
《经济学原理(英)》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 课程代码:16127002 课程名称:经济学原理(英〉 英文名称:Principles of Economics 课程类别:专业课选修课 学时:32 学分:2 适用对象:商务英语专业学生 考核方式:考试 先修课程:综合英语,高等数学 二、课程简介 《经济学原理(革)》品面向广东财经大学商条革语专业高年级学生所开设的 门专业基础必修理论课程。该课程是商务英语专业的核心基础课程,在专业课 程体系中起承前启后的作用。内容较多,难度较大。其基本内容包括:微观经济 学和宏观经济学两部分经济学。微观经济学包括的内容相当广泛,其中主要有 均、衡价格理论、消费者行为理论、生产者行为理论(包括生产理论、成本理论 和市场均衡理论)、分配理论一般均衡理论与福利经济学、市场失灵与微观经济 学政策。宏观经济学,是以国民经济总过程的 活动为研究对象,主要考察就业总 水平、国民总收入等经济总量,因此,宏观经济学也被称做就业理论或收入丑 论。宏观经济学研究的是经济资源的利用问题,包括国民收入决定理论、就业 理论、通货膨胀理论、经济周期理论、经济增长理论、财政与货币政策。学习经 济学有助于帮助学生理解生活于其间的世界是如何运转的:学习经济学有助于理 解政府政策的优与劣:学习经济学可以改进你的思考方式,这些知识对学生将来 的职业规划,生活质量的提高起着决定性的作用 经济学作为一门解决资源配置和资源利用的社会科学,与人们的生活密切相 关,其基本概念和基本原理对人的价值观的形成和发展具有极大的引领作用。经 济学教学中始终坚持理论联系实际的理念,引导学生用经济学的思维来思考人 生。每一个经济学的知识点,都可以成为我们观察生活、分析社会和解读人生的 工具,将经济学理论和知识融入思政教 动是非常有必要的。课 堂案例源于社会但是 系和只点, 尤其多引用中国本土案例,引用中国特色社会 主义的经济案例,为学生带来经济学的亲切感。 Set especially students of business English major in e and Ec onomics the subject of Principles of
1 《经济学原理(英)》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息 课程代码: 16127002 课程名称: 经济学原理(英) 英文名称: Principles of Economics 课程类别:专业课选修课 学 时:32 学 分:2 适用对象:商务英语专业学生 考核方式:考试 先修课程:综合英语,高等数学 二、课程简介 《经济学原理(英)》是面向广东财经大学商务英语专业高年级学生所开设的 一门专业基础必修理论课程。该课程是商务英语专业的核心基础课程,在专业课 程体系中起承前启后的作用。内容较多,难度较大。其基本内容包括:微观经济 学和宏观经济学两部分经济学。微观经济学包括的内容相当广泛,其中主要有: 均、衡价格理论、消费者行为理论、生产者行为理论(包括生产理论、成本理论 和市场均衡理论)、分配理论一般均衡理论与福利经济学、市场失灵与微观经济 学政策。宏观经济学,是以国民经济总过程的活动为研究对象,主要考察就业总 水平、国民总收入等经济总量,因此,宏观经济学也被称做就业理论或收入理 论。 宏观经济学研究的是经济资源的利用问题,包括国民收入决定理论、就业 理论、通货膨胀理论、经济周期理论、经济增长理论、财政与货币政策。学习经 济学有助于帮助学生理解生活于其间的世界是如何运转的;学习经济学有助于理 解政府政策的优与劣;学习经济学可以改进你的思考方式,这些知识对学生将来 的职业规划,生活质量的提高起着决定性的作用。 经济学作为一门解决资源配置和资源利用的社会科学,与人们的生活密切相 关,其基本概念和基本原理对人的价值观的形成和发展具有极大的引领作用。经 济学教学中始终坚持理论联系实际的理念,引导学生用经济学的思维来思考人 生。每一个经济学的知识点,都可以成为我们观察生活、分析社会和解读人生的 工具,将经济学理论和知识融入思政教育变成一种教学活动是非常有必要的。课 堂案例源于社会但是紧扣知识点,尤其多引用中国本土案例,引用中国特色社会 主义的经济案例,为学生带来经济学的亲切感。 Set especially for the junior and senior students of business English major in Guangdong University of Finance and Economics, the subject of Principles of

Economics is identified as a compulsory basic theoretical course.This course is the cours of busines English major,which ting role in the studying.Its basic contents include:microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics includes a wide range of contents,for example,average and balanced price theory,consumer behavior theory,producer behavior theory (including production m theory distribution theor general equilibrium theory an welfare economics,market fa ilure an d microeco policies.Macroeconomics,taking the activities in the general process of national economy as the research obiect.mainly investigates the total emplovment level.gross national income and other economic aggregates.Therefore,macroeconomics is also called employment theory or income theory.Macroeconomics studies the utilization of econor rces,including nat income determinationt eory,emplo theory,inflation theory,economic cycle theory,economic growth theory,fiscal an monetary policies.Learning economics helps students understand how the world in which they live works.Learning economics helps to understand the advantages and disadvantages of govemment policies,Studyingeconomics can improve your way of thinking.This kr eplayof life ecisive roe in studentsfuture career planning and t o their qua y Economics.the social science that solves resource allocation and resource utilization,is closely related to people's lives.Its basic concepts and principles have a leading role in the formation and development of human values.When teaching Economics,we always adhere to the concept of integrating theory with practice and guide students to think about life with eco omic t nking.Ever knowledge point of economics can be a tool for us to observe life,analyze society,and interpret life.It is necessary to integrate economic theory and knowledge into ideological and political education into a teaching activity.Class cases originate from Chinese business but are closely related to knowledge points.In particular,we often cite local economic business to bring students a nse of intimacy in economics 三、课程性质与教学目的 (一)性质:经济学原理是经济学科中的一门基础学科。它是经济学、财经、 管理类各专业普遍开设的基础理论课程。在商务英语学习中,经济学原理处于基 础的地位,为商务英语学生准备经济学科方面的基础知识,为他们以后学习各专 业的专业基础课程和专业课程打下良好的基础。 (二)课程目1:理解和掌握有关微观经济学的基本概念、基本理论和基本 分析方法,了解微观经济学的基本架构和分析逻辑: 课程目标2:能够运用经济学原理观察、分析和解释现实生活中比较简单和 典型的经济现象和问题:
2 Economics is identified as a compulsory basic theoretical course. This course is the core basic course of business English major, which plays a connecting role in the professional curriculum system. There are many contents and difficulties for studying. Its basic contents include: microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics includes a wide range of contents, for example, average and balanced price theory, consumer behavior theory, producer behavior theory (including production theory, cost theory and market equilibrium theory), distribution theory, general equilibrium theory and welfare economics, market failure and microeconomic policies. Macroeconomics, taking the activities in the general process of national economy as the research object, mainly investigates the total employment level, gross national income and other economic aggregates. Therefore, macroeconomics is also called employment theory or income theory. Macroeconomics studies the utilization of economic resources, including national income determination theory, employment theory, inflation theory, economic cycle theory, economic growth theory, fiscal and monetary policies. Learning economics helps students understand how the world in which they live works. Learning economics helps to understand the advantages and disadvantages of government policies; Studying economics can improve your way of thinking. This knowledge plays a decisive role in students' future career planning and improvement of their quality of life. Economics, the social science that solves resource allocation and resource utilization, is closely related to people's lives. Its basic concepts and principles have a leading role in the formation and development of human values. When teaching Economics, we always adhere to the concept of integrating theory with practice and guide students to think about life with economic thinking. Every knowledge point of economics can be a tool for us to observe life, analyze society, and interpret life. It is necessary to integrate economic theory and knowledge into ideological and political education into a teaching activity. Class cases originate from Chinese business but are closely related to knowledge points. In particular, we often cite local economic business to bring students a sense of intimacy in economics. 三、课程性质与教学目的 (一)性质:经济学原理是经济学科中的一门基础学科。它是经济学、财经、 管理类各专业普遍开设的基础理论课程。在商务英语学习中,经济学原理处于基 础的地位,为商务英语学生准备经济学科方面的基础知识,为他们以后学习各专 业的专业基础课程和专业课程打下良好的基础。 (二)课程目1:理解和掌握有关微观经济学的基本概念、基本理论和基本 分析方法,了解微观经济学的基本架构和分析逻辑; 课程目标 2:能够运用经济学原理观察、分析和解释现实生活中比较简单和 典型的经济现象和问题;

课程目标3:初步培养学会运用经济学的基本方法、思维方式分析和解决我 国市场经济运行中存在的各种经济问题的能力,为进一步学习其他专业知识打下 一个坚实的基础。 课程目标4:使学生建立起经济学的基础知识框架,为进一步学习经济学及 其相关课程提供必要的知识和能力储备 课程目标5:运用马克思主义基本观点、立场和方法学习和理解掌握课程内 容重点,引入我国经济市场化改革和政府参与经济运行取得的成效,把社会主 义核心价值观内容融入教学内容,开展课堂教学。通过分析中国政府有效政策 实施和成功的中国企业运营等案例分析,增强学生对社会主义制度和国家经济 政策实施的认同感,帮助树立学生民族自尊心和自豪感,增强他们的凝聚力和 向心力。 四、教学内容及要求 PART 1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER I TEN PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS I.Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter,students should be able to: 1.Understand tenprinciples of economics. 2.Leam to apply the tenp principles of economics in our daily life Ⅱ.Contents:: 1.How People Make Decisions 2.How People Interact 3.How the Economy as a Whole Works II.After-class exercises: 1.List and briefly explain he four principles of individual decision 2.List and briefly explain the three principles conceming people's economi interactions. 3.List and briefly explain the three principles that describe how the economy as a whole works IV.Teaching methods and aids: PPT,instruction,group discussion,case analysis etc
3 课程目标 3:初步培养学会运用经济学的基本方法、思维方式分析和解决我 国市场经济运行中存在的各种经济问题的能力,为进一步学习其他专业知识打下 一个坚实的基础。 课程目标 4:使学生建立起经济学的基础知识框架,为进一步学习经济学及 其相关课程提供必要的知识和能力储备 课程目标 5:运用马克思主义基本观点、立场和方法学习和理解掌握课程内 容重点,引入我国经济市场化改革和政府参与经济运行取得的成效,把社会主 义核心价值观内容融入教学内容,开展课堂教学。通过分析中国政府有效政策 实施和成功的中国企业运营等案例分析,增强学生对社会主义制度和国家经济 政策实施的认同感,帮助树立学生民族自尊心和自豪感,增强他们的凝聚力和 向心力。 四、教学内容及要求 PART 1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1 TEN PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS Ⅰ. Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter, students should be able to : 1. Understand ten principles of economics. 2. Learn to apply the ten principles of economics in our daily life. Ⅱ. Contents: 1. How People Make Decisions 2. How People Interact 3. How the Economy as a Whole Works Ⅲ.After-class exercises: 1.List and briefly explain he four principles of individual decision 2. List and briefly explain the three principles concerning people's economic interactions; 3. List and briefly explain the three principles that describe how the economy as a whole works. Ⅳ. Teaching methods and aids: PPT, instruction, group discussion, case analysis etc. :

CHAPTER2 THINKING LIKE AN ECONOMIST I.Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter.students should be able to 1.Identify the economists'methodology to approach the world. 2.Understand The Circular-Flow Diagram Ⅱ.Contents: .The Economist as Scientist 2.The Economist as Policy Adviser I.After-class exercises: 1.Why might economic advisers to the president disagree about a question of IV.Teaching methods and aids: PPT,instruction,group discussion,case analysis etc CHAPTER 3INTERDEPENDENCEAND THE GAINS FROMTRADE I.Teaching Objectives After studying this chapter.students should be able to 1.Examine how our economy coordinates the activities of millions of people with varying tastes and abilities. 2.Explain why people trade with their neighbors and why nations trade 3.Explain what exactly people gain when they trade with one another 4.Explain why people choose to become interdependent. II.Contents: 1.A Parable for the Modemn Economy 2.The Principle of Compar ative Adva tage 3.Applications of Comparative Advantage II.After-class exereises: Robinson Crusoe can gather 10 coconuts or catch I fish per hour.His friend Friday can gather 30coconuts or catch 2fish per hour.What is Crusoe's tage in ching fish? Who has a comparative advantage in catching fish? PPT,instruction,group discussion,case analysis etc. PART2 HOW MARKETS WORK CHAPTER 4THE MARKET FORCESOF SUPPLY AND DEMAND I.Teaching Objectives:
4 CHAPTER 2 THINKING LIKE AN ECONOMIST Ⅰ. Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter, students should be able to : 1. Identify the economists' methodology to approach the world. 2. Understand The Circular-Flow Diagram Ⅱ. Contents: 1. The Economist as Scientist 2. The Economist as Policy Adviser Ⅲ.After-class exercises: 1. Why might economic advisers to the president disagree about a question of policy? Ⅳ. Teaching methods and aids: PPT, instruction, group discussion, case analysis etc. CHAPTER 3 INTERDEPENDENCE AND THE GAINS FROM TRADE Ⅰ. Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter, students should be able to : 1.Examine how our economy coordinates the activities of millions of people with varying tastes and abilities. 2. Explain why people trade with their neighbors and why nations trade with other nations. 3. Explain what exactly people gain when they trade with one another. 4. Explain why people choose to become interdependent. Ⅱ. Contents: 1. A Parable for the Modern Economy 2. The Principle of Comparative Advantage 3. Applications of Comparative Advantage Ⅲ.After-class exercises: Robinson Crusoe can gather 10 coconuts or catch 1 fish per hour. His friend Friday can gather 30coconuts or catch 2fish per hour. What is Crusoe's opportunity cost of catching one fish? What is Friday's? Who has an absolute advantage in catching fish? Who has a comparative advantage in catching fish? Ⅳ. Teaching methods and aids: PPT, instruction, group discussion, case analysis etc. PART 2 HOW MARKETS WORK CHAPTER 4 THE MARKET FORCES OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND Ⅰ. Teaching Objectives:

After studying this chapter,students should be able to 1.Identify what supply and demand are respectively 2.Understand the theory of supply and demand. 3.Explain how supply and demand interact with one another. 4.Explain how supply and demand how supply and demand determine prices in amarket economy and how prices.in tum,allocate the economy's scarce rces 1.Markets and Competition 2.Demand 3.Supply Ⅲ.Afie and Demand Togcther exercis 1.What is a market?What are the characteristics of a competitive market? 2.Make up an example of a supply schedule for pizza and graph the implied supply curve. 3 Give ean example of something hat would shift this supply curve. uld a ch ice of pizza shift this supply curve? PPT,instruction,group discussion,case analysis etc CHAPTER 5 ELASTICITY ADN ITS APPLICATIN I.Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter,students should be able to 1.Identify the concept of elasticity. 2.Develop the tool of elasticity toanalyze supply and demand with greater precisio 3.Explain how some event or policy affectsa market,we can discuss not only the direction of the effects but their magnitude as well. Ⅱ.Contents:: 1 The elasticity of demand 2 The elastici ofSuppl 3.Three Applications of Supply,Demand .After-class exercises: 1.Define the price elasticity of demand. 2.Explain the relationship between total revenue and the price elasticity of de nand. Teaching methods and aids PPT,instruction,group discussion,case analysis etc. CHAPTER6 SUPPLY,DEMAND,AND GOVERMENT POLICIES
5 After studying this chapter, students should be able to : 1. Identify what supply and demand are respectively 2. Understand the theory of supply and demand. 3. Explain how supply and demand interact with one another. 4. Explain how supply and demand how supply and demand determine prices in a market economy and how prices, in turn, allocate the economy's scarce resources. Ⅱ. Contents: 1. Markets and Competition 2. Demand 3. Supply 4. Supply and Demand Together Ⅲ.After-class exercises: 1. What is a market? What are the characteristics of a competitive market? 2. Make up an example of a supply schedule for pizza and graph the implied supply curve. 3. Give an example of something hat would shift this supply curve. 4. Would a change in the price of pizza shift this supply curve? Ⅳ. Teaching methods and aids: PPT, instruction, group discussion, case analysis etc. CHAPTER 5 ELASTICITY ADN ITS APPLICATIN Ⅰ. Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter, students should be able to : 1. Identify the concept of elasticity. 2. Develop the tool of elasticity to analyze supply and demand with greater precision. 3. Explain how some event or policy affects a market, we can discuss not only the direction of the effects but their magnitude as well. Ⅱ. Contents: 1. The elasticity of Demand 2. The elasticity of Supply 3. Three Applications of Supply, Demand Ⅲ.After-class exercises: 1. Define the price elasticity of demand. 2. Explain the relationship between total revenue and the price elasticity of demand. Ⅳ. Teaching methods and aids: PPT, instruction, group discussion, case analysis etc. CHAPTER 6 SUPPLY, DEMAND, AND GOVERMENT POLICIES

I.Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter,studentsshould be able to: 1.Analyze various types of govemment policy using only the tools of supply and demand. 2.Explain how policymakers use taxes both to influence market outcomes and to raise revenue for public purpose Ⅱ.Contents: 1.Controls on Prices 2.Taxes I.After-class exercises: In a supply-and-demand diagr amshow howa taxoncar buyersof per car affects the quar as s old and the price of cars.Inanother di price of cars.In both of your diagrams,show the change in the price paid by car buyers and the change in price received by car seller. IV.Teaching methods and aids: PPT,instruction,group discussion,case analysis etc PART3 MARKETSAND WELFARE CHAPTER 7 CONSUMERSS,PRODUCERS,ADN THE EFFICIENCY OF MARKETS I.Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter,students should be able to 1.Identify the concept of welfare economics. 2.Explain how the allocation of resources affects economic well-being. 3.Explain how the equilibriun supply and de mand in a market maximizes the total benefits received by buyers and sellers. 4.Develop welfare economics to explain the principle "Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity."more fully. Ⅱ.Contents:: 1 Controls on Prices 2.Taxes III.After-class exercises: Draw a demand curve for turkey.In your diagram,show a price ofturkey and the consumer surplus that results form that price.Explain in words what this IV.Teaching me PPT,instruction,group discussion,case analysis etc CHAPTER8 APPLICATIONS:THE COSTS OF TAXATION
6 Ⅰ. Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter, students should be able to : 1. Analyze various types of government policy using only the tools of supply and demand. 2. Explain how policymakers use taxes both to influence market outcomes and to raise revenue for public purposes. Ⅱ. Contents: 1. Controls on Prices 2. Taxes Ⅲ.After-class exercises: In a supply-and-demand diagram, show how a tax on car buyers of $1,000 per car affects the quantity of cars sold and the price of cars. In another diagram, show how a tax on car sellers of $1,000 per car affects the quantity of cars sold and the price of cars. In both of your diagrams, show the change in the price paid by car buyers and the change in price received by car seller. Ⅳ. Teaching methods and aids: PPT, instruction, group discussion, case analysis etc. PART 3 MARKETS AND WELFARE CHAPTER 7 CONSUMERSS, PRODUCERS, ADN THE EFFICIENCY OF MARKETS Ⅰ. Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter, students should be able to : 1. Identify the concept of welfare economics. 2. Explain how the allocation of resources affects economic well-being. 3. Explain how the equilibrium of supply and demand in a market maximizes the total benefits received by buyers and sellers. 4. Develop welfare economics to explain the principle "Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity." more fully. Ⅱ. Contents: 1. Controls on Prices 2. Taxes Ⅲ.After-class exercises: Draw a demand curve for turkey. In your diagram, show a price of turkey and the consumer surplus that results form that price. Explain in words what this consumer surplus measures. Ⅳ. Teaching methods and aids: PPT, instruction, group discussion, case analysis etc. CHAPTER 8 APPLICATIONS: THE COSTS OF TAXATION

I.Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter,students should be able to: 1.Explain how taxation has a major impact on the modern economy. 2.Explain how taxes affect welfare,the economic well-being of participants in a market Ⅱ.Contents 1.The Deadweight loss of Taxation 2.The Determinants of the Deadweight Loss III.After-class exercises: Draw the supply-and-demand curve for cookies.If the government imposes a tax on cookies. show what the price paid by buyer and the price paid by seller diagram,show the deadweight loss from the tax.Explain the meaning of the deadweight loss. IV.Teaching methods and aids: PPT,instruction,group discussion,case analysis etc. CHAPTER9 APPLICATON:INTERNATIONAL TRADE I.Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter,students should be able to: 1.Review h develop many tools for analyzing how markets work:supply demand,equilibrium,consumer surplus,producer surplus,and soon. Ⅱ.Contents: 1.The Determinants of Trade 2.The Winners and Losers from Trade 3 The Argun ents for Restricting Trade Ⅲ.After-clas The country Autarka does to allow international trade.In Autarka,you can buy a wool suit for 3 ounces of gold.Meanwhile,in neighboring countries,you can buy the same suit for 2 ounces of gold.If Autarka were to allow free trade. would it import or export wool suits? IV.Teaching methods and aids: PPT,instruction,group discussion,case analysis etc. 五、各教学环节学时分配 教学环节 习案例分小
7 Ⅰ. Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter, students should be able to : 1. Explain how taxation has a major impact on the modern economy. 2. Explain how taxes affect welfare, the economic well-being of participants in a market. Ⅱ. Contents: 1. The Deadweight loss of Taxation 2. The Determinants of the Deadweight Loss Ⅲ.After-class exercises: Draw the supply-and-demand curve for cookies. If the government imposes a tax on cookies, show what happens to the quantity sold, the price paid by buyers, and the price paid by sellers. In your diagram, show the deadweight loss from the tax. Explain the meaning of the deadweight loss. Ⅳ. Teaching methods and aids: PPT, instruction, group discussion, case analysis etc. CHAPTER 9 APPLICATON: INTERNATIONAL TRADE Ⅰ. Teaching Objectives: After studying this chapter, students should be able to : 1. Review how develop many tools for analyzing how markets work: supply, demand, equilibrium, consumer surplus, producer surplus, and so on. Ⅱ. Contents: 1. The Determinants of Trade 2. The Winners and Losers from Trade 3. The Arguments for Restricting Trade Ⅲ.After-class exercises: The country Autarka does to allow international trade. In Autarka, you can buy a wool suit for 3 ounces of gold. Meanwhile, in neighboring countries, you can buy the same suit for 2 ounces of gold. If Autarka were to allow free trad e, would it import or export wool suits? Ⅳ. Teaching methods and aids: PPT, instruction, group discussion, case analysis etc. 五、各教学环节学时分配 教学环节 讲 习 题 案例分 析 小
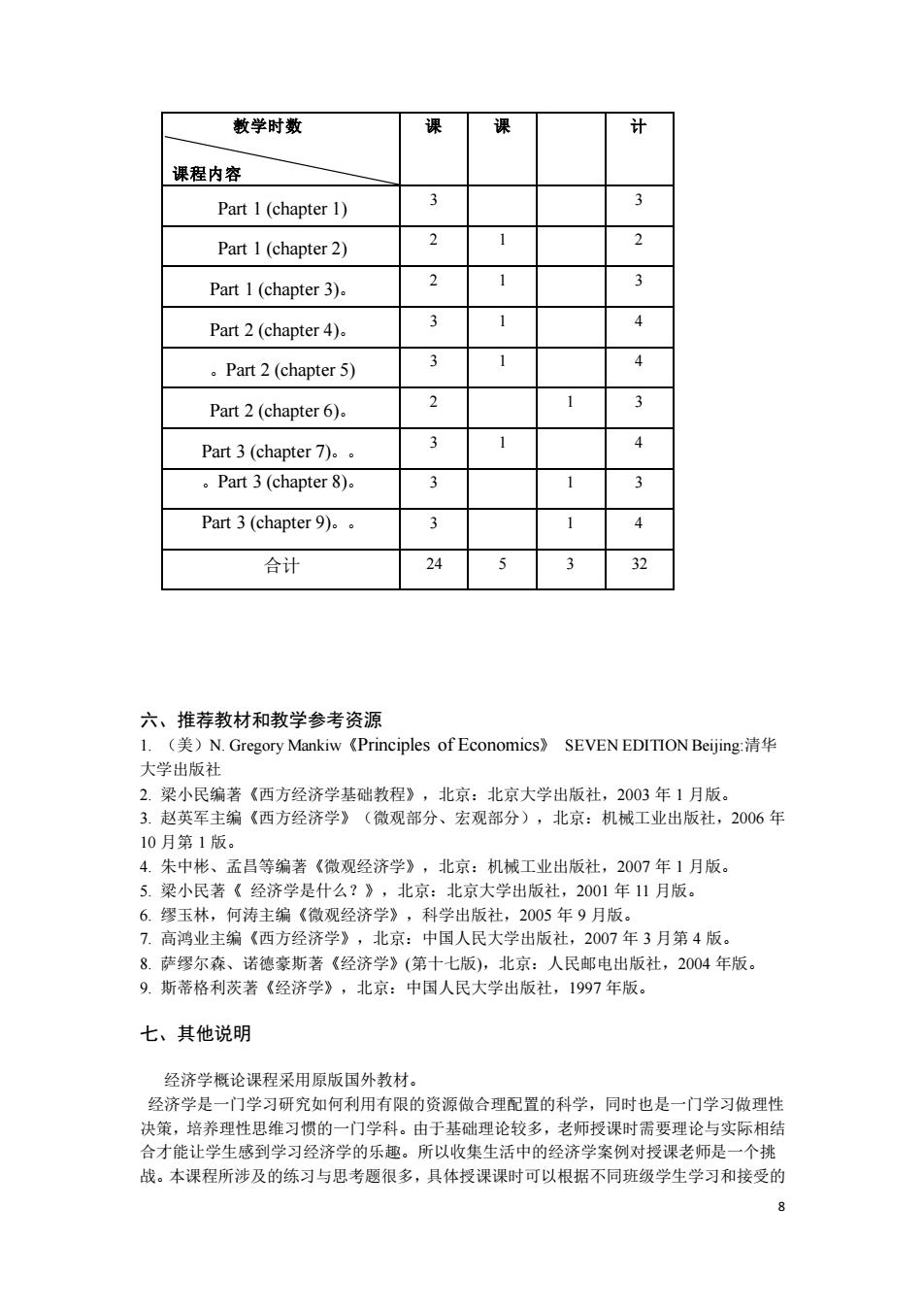
教学时数 课程内容 Part 1(chapter 1) 3 Part 1(chapter 2) Part 1(chapter 3). Part 2(chapter 4). 。Part2(chapter5) Part 2 (chapter 6). Part3(chapter7)。。 。Pat3(chapter8)。 Part3(chapter9)。。 合计 24 六、推荐教材和教学参考资源 l.(美)N.Gregory Mankiw《Principles of Economics》SEVEN EDITION Beijing:清华 大学出版社 小民编著(西方经济学基础教程),北京:北京大学出版社,203年1月版。 主编(西方经济学》(微观部分、宏观部分),北京:机械工业出版社,206年 10月第1版。 4.朱中彬、孟吕等编著《微观经济学》,北京:机械工业出版社,2007年】月版。 5.梁小民著《经济学是什么?》,北京:北京大学出版社,2001年11月版。 6探玉林,何违主编《微观经济学》,科学出版社,2005年9月版 7.高鸿业主编《西方经济学》,北京:中国人民大学出版社,2007年3月第4版 8.萨缪尔森、诺德豪斯著《经济学》(第十七版),北京:人民邮电出版社,2004年版。 9.斯蒂格利茨著《经济学》,北京:中国人民大学出版社,1997年版。 七、其他说明 经济学概论课程采用原版国外教材。 经济学是一门学习研究如何利用有限的资源做合理配置的科学,同时也是一门学习做理性 决策,培养理性思 习惯 。由于基 础理论牧多 老师授课时需要理论 实际相结 合才能让学生感到学习经济学的乐趣。所以收集生活中的经济学案例对授课老师是一个挑 战。本课程所涉及的练习与思考题很多,具体授课课时可以根据不同班级学生学习和接受的
8 教学时数 课程内容 课 课 计 Part 1 (chapter 1) 3 3 Part 1 (chapter 2) 2 1 2 Part 1 (chapter 3)。 2 1 3 Part 2 (chapter 4)。 3 1 4 。Part 2 (chapter 5) 3 1 4 Part 2 (chapter 6)。 2 1 3 Part 3 (chapter 7)。。 3 1 4 。Part 3 (chapter 8)。 3 1 3 Part 3 (chapter 9)。。 3 1 4 合计 24 5 3 32 六、推荐教材和教学参考资源 1. (美)N. Gregory Mankiw《Principles of Economics》 SEVEN EDITION Beijing:清华 大学出版社 2. 梁小民编著《西方经济学基础教程》,北京:北京大学出版社,2003 年 1 月版。 3. 赵英军主编《西方经济学》(微观部分、宏观部分),北京:机械工业出版社,2006 年 10 月第 1 版。 4. 朱中彬、孟昌等编著《微观经济学》,北京:机械工业出版社,2007 年 1 月版。 5. 梁小民著《 经济学是什么?》,北京:北京大学出版社,2001 年 11 月版。 6. 缪玉林,何涛主编《微观经济学》,科学出版社,2005 年 9 月版。 7. 高鸿业主编《西方经济学》,北京:中国人民大学出版社,2007 年 3 月第 4 版。 8. 萨缪尔森、诺德豪斯著《经济学》(第十七版),北京:人民邮电出版社,2004 年版。 9. 斯蒂格利茨著《经济学》,北京:中国人民大学出版社,1997 年版。 七、其他说明 经济学概论课程采用原版国外教材。 经济学是一门学习研究如何利用有限的资源做合理配置的科学,同时也是一门学习做理性 决策,培养理性思维习惯的一门学科。由于基础理论较多,老师授课时需要理论与实际相结 合才能让学生感到学习经济学的乐趣。所以收集生活中的经济学案例对授课老师是一个挑 战。本课程所涉及的练习与思考题很多,具体授课课时可以根据不同班级学生学习和接受的

情况适当调整教学进度。 大纲修订人:欧阳丽蓉 修订日期2017年9月 大纲审定者:欧阳丽蓉 审定日期:2017年10月 9
9 情况适当调整教学进度。 大纲修订人:欧阳丽蓉 修订日期:2017 年 9 月 大纲审定者:欧阳丽蓉 审定日期: 2017 年 10 月