
第十章 无穷级数 数学实验 symsum是Matlab软件系统中符号求和(symbolic summation)函数,它的调用格式和 主要功能如下: symsum(s) 求出通项为s的级数关于默认变量的有限和(如从0到k-1 的有限和) symsum(s,v) 求出通项为s的级数关于变量的有限和(如v从0到k- 的有限和) symsum(s,a,b)symsum(s,v,a,b) 求从a到b的级数的和.其中b可以取有限数, 也可以取无穷 一、级数求和 例1求级数的下列部分和 02r5:e)县-m6a>0a:a) 解(1)相应的Matlab程序为 >syms n x >S50=symsum(-1)(n+1)*x/(n*(n+5),n,1,50) 运行结果为S50=16481582353306899727903/136874465604198187866000*x (2)相应的Matlab程序为 >syms n a k >S=symsum((-1)k*a 2*sin(k),k,0,n-1); >>S1=simple(S1) 运行结果为 S1=(-a^2*(-1)^n*sin(n-1)-(-1)^n*a2*sin(n)-a^2*sin(1)/(2*cos(1)+2) 即(-asin0=-a-1sin(-)-(←-IYdsinn-asinl 2cos1+2 (3)相应的Matlab程序为 >>syms m n >S=symsum(3^(m-1)/2m,m,0,n-1) 无为582A即2器-0得-子
1 第十章 无穷级数 数学实验 symsum 是 Matlab 软件系统中符号求和(symbolic summation)函数,它的调用格式和 主要功能如下: symsum(s) 求出通项为s的级数关于默认变量的有限和(如n从0到 k −1 的有限和) symsum(s,v) 求出通项为 s 的级数关于变量 v 的有限和(如 v 从 0 到 k −1 的有限和) symsum(s,a,b)或 symsum(s,v,a,b) 求从 a 到 b 的级数的和.其中 b 可以取有限数, 也可以取无穷 一、级数求和 例 1 求级数的下列部分和 (1) 50 1 1 ( 1) ( 5) n n x n n + = − + ;(2) 1 2 1 ( 1) sin( )( 0, 1) n k k a k a a − = − ;(3) 1 1 0 3 2 n m m m − + = . 解 (1)相应的 Matlab 程序为 >> syms n x >> S50=symsum((-1)^(n+1)*x/(n*(n+5)),n,1,50) 运行结果为 S50 =16481582353306899727903/136874465604198187866000*x (2)相应的 Matlab 程序为 >> syms n a k >> S=symsum((-1)^k*a^2*sin(k),k,0,n-1); >>S1=simple(S1) 运行结果为 S1 =(-a^2*(-1)^n*sin(n-1)-(-1)^n*a^2*sin(n)-a^2*sin(1))/(2*cos(1)+2) 即 ( ) 2 2 2 1 2 1 ( 1) sin 1 ( 1) sin sin1 ( 1) sin( ) 2cos1 2 n n n k k a n a n a a k − = − − − − − − − = + . (3)相应的 Matlab 程序为 >> syms m n >> S=symsum(3^(m-1)/2^m,m,0,n-1) 运行结果为 S =2/3*(3/2)^n-2/3,即 1 1 0 3 2 3 2 2 3 2 3 m n n m m − + = = −

二、数项级数收敛性的判别 例2讨论下列级数的敛散性 (1)(s)(1):() 解(1)相应的Matlab程序为 >syms n >S=symsum(1)(n+1)/(2^n),0,inf) 运行结果为S=-2/3 放碳数空收或。且芙和为空号 (2)相应的Matlab程序为 >syms n k >a=1/3 >Sn=symsum((-1)"k*a."2*sin(k),k,0,n) >>S=limit(Sn,n,inf) 运行结果为 Sn= -1/18*(-1)(n+1)*sin(n+1)+1/18*sin(1)/(cos(1)+1)*(-1)(n+1)*cos(n+1)-1/18*sin(1 )/(cos(1)+1) S=-1/18-1/9*sin(1)/(cos(1)+1).1/18 即极限Iim∑(-l'a sin(k)不存在,故级数∑(-la'sin(n,(a=1/3)发散. (3)相应的Mat1ab程序为 >syms n k >Sn=symsum(3"(k+1)/2'k,k,0,n) >S=limit(Sn,n,inf) 运行结果为 Sn=6*(3/2)^(n+1)-6 S=Inf 即-之器=,故级空器 名2发散 例3讨论下列级数的敛散性,如果收敛,判别是绝对收敛还是条件收敛 r尝-r品·2 解首先判别这些级数是否绝对收敛,相应的Matlab程序为 >》S1=symsum(3*和/(2^n),n,l,inf) >>S2=symsum(3/(n*log(n)),n,2,inf) >S3=symsum(1/(n+1)2,n,1,inf) 运行结果为 S1=6
2 二、数项级数收敛性的判别 例 2 讨论下列级数的敛散性 (1) 1 0 ( 1) 2 n n n + = − ; (2) ( ) 2 0 ( 1) sin( ) 1/ 3 n n a n a = − = ; (3) 1 0 3 2 n n n + = . 解 (1)相应的 Matlab 程序为 >> syms n >> S=symsum((-1)^(n+1)/(2^n),0,inf) 运行结果为 S =-2/3 故极数 1 0 ( 1) 2 n n n + = − 收敛,且其和为 1 0 ( 1) 2 2 3 n n n + = − = − . (2)相应的 Matlab 程序为 >> syms n k >> a=1/3 >> Sn=symsum((-1)^k*a.^2*sin(k),k,0,n) >>S=limit(Sn,n,inf) 运行结果为 Sn= -1/18*(-1)^(n+1)*sin(n+1)+1/18*sin(1)/(cos(1)+1)*(-1)^(n+1)*cos(n+1)-1/18*sin(1 )/(cos(1)+1) S=-1/18-1/9*sin(1)/(cos(1)+1) . 1/18 即极限 2 0 lim ( 1) sin( ) n n n k a k → = − 不存在,故级数 ( ) 2 0 ( 1) sin( ), 1/ 3 n n a n a = − = 发散. (3)相应的 Matlab 程序为 >> syms n k >> Sn=symsum(3^(k+1)/2^k,k,0,n) >> S=limit(Sn,n,inf) 运行结果为 Sn =6*(3/2)^(n+1)-6 S =Inf 即 1 0 3 lim 2 n k k n k + → = = ,故级数 1 0 3 2 n n n + = 发散. 例 3 讨论下列级数的敛散性,如果收敛,判别是绝对收敛还是条件收敛. 1 3 ( 1) 2 n n n n = − , 2 3 ( 1) ln n n n n = − , 1 2 1 (1) ( 1) n n n + = + . 解 首先判别这些级数是否绝对收敛,相应的 Matlab 程序为 >> S1=symsum(3*n/(2^n),n,1,inf) >> S2=symsum(3/(n*log(n)),n,2,inf) >> S3=symsum(1/(n+1)^2,n,1,inf) 运行结果为 S1 =6

S2 =sum(3/n/log(n),n=2.Inf) S3=-1+1/6*知i^2 数空r宁和空时绝对收致,商空r 台(n+ 一非绝对收敛,是否收敛还需要 in 进一步列别下面根据来布尼表定理判别交错级数空-少。的敛敬性,相应的购1b程 ninn 序为 >>sym n x >>u=limit(3/n/log(n),n,inf) >v=simple(diff(3/x/log(x))) 运行结果为 u=0 v=-3*(1og(x)+1)/x^2/1og(x)2 即回品0,且函数,品当x时,导数值为负,甲为单调迷减通数综上两点,交错 3 级数-旷收敛 三、泰勒级数和傅立叶级数的展开 taylor函数是Matlab软件中求一元函数的泰勒级数展开式的函数,它的调用格式和功 能在第三章第九节数学实验中已经介绍,这里不再详述 例4求函数fx)=n√+x的在x=-2处的5阶泰勒多项式。 解相应的Matlab程序为 >svms x >f=taylor(log(sqrt(1+x)),-2) 结果为f= 1og(exp(-1/2*i*csgm(i*(1+x)*pi)-1/2*x-1-1/4*(x+2)^2-1/6*(x+2)^3-1/8*(x+2) 4-1/10*(x+2)^5 例5求函数fx)=√+x的4阶麦克劳林多项式。 解相应的Matlab程序为 〉)syms x >>f=taylor(sqrt(1+x),5) 结果为f=1+1/2*x-1/8*x^2+1/16*x^3-5/128*x^4 由第六节傅立叶级数知将一个函数∫(x)展开为傅立叶级数 f)=2+立a.cosm+6,snm) 其实就是要求出其中的系数a,和b,.根据三角函数系的正交性,可以得到它们的计算公式如
3 S2 =sum(3/n/log(n),n = 2 . Inf) S3 =-1+1/6*pi^2 即级数 1 3 ( 1) 2 n n n n = − 和 1 2 1 (1) ( 1) n n n + = + 绝对收敛,而级数 2 3 ( 1) ln n n n n = − 非绝对收敛,是否收敛还需要 进一步判别.下面根据莱布尼茨定理判别交错级数 2 3 ( 1) ln n n n n = − 的敛散性,相应的 Matlab 程 序为 >>sym n x >>u= limit(3/n/log(n),n,inf) >> v=simple(diff(3/x/log(x))) 运行结果为 u=0 v =-3*(log(x)+1)/x^2/log(x)^2 即 3 lim 0 n→ n n ln = ,且函数 3 x x ln 当 x 3 时,导数值为负,即为单调递减函数.综上两点,交错 级数 2 3 ( 1) ln n n n n = − 收敛. 三、泰勒级数和傅立叶级数的展开 taylor 函数是 Matlab 软件中求一元函数的泰勒级数展开式的函数,它的调用格式和功 能在第三章第九节数学实验中已经介绍,这里不再详述. 例 4 求函数 f x x ( ) ln 1 = + 的在 x =−2 处的 5 阶泰勒多项式. 解 相应的 Matlab 程序为 >> syms x >> f=taylor(log(sqrt(1+x)),-2) 结果为 f = log(exp(-1/2*i*csgn(i*(1+x))*pi))-1/2*x-1-1/4*(x+2)^2-1/6*(x+2)^3-1/8*(x+2) ^4-1/10*(x+2)^5 例 5 求函数 f x x ( ) 1 = + 的 4 阶麦克劳林多项式. 解 相应的 Matlab 程序为 >> syms x >> f=taylor(sqrt(1+x),5) 结果为 f =1+1/2*x-1/8*x^2+1/16*x^3-5/128*x^4 由第六节傅立叶级数知将一个函数 f x( ) 展开为傅立叶级数 0 1 ( ) ( cos sin ) 2 n n n a f x a nx b nx = = + + 其实就是要求出其中的系数 n a 和 n b .根据三角函数系的正交性,可以得到它们的计算公式如 下:

(ds,a(cosndr,()sin mrds. 这样,结果Matlab的积分函数int就可以计算这些系数,从而就可以进行函数的傅立 叶展开了. 例6求函数f)=x在元,上的傅立叶级数 解相应的Matlab程序为 >syms x; k=3:k为需要展开的项数 f=x: a0=int(f,x,pi,pi)/pi;%求系数a for n=1:k a(n)=int(f*cos(n*x),x,-pi,pi)/pi;%求出傅立叶系数an,存为向量a b(n)=int(f*sin(n*x),x,-pi,pi)/pi; %求出傅立叶系数b。,存为向量b end for n=1:k co(n)=cos(n*x):%傅立叶级数中的余弦函数项 si(n)=sin(n*x): %傅立叶级数中的正弦函数项 end f=c0.*atsi.: g=0: for n=1:k g=f(n)+g: end f=aO+g%求出傅立叶级数前k项展开式 结果为f=2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x) 若将k改为5,则输出结果: f=2/5*sin(5*x)-l/2*sin(4*x)+2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x) 当k改为10时,输出结果: -1/5*sin(10*x)+2/9*sin(9*x)-1/4*sin(8*x)+2/7*sin(7*x)-1/3*sin(6*x)+2/5*sin( 5*x)-1/2*sin(4*x)+2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x) 为了能够直观地展示傅立叶级数的效果,将展开为3,5,10项的效果图绘制出来,其 Matlab程序为 >>x=-Di:0.01:Di: >f3=2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x): >f5=2/5*sin(5*x)-1/2*sin(4*x)+2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x): >》f10=-1/5*sin(10*x)+2/9*sin(9*x)-1/4*sin(8*x)+2/7*sin(7*x)-1/3*sin(6*x) +2/5*sin(5*x)-1/2*sin(4*x)+2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x): >>hold on >plot(x,x,'m','linewidth',2):
4 0 1 a f x x ( )d − = , 1 ( )cos d n a f x nx x − = , 1 ( )sin d n b f x nx x − = ,n =1,2, . 这样,结果 Matlab 的积分函数 int 就可以计算这些系数,从而就可以进行函数的傅立 叶展开了. 例 6 求函数 f x x ( ) = 在 [ , ] − 上的傅立叶级数. 解 相应的 Matlab 程序为 >> syms x; k=3; %k 为需要展开的项数 f=x; a0=int(f,x,-pi,pi)/pi; %求系数 0 a for n=1:k a(n)=int(f*cos(n*x),x,-pi,pi)/pi; %求出傅立叶系数 n a ,存为向量 a b(n)=int(f*sin(n*x),x,-pi,pi)/pi; %求出傅立叶系数 n b ,存为向量 b end for n=1:k co(n)=cos(n*x); %傅立叶级数中的余弦函数项 si(n)=sin(n*x); %傅立叶级数中的正弦函数项 end f=co.*a+si.*b; g=0; for n=1:k g=f(n)+g; end f=a0+g %求出傅立叶级数前 k 项展开式 结果为 f =2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x) 若将 k 改为 5,则输出结果: f =2/5*sin(5*x)-1/2*sin(4*x)+2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x) 当 k 改为 10 时,输出结果: f = -1/5*sin(10*x)+2/9*sin(9*x)-1/4*sin(8*x)+2/7*sin(7*x)-1/3*sin(6*x)+2/5*sin( 5*x)-1/2*sin(4*x)+2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x) 为了能够直观地展示傅立叶级数的效果,将展开为 3,5,10 项的效果图绘制出来,其 Matlab 程序为 >> x=-pi:0.01:pi; >> f3=2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x); >> f5=2/5*sin(5*x)-1/2*sin(4*x)+2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x); >> f10=-1/5*sin(10*x)+2/9*sin(9*x)-1/4*sin(8*x)+2/7*sin(7*x)-1/3*sin(6*x) +2/5*sin(5*x)-1/2*sin(4*x)+2/3*sin(3*x)-sin(2*x)+2*sin(x); >> hold on >> plot(x,x,'m','linewidth',2);
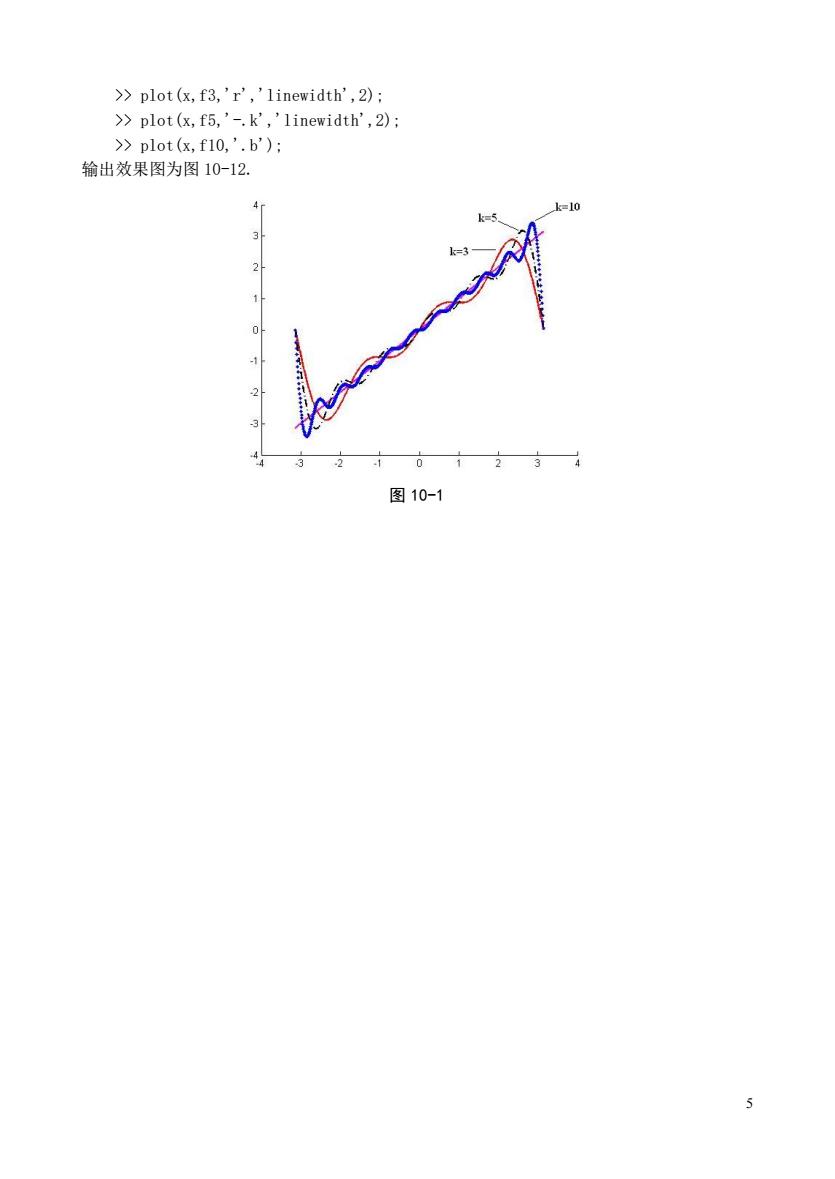
>plot(x,f3,'r','linewidth',2); >plot (x,f5,'-.k','linewidth',2) >plot(x,f10,'.b'): 输出效果图为图10-12. 4 3 2 图10-1
5 >> plot(x,f3,'r','linewidth',2); >> plot(x,f5,'-.k','linewidth',2); >> plot(x,f10,'.b'); 输出效果图为图 10-12. 图 10-1