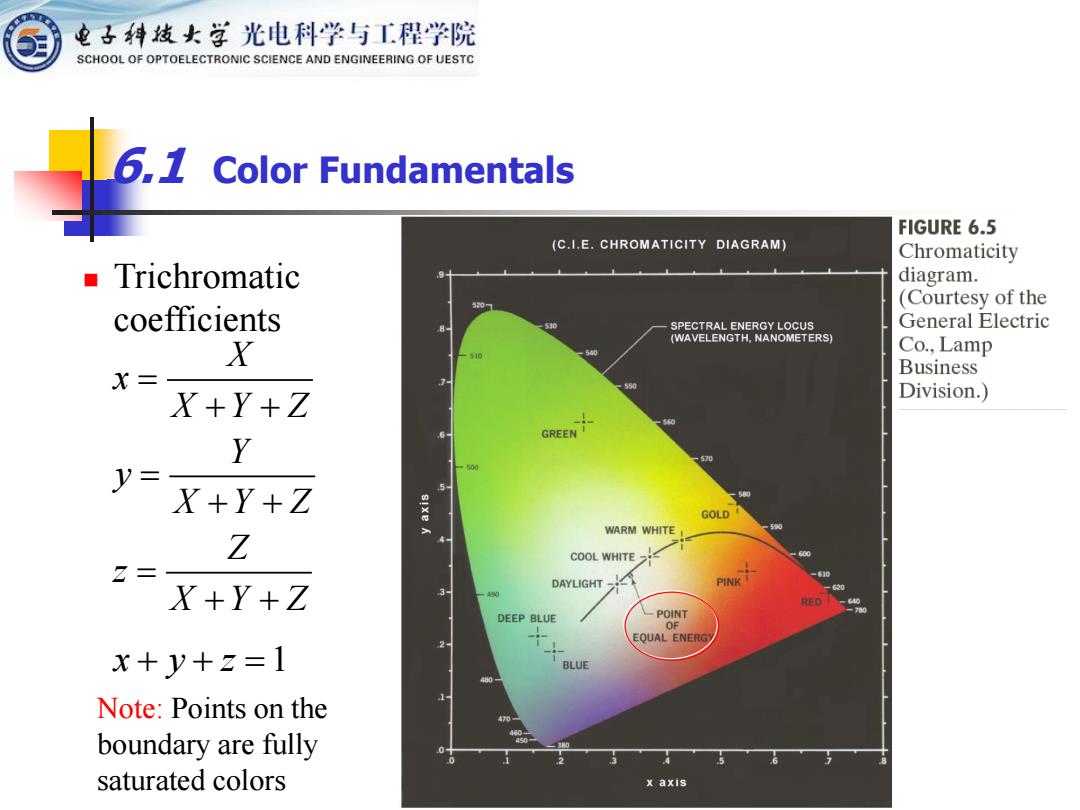
电子科技女学光电科学与工程学院 SCHOOL OF OPTOELECTRONIC SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING OF UESTC 6,1 Color Fundamentals FIGURE 6.5 (C.I.E.CHROMATICITY DIAGRAM) Chromaticity ■Trichromatic diagram. 530 (Courtesy of the coefficients SPECTRAL ENERGY LOCUS General Electric (WAVELENGTH,NANOMETERS) X Co.,Lamp X= Business X+Y+Z Division.) Y 570 y= X+Y+Z GOLD WARM WHITE Z COOL WHITE Z= DAYLIGHT-1 PINK X+Y+Z 69 4 RED DEEP BLUE POINT OF EQUAL ENERG x+y+z=1 BLUE Note:Points on the boundary are fully saturated colors x axis
6.1 Color Fundamentals ◼ Trichromatic coefficients X x X Y Z Y y X Y Z Z z X Y Z = + + = + + = + + x + y + z =1 Note: Points on the boundary are fully saturated colors