Chapter 3 Molecular symmetry and symmetry point group
Chapter 3 Molecular symmetry and symmetry point group
Why do we study the symmetry concept? >The molecular configuration can be expressed more simply and distinctly. >The determination of molecular configuration is greatly simplified. >It assists giving a better understanding of the properties of molecules. >To direct chemical syntheses;the compatibility in symmetry is a factor to be considered in the formation and reconstruction of chemical bonds
The molecular configuration can be expressed more simply and distinctly. The determination of molecular configuration is greatly simplified. It assists giving a better understanding of the properties of molecules. To direct chemical syntheses; the compatibility in symmetry is a factor to be considered in the formation and reconstruction of chemical bonds. Why do we study the symmetry concept?

1 Symmetry elements and symmetry operations >Symmetry exists all around us and many people see it as being a thing of beauty. >A symmetrical object contains within itself some parts which are equivalent to one another. >The systematic discussion of symmetry is called Some objects are more symmetrical than others
§1 Symmetry elements and symmetry operations Symmetry exists all around us and many people see it as being a thing of beauty. A symmetrical object contains within itself some parts which are equivalent to one another. The systematic discussion of symmetry is called : Some objects are more symmetrical than others
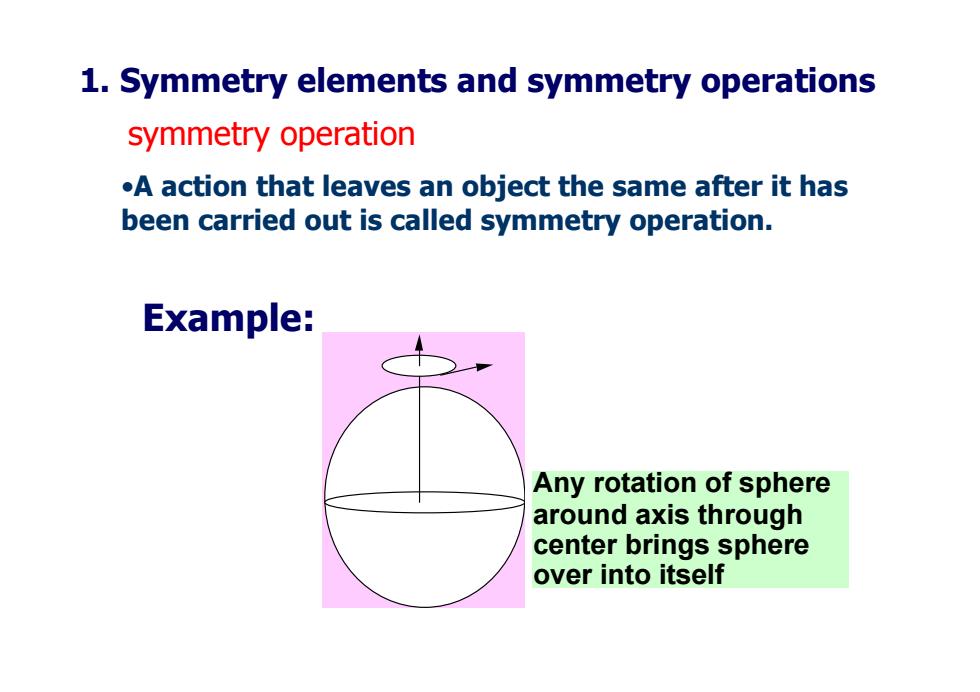
1.Symmetry elements and symmetry operations symmetry operation .A action that leaves an object the same after it has been carried out is called symmetry operation. Example: Any rotation of sphere around axis through center brings sphere over into itself
symmetry operation •A action that leaves an object the same after it has been carried out is called symmetry operation. Any rotation of sphere around axis through center brings sphere over into itself Example: 1. Symmetry elements and symmetry operations

Example: 'b) (a)An NH3 molecule has a (b)an H2O molecule has a threefold (C3)axis twofold (C2)axis
(b) an H2O molecule has a twofold (C2) axis. (a) An NH3 molecule has a threefold (C3) axis Example:
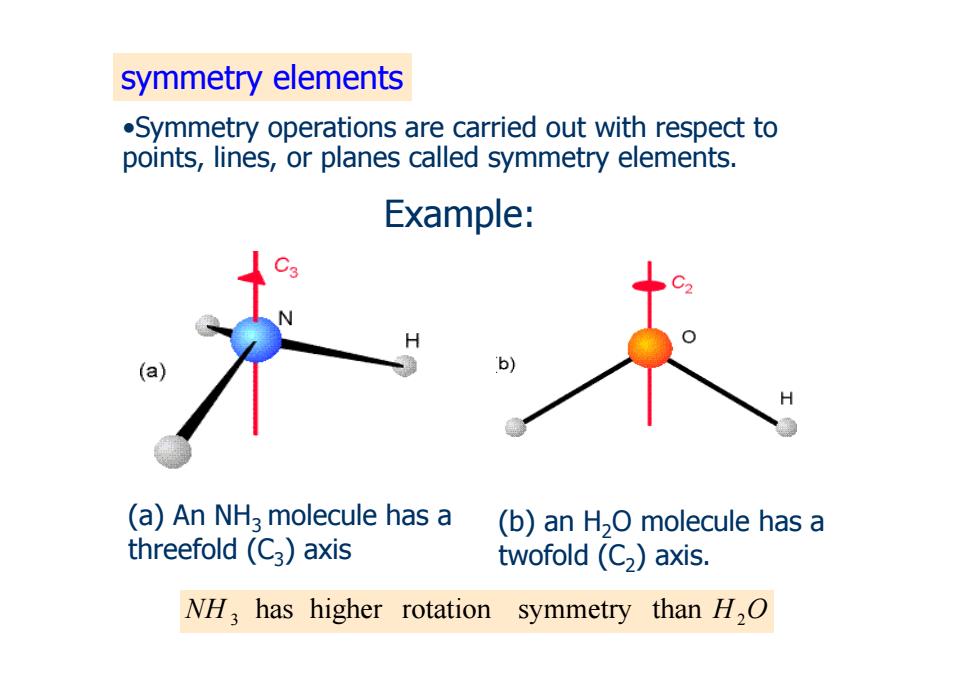
symmetry elements .Symmetry operations are carried out with respect to points,lines,or planes called symmetry elements. Example: (a)An NH2 molecule has a (b)an H2O molecule has a threefold(C3)axis twofold (C2)axis. NH,has higher rotation symmetry than H,O
(b) an H2O molecule has a twofold (C2) axis. (a) An NH3 molecule has a threefold (C3) axis NH 3 has higher rotation symmetry than H2O Example: •Symmetry operations are carried out with respect to points, lines, or planes called symmetry elements. symmetry elements
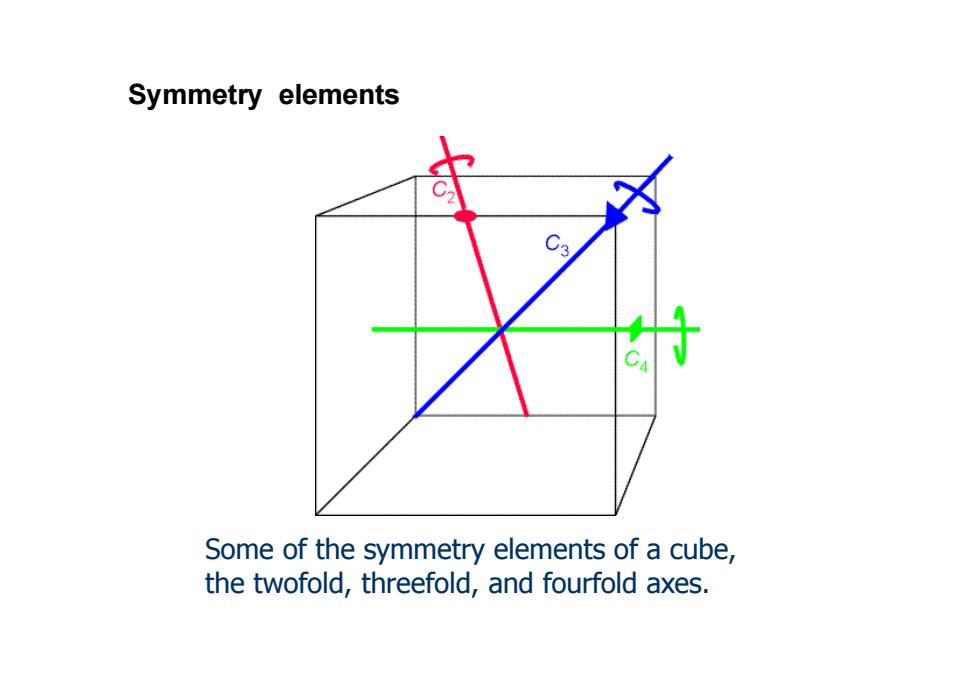
Symmetry elements 3 Some of the symmetry elements of a cube, the twofold,threefold,and fourfold axes
Some of the symmetry elements of a cube, the twofold, threefold, and fourfold axes. Symmetry elements

mmetry Operation Symmetry operations are: Rotation Reflection hversion B6I6600u 012乳6AU The corresponding symmetry elements are: a line a point
Symmetry operations are: The corresponding symmetry elements are:
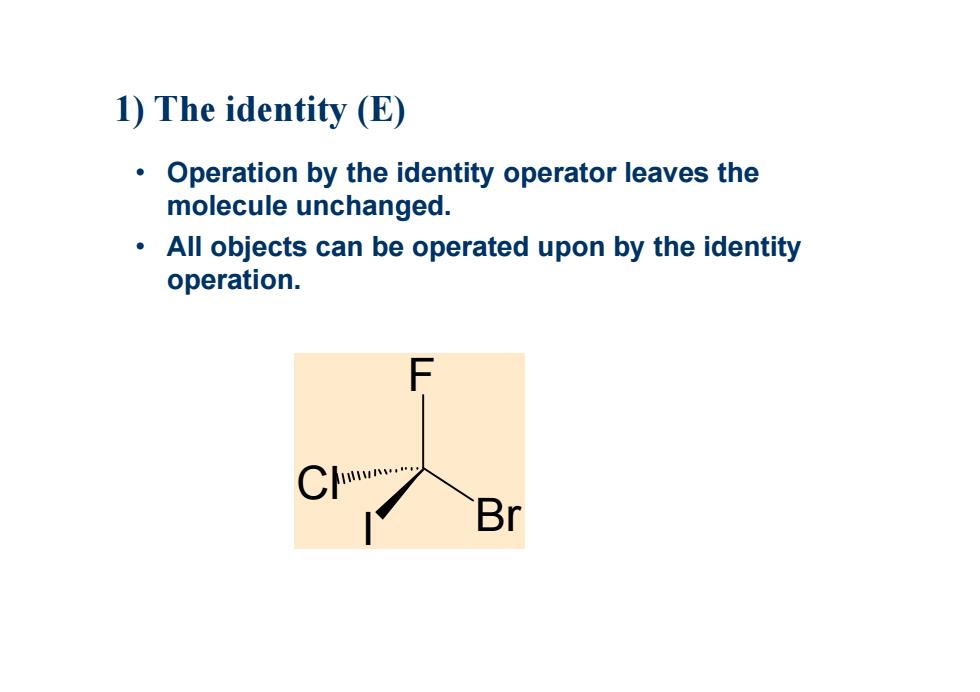
1)The identity (E) Operation by the identity operator leaves the molecule unchanged. All objects can be operated upon by the identity operation. Br
I F Cl Br • Operation by the identity operator leaves the molecule unchanged. • All objects can be operated upon by the identity operation. 1) The identity (E)
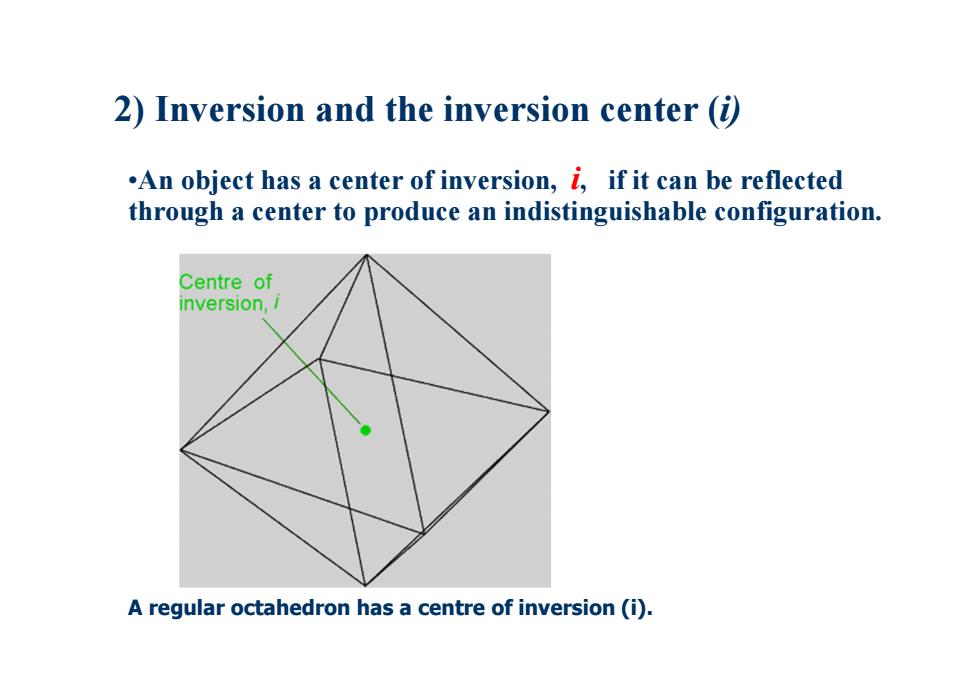
2)Inversion and the inversion center (i) .An object has a center of inversion,i,if it can be reflected through a center to produce an indistinguishable configuration. Centre of inversion,i A regular octahedron has a centre of inversion(i)
2) Inversion and the inversion center (i) •An object has a center of inversion, i, if it can be reflected through a center to produce an indistinguishable configuration. A regular octahedron has a centre of inversion (i)