
第30卷第4期 应 用力 学 学 报 Vol30 No.4 2013年8月 CHINESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED MECHANICS Aug.2013 文章编号:100-49392013)04-054-06 火灾情况下混凝土板温度场的解析解 唐松花2罗迎社3彭相华4 (1东南大学混凝土及预应力混凝土结构教有部重点实验室210096南京:2中南大学土木工程学院410075长沙 3中南林业科技大学流变力学与材料工程研究所410004长沙:4中南林业科技大学涉外学院410004长沙判 摘要,针对火灾情况下火场温度和均件边界的温度均浦时间不断变化的问题,应用杜哈关尔定理 分析了边界温度按 定规律随时间变化的热传导问题。推导得到了火灾情况下混凝土板湿度场的 解析解公式,并应用MATLAB编程计算得到了解析解结果。比较解析解的计算结采和试验结果 发现:两者得到的裁面温度场都里非线性分布;两者的变化趋势一致,即近火面的温度梯度很大 距受火面越远,温度梯度越小;温度曲线都是凸向坐标轴。因此,推乎得到的解析解公式适合于 求解火灾时混疑土城横蔻面的温度场。同时,只要能够求出非齐次项与时间无关时的捕助问题的 解,便可应用杜哈美尔定理求解该热传导问题的温度场,因此该方法可推广应用于火灾情况下其 它构件温度场解析解的计算】 关键词:火灾:混凝土板;温度场;解析解;热传导:杜哈关尔定理 中图分类号:0302文献标识码:AD0L:10.11776cjam.30.04.B133 1引言 和计算点距受火面距离的函数,因此可按照一维无 在对火灾情况下的结构抗火性能进行分析前, 限大平板热传导问题进行解析求解。文献4根据 一般先进行构件和结构内温度场的分析。 维傅立叶导热微分方程,采用拉普拉斯变换求解了 火灾情况下,构件截面的温度场随时间变化 混凝土楼板沿横截面高度的温度分布函数。文献[5 材料的导热系数、 ,质量密度均不是常数, 根据热力学原理研究了火灾时筋混凝士板内的 随时间变化,所以截面热传导问题是一个非线性瞬 度场分布,采用傅立叶变换法,在适当的简化假无 态问题,其控制方程是一个非线性抛物型的偏微分 之后,推导出了求解火灾时钢筋混凝土板内温度场 方程。求解热传导微分方程的方法有分离变量法、 的计算公式。积分变换法的基础是从经典的分离变 积分变换法、近似分析法、数值法等。其中:分 量法中导出的。也就是说,要导出为求解某给定问 离变量法和积分变换法为解析解求解方法,近似分 题所需的正变换与逆变换,需借助于将一任意函数 析法和数值法为近似解求解方法。近似方法的精度 (其定义域与给定问题的定义域相同)用该给定 不易估计,除非将其结果与解析解作对比。因此 齐次部分的分离解来表示,该方法在实际应用中 20
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(51178474);湖南省自然科学基金(11JJ5002);东南大学混凝土及预应力混凝土结构教育部重点实验室开放课题基金 (CPCSME2010-06) 收稿日期:2012-12-04 修回日期:2013-04-09 第一作者简介:唐松花,女,1973 年生,博士,中南大学,副教授;研究方向——固体力学、损伤力学。 通讯作者:罗迎社,E-mail:lys0258@sina.com 应 用 力 学 学 报 CHINESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED MECHANICS 第 30 卷 第 4 期 2013 年 8 月 Vol.30 No.4 Aug. 2013 文章编号:1000- 4939(2013) 04-0544-06 火灾情况下混凝土板温度场的解析解 唐松花 1,2 罗迎社 3 彭相华 4 (1 东南大学混凝土及预应力混凝土结构教育部重点实验室 210096 南京;2 中南大学土木工程学院 410075 长沙; 3 中南林业科技大学流变力学与材料工程研究所 410004 长沙;4 中南林业科技大学涉外学院 410004 长沙) 摘要:针对火灾情况下火场温度和构件边界的温度均随时间不断变化的问题,应用杜哈美尔定理 分析了边界温度按一定规律随时间变化的热传导问题。推导得到了火灾情况下混凝土板温度场的 解析解公式,并应用 MATLAB 编程计算得到了解析解结果。比较解析解的计算结果和试验结果 发现:两者得到的截面温度场都呈非线性分布;两者的变化趋势一致,即近火面的温度梯度很大, 距受火面越远,温度梯度越小;温度曲线都是凸向坐标轴。因此,推导得到的解析解公式适合于 求解火灾时混凝土板横截面的温度场。同时,只要能够求出非齐次项与时间无关时的辅助问题的 解,便可应用杜哈美尔定理求解该热传导问题的温度场,因此该方法可推广应用于火灾情况下其 它构件温度场解析解的计算。 关键词:火灾;混凝土板;温度场;解析解;热传导;杜哈美尔定理 中图分类号:O302 文献标识码:A DOI:10.11776/cjam.30.04.B133 1 引 言 在对火灾情况下的结构抗火性能进行分析前, 一般先进行构件和结构内温度场的分析。 火灾情况下,构件截面的温度场随时间变化, 材料的导热系数、比热、质量密度均不是常数,也 随时间变化,所以截面热传导问题是一个非线性瞬 态问题,其控制方程是一个非线性抛物型的偏微分 方程。求解热传导微分方程的方法有分离变量法、 积分变换法、近似分析法、数值法等[1-3]。其中:分 离变量法和积分变换法为解析解求解方法,近似分 析法和数值法为近似解求解方法。近似方法的精度 不易估计,除非将其结果与解析解作对比。因此, 解析解在温度场研究中显得十分重要。 混凝土板的火灾温度场可视为火灾燃烧时间 和计算点距受火面距离的函数,因此可按照一维无 限大平板热传导问题进行解析求解。文献[4]根据一 维傅立叶导热微分方程,采用拉普拉斯变换求解了 混凝土楼板沿横截面高度的温度分布函数。文献[5] 根据热力学原理研究了火灾时钢筋混凝土板内的温 度场分布,采用傅立叶变换法,在适当的简化假定 之后,推导出了求解火灾时钢筋混凝土板内温度场 的计算公式。积分变换法的基础是从经典的分离变 量法中导出的。也就是说,要导出为求解某给定问 题所需的正变换与逆变换,需借助于将一任意函数 (其定义域与给定问题的定义域相同)用该给定问题 齐次部分的分离解来表示,该方法在实际应用中非

第4别 唐松花,等:火火特况下混凝士板温度场的解析解 545 常有效。但是积分变换法要求逆变换过程可直接进 式(1)的解T(r,),即所求温度场与辅助问题式(2) 行,即在问题开始处理时,这种逆变换的公式必须 的解,)由如下的积分表示式联系起来,即 已具备,这是使用积分变换法的限制, 灾时火场温度及构件边界的温度也随时 Tt小-1-r 3 不断变化,文献6]中的杜哈美尔定理能够分析边界 温度按一定规律随时间变化的热传导问题。本文将 3 应用杜哈美尔定理求解火灾时 应用杜哈美尔定理求解火灾情况下混凝土板温度场 混凝土板的温度场 的解析解。 理论计算中常将混凝土板视为无限大平板(以 2杜哈美尔定理 下简称大平板),通常可以理解为该平板的长和宽与 厚度相比为无限大。因此无限大平板是 个以两可 行平面为界限的物体 边界条件随时间变化区域内的三维非齐次热 温度只在厚度方向发生变化 不变, 传导问题可表示为 在其它两 问题 维的 (aT(r1 1ar(r1) 如图1所示为 大平板,0≤x≤L in R t>0 L=120mm:初始温度分布为20℃:当时间1>0时 32 a dl x=0和x=L处的边界面分别维持f(0和20℃。 高+AT=c小, on S.1>0 (1) ∫()为模拟火灾时随时间1变化的空气流体温度 T(r,)=F(r) in R.t=0 即大平板的底面受火。下面求解1>0时平板内温度 分布T(x,),即板的温度场。 其中:/m为垂直于边界面S,的外法线方向导数 (其中i=12 日h2=e为热这里是区城R连续的 k为导热系数:c为 比热:p为密度。 将系数k与h假定为常数。若令k=0,则为 Fe限大的黑生板 热传导第一类边界条件:若令h=0,则为热传导 混凝土板温度场的热传导方程和初始边界条 第二类边界条件 件为 由上式表示的问题不能采用通常的热传导求 (aT(x.1)1 aT(x.1) 解方法(如分离变量法)求解,因为非齐次项∫(,) 00 a 是时间的函数。因此用下面定义的较为简单的铺围 问题的解来表示上述问题的解,以此来代替对式(山 T(x,)=f0,x=0,1>0 多 T=20.x=L.1>0 的直接求解。令(r,1,)为式(1)中假定非齐次可 T=F(x),0≤x≤L,1=0 ∫(:,)不是时间的函数的情况下的解,即变量x只 因此混凝土板的温度场为一维非稳态热传导 是一个参量,它不是时间的函数。因此(,1)为 较为简单的辅助问题的解, 即可表示为如下公式 问题。这里考虑到火灾时火场温度上升很快,随若 温度的升高, 受火边界的温度会越来越接近火场 8(r.t,r)186(r.1.) .in R.1>0 温度,同时为了简化计算,将受火边界设为第一边 a Ct 界条件 8d+h,)=f) (2 分析式(4)发聊,火灾高温环境下板的受火边界 an. 温度是不断变化的,因此可以在同一热传导司题但 on S.1>0 非齐次项与时间无关时的解的基础上, 利用杜哈美 (r,r)=F(r) in R.=0 尔定理进行求解 由于f心,)与时间无关,式(2)就可以用通常的 令(x1,x)为式(4)中假定非齐次项∫(r)不是 热传导求解方法进行求解。假定轴助问题式(2)的解 时间函数的间题的解,即变量x只是一个参量,它 (,4)已经求得,则应用杜哈美尔定理即可把 不是时间的函数。因此,(x)为如下较为简单
第 4 期 唐松花,等:火灾情况下混凝土板温度场的解析解 545 常有效。但是积分变换法要求逆变换过程可直接进 行,即在问题开始处理时,这种逆变换的公式必须 已具备,这是使用积分变换法的限制。 火灾时火场温度及构件边界的温度也随时间 不断变化,文献[6]中的杜哈美尔定理能够分析边界 温度按一定规律随时间变化的热传导问题。本文将 应用杜哈美尔定理求解火灾情况下混凝土板温度场 的解析解。 2 杜哈美尔定理 边界条件随时间变化区域内的三维非齐次热 传导问题可表示为 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) () 2 2 , , 1 , in , 0 , , on , 0 , , in , 0 i ii i i T rt T rt R t r t T k hT f r t S t n T rt F r R t α ⎧∂ ∂ ⎪ = > ∂ ∂ ⎪ ⎪ ∂ ⎨ += > ∂ ⎪ ⎪ = = ⎪ ⎩ (1) 其中: i ∂ ∂n 为垂直于边界面 i S 的外法线方向导数, (其中 i s =1,2, , L ,这里 s 是区域 R 连续边界的数 目);α = k c/ ρ 为热扩散系数;k 为导热系数;c 为 比热; ρ 为密度。 将系数 i k 与 i h 假定为常数。若令 0 i k = ,则为 热传导第一类边界条件;若令 0 i h = ,则为热传导 第二类边界条件。 由上式表示的问题不能采用通常的热传导求 解方法(如分离变量法)求解,因为非齐次项 f (r t, ) 是时间的函数。因此用下面定义的较为简单的辅助 问题的解来表示上述问题的解,以此来代替对式(1) 的直接求解。令φ (r t, ,τ ) 为式(1)中假定非齐次项 f (r t, ) 不是时间的函数的情况下的解,即变量τ 只 是一个参量,它不是时间的函数。因此φ (r t, ,τ ) 为 较为简单的辅助问题的解,即可表示为如下公式 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) () ( ) () 2 2 ,, ,, 1 , in , 0 , , ,, , on , 0 , , , in , 0 i ii i i rt rt R t r t r t k h rt f r n S t rt F r R t φτ φτ α φ τ φτ τ φ τ ⎧∂ ∂ ⎪ = > ∂ ∂ ⎪ ⎪ ∂ ⎪ + = ⎨ ∂ ⎪ ⎪ > ⎪ ⎪ = = ⎩ (2) 由于 f (r,τ ) 与时间无关,式(2)就可以用通常的 热传导求解方法进行求解。假定辅助问题式(2)的解 φ (r t, ,τ ) 已经求得,则应用杜哈美尔定理即可把 式(1)的解T rt ( , ) ,即所求温度场与辅助问题式(2) 的解φ (r t, ,τ ) 由如下的积分表示式联系起来,即 ( ) ( ) 0 , , ,d t T rt rt t τ φ ττ τ = ∂ = − ∂ ∫ (3) 3 应用杜哈美尔定理求解火灾时 混凝土板的温度场 理论计算中常将混凝土板视为无限大平板(以 下简称大平板),通常可以理解为该平板的长和宽与 厚度相比为无限大。因此无限大平板是一个以两平 行平面为界限的物体,温度只在厚度方向发生变化, 在其它两个方向温度不变,因而问题是一维的。 如 图 1 所示为一大平板, 0≤ ≤x L , L =120mm;初始温度分布为20℃;当时间t > 0 时, x = 0 和 x = L 处的边界面分别维持 f (t) 和20℃。 f (t) 为模拟火灾时随时间t 变化的空气流体温度, 即大平板的底面受火。下面求解t > 0 时平板内温度 分布T xt ( , ) ,即板的温度场。 图1 底面受火的混凝土板 Fig.1 Slab exposed to fire at the bottom 混凝土板温度场的热传导方程和初始边界条 件为 ( ) ( ) ( ) () ( ) 2 2 , , 1 ,0 , 0 , , 0, 0 20 , , 0 ,0 , 0 T xt T xt x L t x t T xt f t x t T x Lt T Fx x Lt α ⎧∂ ∂ ⎪ = ∂ ∂ ⎪ ⎪ = => ⎨ ⎪ = => ⎪ ⎪ = = ⎩ ≤ ≤ (4) 因此混凝土板的温度场为一维非稳态热传导 问题。这里考虑到火灾时火场温度上升很快,随着 温度的升高,受火边界的温度会越来越接近火场的 温度,同时为了简化计算,将受火边界设为第一边 界条件。 分析式(4)发现,火灾高温环境下板的受火边界 温度是不断变化的,因此可以在同一热传导问题但 非齐次项与时间无关时的解的基础上,利用杜哈美 尔定理进行求解。 令φ ( x, ,t τ ) 为式(4)中假定非齐次项 f (τ ) 不是 时间函数的问题的解,即变量τ 只是一个参量,它 不是时间的函数。因此,φ ( x, ,t τ ) 为如下较为简单

546 应用力学学根 第30卷 的辅助司颗的邮,即 1,00 5 (x.1.x)=20.x=L.1>0 (x1,)=F(x,0≤x≤L,1=0 2注F()omp 铺助句题是由于边界条件的非客次造成的非 (13 齐次热传导问题,可将该非齐次问题分解成几个简 式叶 单的问题,再分别用分离变量法求解。这里辅助问 题中的非齐次部分都是与时间无关的。 ,c0sm=(-1) 由于问题是一维的,本文将其分解成一个 由此可得 T(x)的稳态问题和一个T(x,)的齐次问题,对应 的公式分别为 B g-0,02 I=f(r),x=0 (6) =20,x=L nF()sin( a'T 1 aT .00 2a2 T=0.x=0.x=L.1>0 (7) 如下的积分表示式联系起来,即 =F(x)-T(x)=了(x),0<x<L,1=0 则式(5)的解可由下式求得 T0-号1-rr (x,r)=T(x,t)+T(x,, 式(6)的解为 T,(x)=f)+[20-f]月 (9) 22-旷.n月寸20-ear 对于各种可能的齐次边界条件,大平板中一维 22或F咖 非稳态热传导问题的解可统一表示为 x-立eaa ∫et-rldz 15) 该解在x=0与x=L处都不收敛于边界条件】 其佰因 ∫f(x)x(B,x)dr (10) 是对应于边 那些项都以傅立 形式 而傅立叶级数有 =0 x=L的边界 则式(7)的解可根据式(10)直接得到,即 不均匀收敛 ,解决该难点的方法是 将式(15)进行分 .(.)( 部积分,且将上述级数用下面介绍的等价封闭形式 的表达式表示。 [(x)x(B.x)d (1) 将式(15)写为 其中特征函数X(B,x)、范数N(B)、特征值B。可 由文献6中的附表1得到,即 x(B)=sinBx.N(B.) (12) 光2-旷Asm及.40- 式(5)的解(x,1)可由式(9)和式11)代入式(8)并经 sinF()sin(() 过积分整理后获得,即 (16)
546 应 用 力 学 学 报 第 30 卷 的辅助问题的解,即 ( ) ( ) ( ) () ( ) ( ) () 2 2 ,, ,, 1 ,0 , 0 , , , 0, 0 , , 20, , 0 ,, ,0 , 0 xt xt x Lt x t xt f x t xt x L t xt F x x L t φτ φτ α φτ τ φ τ φ τ ⎧∂ ∂ ⎪ = ∂ ∂ ⎪ ⎪ = => ⎨ ⎪ = => ⎪ ⎪ = = ⎩ ≤ ≤ (5) 辅助问题是由于边界条件的非齐次造成的非 齐次热传导问题,可将该非齐次问题分解成几个简 单的问题,再分别用分离变量法求解。这里辅助问 题中的非齐次部分都是与时间无关的。 由于问题是一维的,本文将其分解成一个 T x s ( ) 的稳态问题和一个T xt h ( , ) 的齐次问题,对应 的公式分别为 ( ) 2 2 d 0,0 d , 0 (6) 20 , s s s T x L x Tf x T xL τ ⎧ ⎪ = ⎪ ∂ ∂ ⎨ ===> ⎪ ⎪ = − ≡ << = ⎩ 则式(5)的解可由下式求得 φ ( x,, , ,, t T x T xt ττ τ ) = + s h ( ) ( ) (8) 式(6)的解为 ( ) () () , 20 s x Tx f f L ττ τ = +− ⎡ ⎤ ⎣ ⎦ (9) 对于各种可能的齐次边界条件,大平板中一维 非稳态热传导问题的解可统一表示为 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 1 * 0 1 ,, e , , d mt m m m L m x t Xx N f xX x x αβ θ β β β ∞ − = = ⋅ ′ ′′ ∑ ∫ (10) 则式(7)的解可根据式(10)直接得到,即 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 1 * 0 1 ,, e , , d mt h m m m L m T xt X x N f xX x x αβ τ β β β ∞ − = = ⋅ ′ ′′ ∑ ∫ (11) 其中特征函数 ( ) , X x β m 、范数 N ( ) β m 、特征值 β m 可 由文献[6]中的附表 1 得到,即 ( ) , sin Xx x β m m = β , ( ) 1 2 N L β m = (12) 式(5)的解φ ( ) x, ,t τ 可由式(9)和式(11)代入式(8)并经 过积分整理后获得,即 ( ) () ( ) 2 2 2 1 1 0 1 2 1 , , 1 e sin( ) 2 1 20 e sin( ) cos π 2 e sin( ) sin( )d m m m t m m m t m m m L t m m m x xt f x L L x x m L L x Fx x x L αβ αβ αβ φτ τ β β β β β β ∞ − = ∞ − = ∞ − = ⎡ ⎤ = ⎢ −− ⋅ +⎥ ⎣ ⎦ ⎡ ⎤ ⎢ + ⋅ +⎥ ⎣ ⎦ ′ ′′ ∑ ∑ ∑ ∫ (13) 式中 ( ) π , cos π 1 m m m m L β = = − 由此可得 ( ) () ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 1 1 0 1 2 sin ,, 1 e 2 1 20 e sin 2 e sin sin d m m m t m m m m t m m m L t m m m x x xt f L L x x L L x Fx x x L αβ τ αβ τ αβ τ β φ ττ τ β β β β β ∞ − − = ∞ − − = ∞ − − = ⎡ ⎤ − = −− + ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ ⎦ ⎡ ⎤ − ⎢ ⎥ + + ⎣ ⎦ ′ ′′ ∑ ∑ ∑ ∫ (14) 应用杜哈美尔定理,式(4)的解与式(5)的解可由 如下的积分表示式联系起来,即 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 0 0 1 0 1 2 0 1 0 , , ,d 2 sin e d 2 1 sin 20 e d 2 sin sin d e d (15) m m m t t t m m m m t t m m m L mm m m t t T xt xt t x f L x L x Fx x x L τ αβ τ τ αβ τ τ αβ τ τ φ ττ τ α β β ττ α β β τ αβ β β τ = ∞ − − = = ∞ − − = = ∞ = − − = ∂ = − ∂ = − − ⋅ − ′ ′′ ⋅ ∫ ∑ ∫ ∑ ∫ ∑ ∫ ∫ 该解在 x = 0 与 x = L 处都不收敛于边界条件。 其原因是对应于边界条件的那些项都以傅立叶级数 形式表示,而傅立叶级数在 x = 0 与 x = L 的边界上 不均匀收敛。解决该难点的方法是将式(15)进行分 部积分,且将上述级数用下面介绍的等价封闭形式 的表达式表示。 将式(15)写为 ( ) ( ) ( ) () ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 1 2 1 2 3 0 1 2 , sin 2 1 sin 2 sin sin d m m m m m m m L mm m m T x t xI t L xI t L x F x x xI t L α β β α β β αβ β β ∞ = ∞ = ∞ = = − − − ′ ′′ ∑ ∑ ∑ ∫ (16)
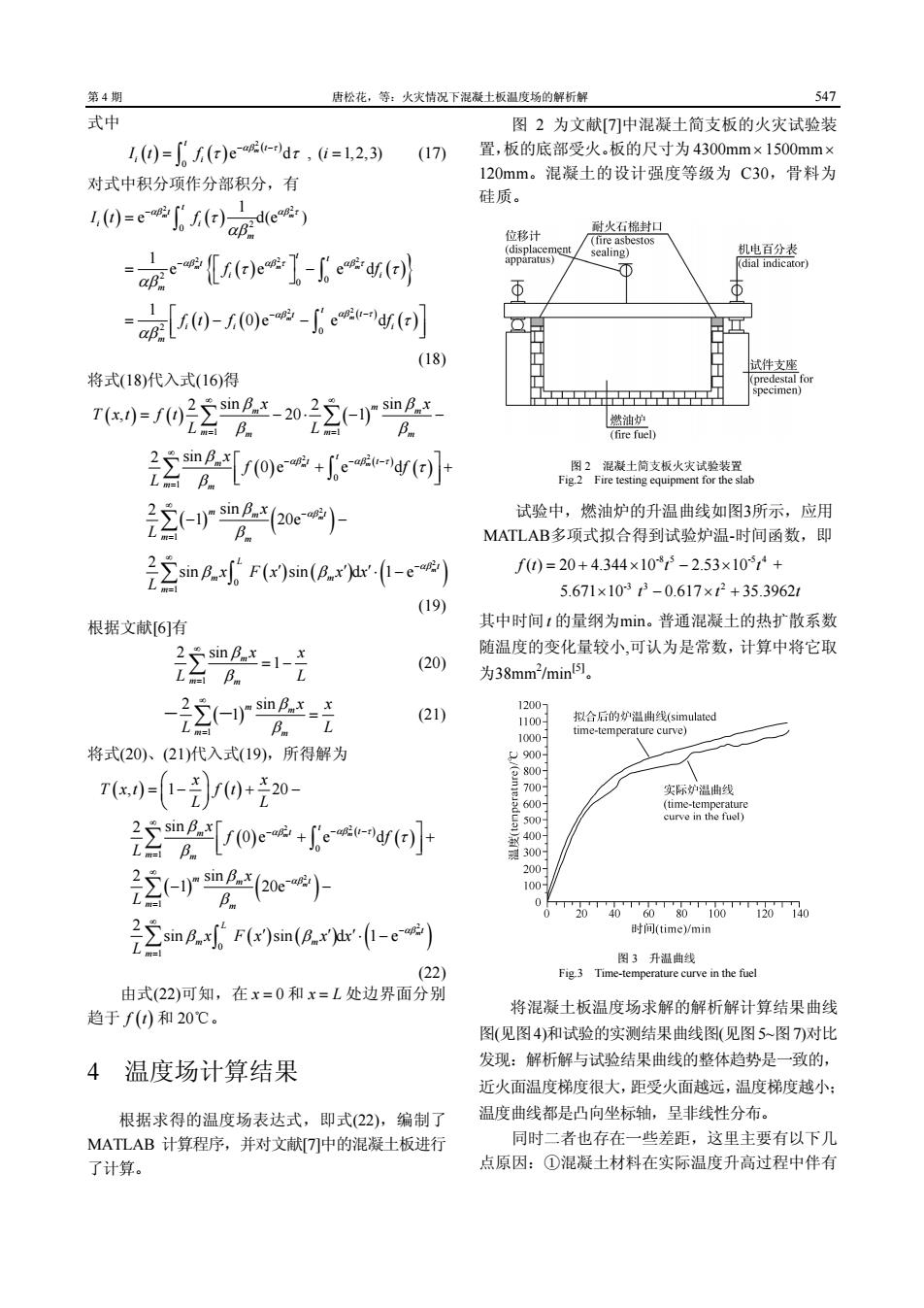
第4 唐松化,等:火火情况下混凝士版温度场的解析解 547 式中 图2为文献[中混凝土简支板的火灾试验装 0=f)ee-dr,=l2,3) (17) 置,板的底部受火。板的尺寸为4300mm×1500mm 对式中积分项作分部积分,有 120 nm。混凝士的设计强度等级为C30,骨料为 硅质。 0=eede 时火石棉封 -安ee了-edga 机此百分表 (-(0)e(] (18) 将式(18)代入式(16)得 20:ey间 图2十支板大线装R () 试验中,燃油炉的升温曲线如图3所示,应用 MATLAB多项式拟合得到试验炉温-时间函数,即 2a2mFma如-e) f0=20+4.344×107-2.53×10+ 5.671×103t3-0.617×+35.3962 (19 根据文献6)有 其中时间!的量纲为min。普通混凝土的热扩散系数 片 随温度的变化量较小可认为是常数,计算中将它取 (20) 为38mm2min间. 2这r2- (21) 将式(20、(21)代入式(19),所得解为 7c--/0+产20 22s+ewo 2-少Ae B. T20406的00T20T4o 22Pmax-e) rve in the fuc 趋于f(0)和20C. 将混凝士板温度场求解的解析解计算结果曲线 图(见图4)和试验的实测结果曲线图(见图5-图7)对比 4温度场计算结果 发现:解析解与试验结果曲线的整体趋势是一致的, 近火面温度梯度很大,距受火面越远,温度梯度越小: 根据求得的温度场表达式,即式(22),编制了 温度曲线都是凸向坐标轴,呈非线性分布。 MATLAB计算程序,并对文献7中的混凝土板进行 同时二者也存在一些差距,这里主要有以下几 了计算。 点原因:①混凝土材料在实际温度升高过程中伴有
第 4 期 唐松花,等:火灾情况下混凝土板温度场的解析解 547 式中 () ( ) ( ) 2 0 e d , ( 1,2,3) m t t i i It f i αβ τ τ τ − − = = ∫ (17) 对式中积分项作分部积分,有 () ( ) { ( ) ( )} () ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 22 2 2 2 0 2 0 0 2 0 1 e d(e ) 1 e e ed 1 0e e d m m m mm m m t t i i m t t t i i m t t t ii i m It f f f ft f f αβ αβ τ αβ αβ τ αβ τ αβ αβ τ τ αβ τ τ αβ τ αβ − − − − = = − ⎡ ⎤ ⎣ ⎦ ⎡ ⎤ =−− ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ ⎦ ∫ ∫ ∫ (18) 将式(18)代入式(16)得 ( ) () ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 2 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 2 2 sin sin , 20 1 2 sin 0e e d 2 sin 1 20e 2 sin sin d 1 e m m m m m m m m m m m t m t t m m m m t m m L t m m m x x T xt f t L L x f f L x L x Fx x x L αβ αβ τ αβ αβ β β β β β τ β β β β β ∞ ∞ = = ∞ − − − = ∞ − = ∞ − = = −⋅ − − ⎡ ⎤ + + ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ ⎦ − − ′ ′′ ⋅ − ∑ ∑ ∑ ∫ ∑ ∑ ∫ (19) 根据文献[6]有 1 2 sin 1 m m m x x L L β β ∞ = ∑ = − (20) ( ) 1 2 sin 1 m m m m x x L L β β ∞ = - - ∑ = (21) 将式(20)、(21)代入式(19),所得解为 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 2 0 1 1 0 1 , 1 20 2 sin 0e e d 2 sin 1 20e 2 sin sin d 1 e m m m m t m t t m m m m t m m L t m m m x x T xt f t L L x f f L x L x Fx x x L αβ αβ τ αβ αβ β τ β β β β β ∞ − − − = ∞ − = ∞ − = ⎛ ⎞ =− + − ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠ ⎡ ⎤ + + ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ ⎦ − − ′ ′′⋅ − ∑ ∫ ∑ ∑ ∫ (22) 由式(22)可知,在 x = 0 和 x = L 处边界面分别 趋于 f (t) 和 20℃。 4 温度场计算结果 根据求得的温度场表达式,即式(22),编制了 MATLAB 计算程序,并对文献[7]中的混凝土板进行 了计算。 图 2 为文献[7]中混凝土简支板的火灾试验装 置,板的底部受火。板的尺寸为 4300mm× 1500mm× 120mm。混凝土的设计强度等级为 C30,骨料为 硅质。 图 2 混凝土简支板火灾试验装置 Fig.2 Fire testing equipment for the slab 试验中,燃油炉的升温曲线如图3所示,应用 MATLAB多项式拟合得到试验炉温-时间函数,即 -8 5 -5 4 -3 3 2 ( ) 20 4.344 10 2.53 10 + 5.671 10 0.617 35.3962 ft t t tt t =+ × − × × − ×+ 其中时间t 的量纲为min。普通混凝土的热扩散系数 随温度的变化量较小,可认为是常数,计算中将它取 为38mm2 /min[5]。 图 3 升温曲线 Fig.3 Time-temperature curve in the fuel 将混凝土板温度场求解的解析解计算结果曲线 图(见图4)和试验的实测结果曲线图(见图5~图7)对比 发现:解析解与试验结果曲线的整体趋势是一致的, 近火面温度梯度很大,距受火面越远,温度梯度越小; 温度曲线都是凸向坐标轴,呈非线性分布。 同时二者也存在一些差距,这里主要有以下几 点原因:①混凝土材料在实际温度升高过程中伴有
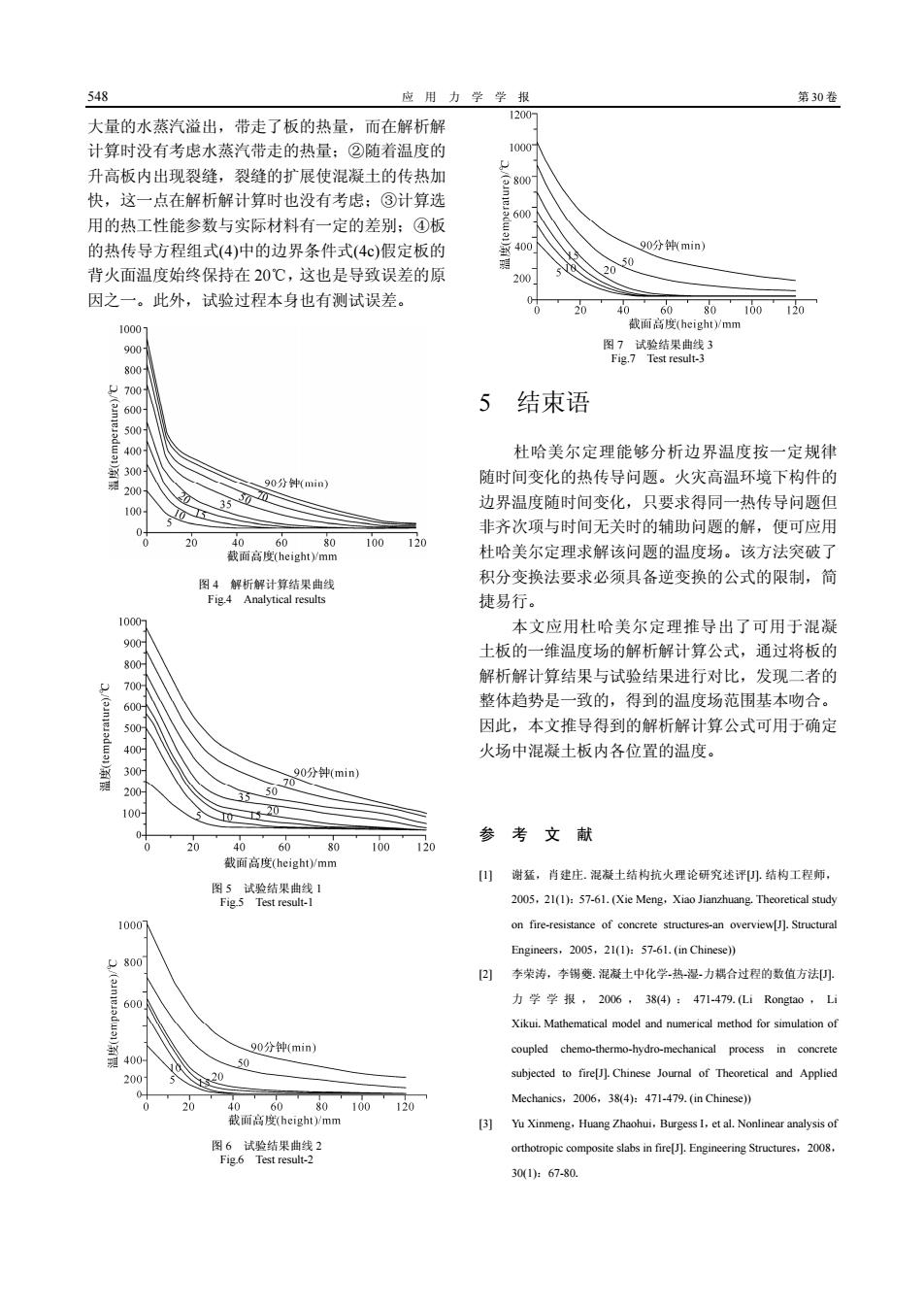
48 应用力学学报 第30卷 大最的水蔻汽治出,带走了板的热量,而在解析解 计算时没有考虑水蒸汽带走的热量: ②随着温度的 升高板内出现裂缝,裂缝的扩展使混凝土的传热加 快,议一点在解析解计算时也没有考虑:③计算洗 用的热工性能参数与实际材料有一定的差别:④板 的热传导方程组式4)中的边界条件式(4e)假定板的 Q0分钟min 背火面温度始终保持在20℃,这也是导致误差的原 因之一。此外,试验过程本身也有测试误差。 0 20 110 图,试验饰果3 700 '60 5结束语 杜哈美尔定理能够分析边界温度按一定规 随时间变化的热传导问题。火灾高温环境下构件的 边界温度随时间变化,只要求得同一热传导间题但 非齐次项与时间无关时的辅助问题的解,便可应用 20 100 720 杜哈美尔定理求解该问题的温度场。该方法突破丁 积分变换法要求必须具备逆变换的公式的限制,简 捷易行。 本文应用杜哈美尔定理推导出了可用于混凝 土板的一维温度场的解析解计算公式,通过将板 解析解计算结果与试验结果进行对比,发现二者的 整体趋势是一致的,得到的温度场范围基本吻合。 因此,本文推导得到的解析解计算公式可用于确定 火场中混凝土板内各位置的温度。 0分min 参考文献 20 60 】谢猛,肖建庄.混凝士结构抗火理论研究述评小结构工程师 图5试验箱果曲线 2005.21(1)57-61.(Xie Mene.Xioo Jianzhuong,Theoretical studv 205.21h57-61.(n Chinese) 以)李荣涛,李锡菱.混凝土中化学热漫力棉合过程的数值方 力学学报,2006.384)1471479.Li Rongta0.L Xikui Mathematical model and numerical method for simulation of 分钟(min budro-mechanical 0 subjected to fire]Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applie 12 Mechanics.2006.38(4):471-479.(in Chinese)) 100 301:67-0
548 应 用 力 学 学 报 第 30 卷 大量的水蒸汽溢出,带走了板的热量,而在解析解 计算时没有考虑水蒸汽带走的热量;②随着温度的 升高板内出现裂缝,裂缝的扩展使混凝土的传热加 快,这一点在解析解计算时也没有考虑;③计算选 用的热工性能参数与实际材料有一定的差别;④板 的热传导方程组式(4)中的边界条件式(4c)假定板的 背火面温度始终保持在 20℃,这也是导致误差的原 因之一。此外,试验过程本身也有测试误差。 图 4 解析解计算结果曲线 Fig.4 Analytical results 图 5 试验结果曲线 1 Fig.5 Test result-1 图 6 试验结果曲线 2 Fig.6 Test result-2 图 7 试验结果曲线 3 Fig.7 Test result-3 5 结束语 杜哈美尔定理能够分析边界温度按一定规律 随时间变化的热传导问题。火灾高温环境下构件的 边界温度随时间变化,只要求得同一热传导问题但 非齐次项与时间无关时的辅助问题的解,便可应用 杜哈美尔定理求解该问题的温度场。该方法突破了 积分变换法要求必须具备逆变换的公式的限制,简 捷易行。 本文应用杜哈美尔定理推导出了可用于混凝 土板的一维温度场的解析解计算公式,通过将板的 解析解计算结果与试验结果进行对比,发现二者的 整体趋势是一致的,得到的温度场范围基本吻合。 因此,本文推导得到的解析解计算公式可用于确定 火场中混凝土板内各位置的温度。 参 考 文 献 [1] 谢猛,肖建庄.混凝土结构抗火理论研究述评[J].结构工程师, 2005,21(1):57-61.(Xie Meng,Xiao Jianzhuang.Theoretical study on fire-resistance of concrete structures-an overview[J].Structural Engineers,2005,21(1):57-61.(in Chinese)) [2] 李荣涛,李锡夔.混凝土中化学-热-湿-力耦合过程的数值方法[J]. 力学学报, 2006 , 38(4) : 471-479.(Li Rongtao , Li Xikui.Mathematical model and numerical method for simulation of coupled chemo-thermo-hydro-mechanical process in concrete subjected to fire[J].Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2006,38(4):471-479.(in Chinese)) [3] Yu Xinmeng,Huang Zhaohui,Burgess I,et al.Nonlinear analysis of orthotropic composite slabs in fire[J].Engineering Structures,2008, 30(1):67-80

第4期 唐松花,等:火火特况下混凝土板温度场的解析解 549 畅泽安火温度作用下销筋混凝士构作温度场计算方法及吃用 Science and Engineering.0():() 箱防技术与产品信息,1992:18-24.Mg7m. 奥齐西克,热传导M命昌铭,译,北京:高等教有出版社 temperature field calculating method and application of reniforced 1983.(Ozisik M N.Hcat conduction[M]Yu Changming concrete members at fire temperature.Fire technique and products translated.Beiiing:Higher Education Press.1983. nformation.199902):18-24.(in Chinese)) [门陈礼刚.解筋混凝土板受火性能的试验研究D,西安:西安健筑 问余志武。王中,藉丽忠火灾下钢混凝土板的温度场分析 铁道科学与工程学报,2004,1(1):58-61.(Yu Zhiwu,Wang reinforced concrete slab[D).Xi'an:Xi'an University of Architectur Zhongqiang.Jiang Lizhong.Anslysis of temperature field in and Techology4 (in Chinese)) reinforced concrete slabs exposed to Journal of Railway
第 4 期 唐松花,等:火灾情况下混凝土板温度场的解析解 549 [4] 杨泽安.火灾温度作用下钢筋混凝土构件温度场计算方法及应用[J]. 消防技术与产品信息, 1999(2) : 18-24.(Yang Ze’an.The temperature field calculating method and application of reniforced concrete members at fire temperature[J].Fire technique and products information,1999(2):18-24.(in Chinese)) [5] 余志武,王中强,蒋丽忠.火灾下钢筋混凝土板的温度场分析[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2004,1(1):58-61.(Yu Zhiwu,Wang Zhongqiang , Jiang Lizhong.Analysis of temperature field in reinforced concrete slabs exposed to fire[J].Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2004,1(1):58-61.(in Chinese)) [6] 奥齐西克.热传导[M].俞昌铭,译.北京:高等教育出版社, 1983.(Ozisik M N.Heat conduction[M].Yu Changming , translated.Beijing:Higher Education Press,1983. [7] 陈礼刚.钢筋混凝土板受火性能的试验研究[D].西安:西安建筑科 技大学, 2004.(Chen Ligang.The experimental research of reinforced concrete slab[D].Xi’an:Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology,2004.(in Chinese))

CHINESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED MECHANICS 130 Microscopic strength model for eutectic composite ceramics with platelet defects Fu Yunwei Liu Xiequan Ni Xinhua Chen Cheng Abstract:According to the distribution feature of inherent defect in eutectic ceramics a relevant micro-mechanic model is established.Defects are assumed to be platelet and matrix around is rans stress field is obtained basedon damage theory,and Griffith strength of anisotropic material is obtained based on equivalent inclusion method.By considering the random tropism of defects,the relationship between defect size, defect fraction and strength is analyzed.Result obtained indicates that strength and reciprocal of defect radius's quadratic root reveals liner relation.The strength reduces as defect size increase and this reduction is sharp especially when the defect is small.Defects fraction has significant itte fraction change may ce compsie rengh reduce rapily as the than property of matrix has great influence on defect extending,and defect always extends from the smaller axis in isotropic matrix while it will extend from the axis of greater elastic modulus for penny shaped defect in anisotropic,and finally the defect shape and elastic modulus keep the specific proportional relation under simple tension condition Keywords:platelet defect,equtvalent inclusion method.microscopic strength model,Griffith strength. Improved threshold de-noising of embedded piezoelectric ultrasonic signal based on lifting wavelet Wang Qin Chen Yu Tan Bin Li Pengcheng Xu Zhilong Abstra:De-noising is akey step to improve the detection of structure and to realize structures to be intelligent.On the basis of traditional wavelet threshold de-noising akin of modified threshold de-noising technique based on lifting wavelets is put forwarded.The measured ultrasonic signal is de-noised on conditions of different SNR(Signal Noise Ratio)by the modified method and traditional method.respectively.Results obtained show that the modified method can be able to reduce signal oscillation Compared with hard and soft threshold de-noising.SNR value increased by58%at most and MSE (Mear Square Error)value is creased by 64.28%at least.Furthermore,the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by the Wigner-Ville time-frequency distribution of the measured signal. Keywords:lifting wavelet.piezoelectric.embedded.concrete.ultrasonic. Analytical solutions of temperature field in the concrete slab on fire Tang Songhua2 Luo Yingshe Peng Xianghua (1 Key Laboratory .410004.Ch a,Chin Abstract:Analytical solutions are important in the study of effect of fire temperature field on components in it
vi CHINESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED MECHANICS Vol.30 Microscopic strength model for eutectic composite ceramics with platelet defects Fu Yunwei1 Liu Xiequan2 Ni Xinhua1 Chen Cheng1 (1 Department of Vehicle and Electrical Engineering, Ordnance Engineering College, 050003, Shijiazhuang, China; 2 Department of Basic Courses, Ordnance Engineering College, 050003, Shijiazhuang, China) Abstract: According to the distribution feature of inherent defect in eutectic ceramics, a relevant micro-mechanic model is established. Defects are assumed to be platelet, and matrix around is transversely isotropic. Effective stress field is obtained based on damage theory, and Griffith strength of anisotropic material is obtained based on equivalent inclusion method. By considering the random tropism of defects, the relationship between defect size, defect fraction and strength is analyzed. Result obtained indicates that strength and reciprocal of defect radius’s quadratic root reveals liner relation. The strength reduces as defect size increase and this reduction is sharp especially when the defect is small. Defects fraction has significant influence on strength also, a little fraction change may cause composite strength reduce rapidly as the fraction is lower than 3%. Anisotropic property of matrix has great influence on defect extending, and defect always extends from the smaller axis in isotropic matrix while it will extend from the axis of greater elastic modulus for penny shaped defect in anisotropic, and finally the defect shape and elastic modulus keep the specific proportional relation under simple tension condition. Keywords: platelet defect, equivalent inclusion method, microscopic strength model, Griffith strength. Improved threshold de-noising of embedded piezoelectric ultrasonic signal based on lifting wavelet Wang Qin Chen Yu Tan Bin Li Pengcheng Xu Zhilong (College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Sichuan University, 610065, Chengdu, China) Abstract: De-noising is a key step to improve the detection quality of piezoelectric embedded concrete structures, and to realize concrete structures to be intelligent. On the basis of traditional wavelet threshold de-noising, a kind of modified threshold de-noising technique based on lifting wavelets is put forwarded. The measured ultrasonic signal is de-noised on conditions of different SNR (Signal Noise Ratio) by the modified method and traditional method, respectively. Results obtained show that the modified method can be able to reduce signal oscillation. Compared with hard and soft threshold de-noising, SNR value increased by 58.32% at most and MSE (Mean Square Error) value is decreased by 64.28% at least. Furthermore, the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by the Wigner-Ville time-frequency distribution of the measured signal. Keywords: lifting wavelet, piezoelectric, embedded, concrete, ultrasonic. Analytical solutions of temperature field in the concrete slab on fire Tang Songhua1,2 Luo Yingshe3 Peng Xianghua4 (1 Key Laboratory of Concrete and Prestressed Concrete Structures of Ministry of Education, Southeast University, 210096, Nanjing, China; 2 School of Civil and Architectural Engineering, Central South University, 410075, Changsha, China; 3 Institute of Rheological Mechanics and Material Engineering, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 410004, Changsha, China; 4 Institute of Foreign Affair, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 410004, Changsha, China) Abstract: Analytical solutions are important in the study of effect of fire temperature field on components in it

No.4 CHINESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED MECHANICS The temperature varies with time on fire,and the temperature of the components boundaries varies too.Duhamel theorem.which can na such he co problemsthat the boudary re acco ordance with ain laws,is applied todeduce the formula of th eanalytic in the concrete slab on fire e.The analytical solutions are calculated through MATLAB programming.By comparing the analytical and the test results obtained,it is shown that both of the temperature distributions are nonlinear,and the distributions have the same trend,that is,the surfaces near the fire have great temperature gradient,the farther the slab near the fire,the smaller the temperature gradient is.Both the temperature distribution erature field in the .on the assistant problem is obtained,which same heat conduction but the non-homogeneous items are unrelated to the times,the corresponding heat conduction problem can be solved by using Duhamel theorem.thus this method can be extended to obtain the analytical solutions of the temperature field of other construction members on fire. Study on cooperation mechanism of hybrid masonry structure with RC framing under the action of vertical force Guo Xiuqin Ma Jianxun' Cheng Litao 2 CCCC First Hig Abstraet:Firstly,the computational formula of axial force distribution for the framework and wall on hybrid masonry structure with RC frame is derived under the action of the vertical force.Theoretical analysis to determine the affecting factors of cooperative work on structures under vertical forces and finite element model is established to study the impact of beam height column height.wall height etc.on axial force distribution of frame and wall.Results obtained indicate that imp of column section height on axial force distribution of frame e and wall is and the variation is around%mpact of of frame and wall takes the second place.Impact of beam height and wall height on axial force distribution of frame and wall is not obvious.The accuracy of computational formula is verified by the comparison of results from the model analysis and formula calculation respectively. Keywords:vertical force.axial force distribution.cooperative work Dynamic characteristics of a cylindrical tunnel considering interaction between saturated soil and lining Chen Xueli Wen Minjie (nVcationl Technical Col46nChina) Abstraet:Based n Darey law,the partial permeable conditions on the boundary of tunnel are established by medium with fractional derivative constitutive relations.Based on Biot's theory,the expressions of displacement, stress and pore water pressure for coupled vibrations of saturated viscoelastic soil and elastic lining system subjected to harmonic axisymmetric load or fluid pressure are given in frequency domain by the continuity conditions at the interface between lining and soil Infuences of the order of fractional derivative,materials
No.4 CHINESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED MECHANICS vii The temperature varies with time on fire, and the temperature of the components boundaries varies too. Duhamel theorem, which can analyze such heat conduction problems that the boundary temperature varies with time and in accordance with certain laws, is applied to deduce the formula of the analytical solutions of the temperature field in the concrete slab on fire. The analytical solutions are calculated through MATLAB programming. By comparing the analytical and the test results obtained, it is shown that both of the temperature distributions are nonlinear, and the distributions have the same trend, that is, the surfaces near the fire have great temperature gradient, the farther the slab near the fire, the smaller the temperature gradient is. Both the temperature distribution curves are convex toward the coordinate axes. So the formula is suitable for solving the temperature field in the concrete slab on fire. Furthermore, if only the solution of the assistant problem is obtained, which belongs to the same heat conduction but the non-homogeneous items are unrelated to the times, the corresponding heat conduction problem can be solved by using Duhamel theorem, thus this method can be extended to obtain the analytical solutions of the temperature field of other construction members on fire. Keywords: fire, concrete slab, temperature field, analytical solutions, heat conduction, Duhamel theorem. Study on cooperation mechanism of hybrid masonry structure with RC framing under the action of vertical force Guo Xiuqin1 Ma Jianxun1 Cheng Litao2 (1 School of Human Settlements and Civil Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, 710049, Xi’an, China; 2 CCCC First Highway Consultants Co., Ltd, 710049, Xi’an, China) Abstract: Firstly, the computational formula of axial force distribution coefficient for the framework and wall on hybrid masonry structure with RC frame is derived under the action of the vertical force. Theoretical analysis to determine the affecting factors of cooperative work on structures under vertical forces and finite element model is established to study the impact of beam height, column height, wall height etc. on axial force distribution of frame and wall. Results obtained indicate that impact of column section height on axial force distribution of frame and wall is the largest and the variation is around 10%. Impact of masonry elastic modulus on axial force distribution of frame and wall takes the second place. Impact of beam height and wall height on axial force distribution of frame and wall is not obvious. The accuracy of computational formula is verified by the comparison of results from the model analysis and formula calculation respectively. Keywords: vertical force, axial force distribution, cooperative work. Dynamic characteristics of a cylindrical tunnel considering interaction between saturated soil and lining Chen Xueli Wen Minjie (Jiaxing Vocational Technical College, 314036, Jiaxing, China) Abstract: Based on Darcy law, the partial permeable conditions on the boundary of tunnel are established by introducing the relative permeability coefficient of lining and soil. The soil skeleton is treated as a viscoelastic medium with fractional derivative constitutive relations. Based on Biot’s theory, the expressions of displacement, stress and pore water pressure for coupled vibrations of saturated viscoelastic soil and elastic lining system subjected to harmonic axisymmetric load or fluid pressure are given in frequency domain by the continuity conditions at the interface between lining and soil. Influences of the order of fractional derivative, materials